Summary
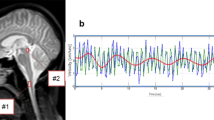
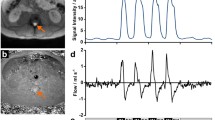
Cardiac-related motion of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was investigated by analysis of the velocity-dependent phase of CSF protons and flow-dependent signal enhancement in magnitude images using ECG-gated FLASH sequences. In the cerebral aqueduct, CSF flow from the third to the fourth ventricle begins 200 msafter the R-wave of the ECG and simulates an arterial pulse wave pattern. It lasts about 60% of the cardiac cycle and is followed by backflow from the fourth to the third ventricle, which is slower and shorter. In the spinal canal, oscillating caudad motion precedes flow from the third to the fourth ventricle by about 50–100 ms and issuperimposed on a bulk flow, which moves simultaneously in opposite directions in separate subarachnoid channels; it is directed mainly caudally in the anterior cervical subarachnoid space.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Chiro G (1964) Movement of the cerebrospinal fluid in human beings. Nature 204: 290–291
Di Chiro G (1966) Observations on the circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Radiol 5: 988–1002
Du Boulay GH (1966) Pulsatile movements in the CSF pathways. Br J Radiol 39: 255–262
Du Boulay GH, O'Connell J, Currie J, Bostick T, Verity P (1972) Further investigations on pulsatile movements in the cerebrospinal fluid pathways. Acta Radiol 13: 496–523
Lane B, Kricheff II (1974) Cerebrospinal fluid pulsations at myelography: a videodensitometric study. Radiology 110: 579–587
Bergstrand G, Bergström M, Nordell B, Stahlberg F, Ericsson A, Hemmingson A, Sperber G, Thuomas KA, Jung B (1985) Cardiac gated MR imaging of cerebrospinal fluid flow. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9: 1003–1006
Edelman RR, Wedeen VJ, Davis KR, Widder D, Hahn P, Shoukimas G, Brady TJ (1986) Multiphasic MR imaging: a new method for direct imaging of pulsatile CSF flow. Radiology 161: 779–783
Feinberg DA, Marks AS (1987) Human brain motion and cerebrospinal fluid circulation demonstrated with MR velocity imaging. Radiology 163: 793–799
Schroth G, Klose U, Gawehn J, Petersen D, Varallay G (1987) ECG-related pulsations of the CSF. Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 6th Annual Meeting, New York, Book of Abstracts, p 119
Sherman JL, Citrin CM (1986) Magnetic resonance demonstration of normal CSF flow. AJNR 7: 3–6
Haase A, Frahm J, Matthaei D, Hänicke W, Merboldt KD (1986) FLASH Imaging. Rapid NMR imaging using low flip-angle pulses. J Magn Reson 67: 258–266
Firmin DN, Nayler GL, Klipstein RH, Underwood SR, Rees RSO, Longmore DB (1987) In vivo validation of MR velocity imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 11: 751–756
Bering AE (1962) Circulation of cerebro-spinal fluid. Demonstration of the chorioid plexus as the generator of the force for flow of fluid and ventricular enlargement. J Neurosurg 19:405–412
Gardner WJ (1965) Hydrodynamic mechanism of syringomyelia. Its relationship to myelocele. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 28: 247–259
O'Connell JEA (1943) Vascular factor in intracranial pressure and maintenance of cerebro-spinal fluid circulation. Brain 66: 204–225
Schroth G, Naegele T, Klose U, Mann K, Petersen D (1988) Reversible brain shrinking in abstinent alcoholics measured by MRI. Neuroradiology 30: 385–389
Klose U, Schroth G, Müller E, Grodd W (1988) Echtzeit-Darstellungsmöglichkeiten von Liquorbewegungen in der Kernspintomographie. In: Nüsslin F (ed) Medizinische Physik—Deutsche Gesellschaft für Medizinische Physik, Tübingen, pp 562–566
Mueller E, Laub G, Graumann R, Loeffler W (1988) RACE — real time acquisition and evaluation of pulsatile blood flow on a whole body MRI unit. Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 7th Annual Meeting, San Franzisco, Book of Abstracts, vol. 1, p 729
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroth, G., Klose, U. Cerebrospinal fluid flow. Neuroradiology 35, 1–9 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588270
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588270