Summary
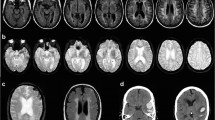
A retrospective postmortem analysis of 25 cases of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) in the setting of Alzheimer's disease or senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (AD/SDAT) is reported. Seven patients experienced clinically significant cerebral infarcts or hemorrhages or both. There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of infarcts or hemorrhages in hypertensive and nonhypertensive patients. Hypertension does not appear to be an additional risk factor in the causation of cerebral infarct or hemorrhage associated with CAA in the setting of AD/SDAT. Just over half of patients with CAA and significant ischemic and/or hemorrhagic brain lesions showed atherosclerosis of the circle of Willis, sometimes in the context of severe disseminated atheromatous disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam J, Crow TJ, Duchen LW, Scaravilli F, Spokes E (1982) Familial cerebral amyloidosis and spongiform encephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:37–45
Bahemuka M (1987) Primary intracerebral hemorrhage and heart weight. Stroke 18:531–536
Batsakis JG (1968) Cardiac enlargement. In: Gould SE (ed) Pathology of the heart and blood vessels. Thomas. Springfield, Ill.
Brandenburg W, Hallervorden J (1954) Dementia pugilistica mit anatomischem Befund. Virchows Arch 325:680–709
Brewer DB, Fawcett FJ, Hordsfield GI (1968) A necropsy series of non-traumatic cerebral haemorrhages and softenings, with particular refernce to heart weight. J Pathol Bacteriol 96:311–320
Freytag E (1968) Fatal hypertensive intracerebral haematomas: a survey of the pathological anatomy of 393 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 31:616–620
Gilbert JJ, Vinters HV (1983) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: incidence and complications in the aging brain. I. Cerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 14:915–923
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122:1131–1135
Glenner GG, Henry JH, Fujihara S (1981) Congophilic angiopathy in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's degeneration. Ann Pathol 1:120–129
Heffner RR Jr, Porro RS, Olson ME, Earle KM (1976) A demyelinating disorder associated with cerebrovascular amyloid angiopathy. Arch Neurol 33:501–506
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42:1097–1105
Mandybur TI (1979) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: possible relationship to rheumatoid vasculitis. Neurology 29:1336–1340
Mandybur TI (1986) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: the vascular pathology and complications. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:79–90
Mandybur TI, Gore I (1969) Amyloid in late postirradiation necrosis of brain. Neurology 19:983–992
Masuda J, Tanaka K, Ueda T, Omae T (1988) Autopsy study of incidence and distribution of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Hisayama, Japan. Stroke 19:205–210
Miller Fisher C (1975) The anatomy and pathology of the cerebral vasculature. In: Meyer JS (ed) Modern concepts of cerebrovascular disease. Spectrum, New York
Murphy MN, Sima AAF (1985) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy associated with giant cell arteritis: a case report. Stroke 16:514–517
Ojemann RG, Heros RC (1983) Spontaneous brain hemorrhage. Stroke 14:468–475
Okazaki H, Reagan TJ, Campbell RJ (1979) Clinicopathologic studies of primary cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Mayo Clin Proc 54:22–31
Tomlinson BE, Corsellis JAN (1984) Ageing and the dementias. In: Adams JH, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 4th edn. Arnold, London
Vinters HV (1987) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy — a critical review. Stroke 18:311–324
Vinters HV, Gilbert JJ (1983) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: incidence and complications in the aging brain. II. The distribution of amyloid vascular changes. Stroke 14:924–928
Vinters HV, Pardridge WM, Secor DL, Ishii N (1988) Immunohistochemical study of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. II. Enhancement of immunostaining using formic acid pretreatment of tissue sections. Am J Pathol 133:150–162
Vinters HV, Pardridge WM, Yang J (1988) Immunohistochemical study of cerebral amyloid angiopathy: use of an antiserum to a synthetic 28-amino-acid peptide fragment of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor. Hum Pathol 19:214–222
Wattendorff AR, Bots GTAM, Went LN, Endtz LJ (1982) Familial cerebral amyloid angiopathy presenting as recurrent cerebral haemorrhage. J Neurol Sci 55:121–135
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreiro, J.A., Ansbacher, L.E. & Vinters, H.V. Stroke related to cerebral amyloid angiopathy: the significance of systemic vascular disease. J Neurol 236, 267–272 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314454
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314454