Summary
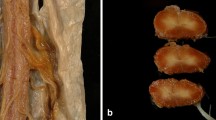
Peroneal muscular atrophy (PMA) associated with hereditary spastic paraparesis (HSP) is a nosologically ill-defined disease, which has been classified by Dyck as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type V (HMSN V). Nerve biopsy has been rarely reported in this condition. We examined sural nerve biopsies in four patients, demonstrating the following: severe myelinated fiber loss especially of large fibers, with moderate (one case) or prominent (one case) onion bulb formation; selective decrease of large fibers with moderate Schwann cell hyperplasia (one case); normal myelinated fiber population with minimal changes (one case). After reviewing previously reported cases, we conclude that in PMA with HSP sural nerve biopsy may show features either of hypertrophic type of PMA, of neuronal type, or of spinal type; thus, it seems inappropriate to allocate PMA with HSP in a unique subtype of HMSN. In addition, HSP may be not associated with peripheral neuropathy, and thus the classification in the HMSN group may be incongrous. A proper classification of PMA with HSP may be in the “complicated” forms of HSP according to Harding [Lancet I: 1151–1155 (1983)]; however, the nosology of this condition needs to be further elucidated, possibly on the basis of the underlying molecular genetic mechanisms of HSP and PMA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallat A, Davis SM, Farrage J, MacDonald WJ (1980) Disordered pigmentation, spastic paraparesis and peripheral neuropathy in three siblings: a new neurocutaneous syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:962–966
Behan WMH, Maia M (1974) Strümpell's familial spastic paraplegia: genetics and neuropathology. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 37:8–20
Behse F, Buchthal F (1977) Peroneal muscular atrophy (PMA) and related disorders. II. Histological findings in sural nervers. Brain 100:67–85
Ben Hamida M, Hentati F, Ben Hamida C (1990) Hereditary motor system diseases (chronic juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). Brain 113:347–363
Boustany R-MN, Fleischnick E, Alper Ca, Marazita ML, Spence MA Martin JB, Kolodny EH (1987) The autosomal dominant form of “pure” familial spastic paraplegia: clinical findings and linkage analyses of a large pedigree. Neurology 37:910–915
Cavanagh NPC, Eames RA, Galvin RJ, Brett EM, Kelly RE (1979) Hereditary sensory neuropathy with paraplegia. Brain 102:79–84
Claus D, Waddy HM, Harding AE, Murray NMF, Thomas PK (1990) Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies and hereditary spastic paraplegia: a magnetic stimulation study. Ann Neurol 28:43–49
Defesche JC, Hoogendijk JE, de Visser M, Ongerboer de Visser BW, Bolhuis PA (1990) Genetic linkage of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type I (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease) to markers of chromosomes 1 and 17. Neurology 40:1450–1453
de Visser M, de Visser BWO, Verjaal M (1988) Amyotrophy of the hands and pyramidal features of predominantly the legs segregating within one large family. J Neurol Sci 88:241–246
Dimitrijevic MR, Lenman JAR, Prevec T, Wheatley K (1982) A study of posterior column function in familial spastic paraplegia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:46–49
Dyck PJ (1984) Inherited neuronal degeneration and atrophy affecting motor, sensory and autonomic neurons. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Lambert EH, Bunge R (eds) Peripheral neuropathy, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1600–1642
Dyck PJ, Lambert EH (1968) Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. II. Neurologic, genetic and electrophysiologic findings in various neuronal degenerations. Arch Neurol 18:19–625
Dyck PJ, Karnes JL, Lais AC, Lofgren EP, Stevens JC (1984) Pathologic alterations of the peripheral nervous system of humans. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Lambert EH, Bunge R (eds) Peripheral neuropathy, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 760–870
Garland HG, Astley CE (1950) Hereditary spastic paraplegia with amyotrophy and pes cavus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 13:130–133
Guiloff RJ, Thomas PK, Contreras M, Armitage S, Schwarz G, Sedgwick EM (1982) Linkage of autosomal dominant type 1 hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy to the Duffy locus on chromosome 1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:669–674
Harding AE (1981) Hereditary “pure” spastic paraplegia: a clinical and genetic study of 22 families. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 44:871–883
Harding AE (1983) Classification of the hereditary ataxias and paraplegias. Lancet I:1151–1155
Harding AE (1984) The hereditary ataxias and related disorder. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Harding AE, Thomas PK (1984) Peroneal muscular atrophy with pyramidal features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:168–172
Khalifeh RR, Zellweger H, (1963) Hereditary sensory neuropathy with spinal cord disease. Neurology 13:405–411
Koenig RH, Spiro AJ (1970) Hereditary spastic paraparesis with sensory neuropathy. Dev Med Child Neurol 12:576–581
Krinke G, Schaumburg H, Spencer PS, Thomann P, Hess R (1979) Clioquinol and 2,5 hexanedione produce different types of distal axonopathy: a comparative experimental study in the dog. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 47:213–221
MacDermot KD, Walker RWH (1987) Autosomal recessive hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with mental retardation, optic atrophy and pyramidal signs. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50:1342–1347
Marbini A, Gemignani F, Ferrarini G, Maccari S, Lucci B, Bragaglia MM, Plancher C, Vergani C (1985) Tangier disease. A case with sensorimotor distal polyneuropathy and lipid accumulation in striated muscle and vasa nervorum. Acta Neuropatho (Berl), 67:121–127
Marbini A, Gemignani F, Rustichelli P, Pavesi G, Bragaglia M (1985) Nerve biopsy findings in two patients with heredoataxia “plus”. Acta Neurol 41:113–114
McLeod JG, Prineas JW (1971) Distal type of chronic spinal muscular atrophy. Clinical, electrophysiological and pathological studies. Brain 94:703–714
McLeod JG, Morgan JA, Reye C (1977) Electrophysiological studies in familial spastic paraplegia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40:611–615
Mellgren SI, Conn DL, Stevens JC, Dyck PJ (1989) Peripheral neuropathy in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Neurology 39:390–394
Middleton-Price HR, Harding AE, Monteiro C, Berciano J, Malcolm S (1990) Linkage of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type I to the pericentric region of chromosome 17. Am J Hum Genet 46:92–94
Pagès M, Pagès A-M (1983) Leber's disease with spastic paraplegia and peripheral neuropathy. Case report with nerve biopsy study. Eur Neurol. 22:181–185
Pedersen L, Trojaborg W (1981) Visual, auditory and somatosensory pathway involvement in hereditary cerebellar ataxia, Friedreich's ataxia and familial spastic paraplegia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 52:283–287
Schady W, Sheard A (1990) A quantitative study of sensory function in hereditary spastic paraplegia. Brain 113:709–720
Scheltens P, Bruyn RPM, Hazenberg GJ (1990) A Dutch family with autosomal dominant pure spastic paraparesis (Strümpell's disease) Acta Neurol Scand 82:169–173
Schwarz GA (1952) Hereditary (familial) spastic paraplegia. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 68:655–682
Schwarz GA, Liu CN (1956) Hereditary familial spastic paraplegia. Further clinical and pathologic observations. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 75:144–162
Serena M, Rizzuto N, Moretto G, Arrigoni G (1990) Familial spastic paraplegia with peroneal amyotrophy. A family with hypersensitivity to pyrexia. Ital J Neurol Sci 11:583–588
Shibasaki H, Kagigi R, Ohnishi A, Kuroiwa Y (1982) Peripheral and central nerve conduction in subacute myelo-optic neuropathy. Neurology 32:1186–1188
Silver JR (1966) Familial spastic paraplegia with amyotrophy of the hands. Ann Hum Genet 30:69–75
Strümpell A (1886) Über eine bestimmte Form der primären kombinierten Systemkrankung des Rückenmarks. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 17:227–238
Thomas PK (1982) Selective vulnerability of the centrifugal and centripetal axons of primary sensory neurons. Muscle Nerve 5:S117-S121
Thomas PK, Jefferys JGR, Smith IS, Loulakis D (1981) Spinal somatosensory evoked potentials in hereditary spastic paraplegia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 44:243–246
Thomas PK, Schaumburg HH, Spencer PS, Kaeser HE, Pallis CA, Clifford Rose F, Wadia NH (1984) Central distal axonopathy syndromes: newly recognized models of naturally occurring human degenerative diseases Ann Neurol 15:313–315
Thomas PK, Workman JM, Thage O (1984) Behr's syndrome. A family exhibiting pseudodominant inheritance. J Neurol Sci 64:137–148
Tredici G, Minoli G (1979) Peripheral nerve involvement in familial spastic paraplegia. Arch Neurol 36:236–239
Uncini A, Treviso M, Basciani M, Gambi D (1987) Strümpell familial spastic paraplegia: an electrophysiological demonstration of selective central distal axonopathy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 66:132–136
Van Epps C, Kerr HD (1940) Familial lumbosacral syringomyelia. Radiology 35:160–173
Van Gent EM, Hoogland RA, Jennekens FGI (1985) Distal amyotrophy of predominantly the upper limbs with pyramidal features in a large kinship. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:269
Wichman A, Buchthal F, Pezeshkpour GH, Fauci AS (1985) Peripheral neuropathy in hypereosinophilic syndrome. Neurology 35:1140–1145
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by a grant from the Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica (quota 40% per ricerche di rilevante interesse nazionale)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gemignani, F., Guidetti, D., Bizzi, P. et al. Peroneal muscular atrophy with hereditary spastic paraparesis (HMSN V) is pathologically heterogeneous. Acta Neuropathol 83, 196–201 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308479
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00308479