Abstract
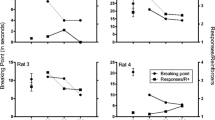
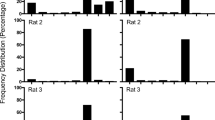
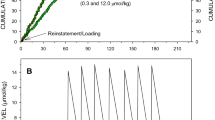
Forty rats were trained to make a left lever response if a signal (white noise) was 2.5s and to make a right lever response if the signal was 6.3s. When seven intermediate signal durations, to which responses were not reinforced, were randomly interspersed the probability of a right-lever (‘long’) response increased as a function of signal duration. Methamphetamine shifted this psychometric function leftward and decreased its slope: haloperidol also decreased the slope but shifted the function rightward. A combination of haloperidol and methamphetamine led to a function similar to the saline control function. The leftward shift probably reflects an increase in the speed of an internal clock, and the rightward shift probably reflects a decrease in its speed. Since methamphetamine releases several catecholamines, including dopamine, and haloperidol blocks dopamine receptors, it is plausible that the horizontal location of the psychometric function (the speed of the clock) is related to the effective level of dopamine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branch MN, Gollub LR (1974) A detailed analysis of the effects of d-amphetamine on behavior under fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav 21:519–539
Carlsson A (1970) Amphetamine and brain catecholamines. In: Costa E, Garratini S (eds) International symposium on amphetamines and related compounds. Raven, New York, pp 289–300
Church RM, Deluty MZ (1977) Bisection of temporal intervals. J Exp Psychol (Anim Behav) 3:216–228
Glowinski J (1970) Effects of amphetamine on various aspects of catecholamine metabolism in the central nervous system of the rat. In: Costa E, Garratini S (eds) International symposium on amphetamines and related compounds. Raven, New York, pp 301–316
Maricq AV, Roberts S, Church RM (1981) Methamphetamine and time estimation. J Exp Psychol (Anim Behav) 7:18–30
Ridley RM, Haystead TAJ, Baker HF (1981) An analysis of visual object reversal learning in the marmoset after amphetamine and haloperidol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 14:345–351
Robbins TW, Iversen SD (1973) Amphetamine-induced disruption of temporal discrimination by response disinhibition. Nature (New Biol) 245:191–192
Roberts S (1981) Isolation of an internal clock. J Exp Psychol (Anim Behav) 7:242–268
Sanger DJ, Key M, Blackman DE (1974) Differential effects of chlordiazepoxide and d-amphetamine on responding maintained by a DRL schedule of reinforcement. Psychopharmacologia 38:159–171
Schechter MD, Cook PG (1975) Dopaminergic mediation of the interoceptive cue produced by d-amphetamine in rats. Psychopharmacologia 42:185–193
Segal EF (1962) Effects of d,l-amphetamine under concurrent VI DRL reinforcement. J Exp Anal Beh 5:105–112
Yokel RA, Wise RA (1976) Attenuation of intravenous amphetamine reinforcement by central dopamine blockade in rats. Psychopharmacology 48:311–318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maricq, A.V., Church, R.M. The differential effects of haloperidol and methamphetamine on time estimation in the rat. Psychopharmacology 79, 10–15 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433008
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433008