Summary
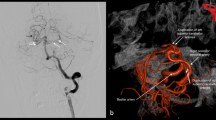
The magnetic resonance (MR) findings of three cases with vertebro-basilar dissecting aneurysms (DA) were compared with those of two cases with vertebro-basilar fusiform aneurysms (FA). No abnormal findings, excepting a dilatation of a signal-void area corresponding to the arterial blood flow, were shown on the MR images in the patients with a FA. In contrast to the FA cases, various abnormalities were detected by the MR studies in all three DA cases. An intimal flap and a double lumen were demonstrated in one case. An intra-mural hematoma was shown in one case. A hematoma neighboring the parent artery was demonstrated in two cases. MR imaging was thought to be useful for detecting intracranial vascular lesions, such as a DA, and for discriminating between a DA and a FA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yonas H, Agamanolis D, Takaoka Y, White RJ (1977) Dissecting intracranial aneurysm. Surg Neurol 8: 407–415
Berger MS, Wilson CB (1984) Intracranial dissecting aneurysms of the posterior circulation: report of six cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 61: 882–894
Miyazaki S, Yamaura A, Kamata K, Fukushima H (1984) A dissecting aneurysm of the vertebral artery. Surg Neurol 21: 171–174
Waespe W, Niesper J, Imhof H, Valavanis A (1988) Lower cranial nerve palsies due to internal carotid dissection. Stroke 19: 1561–1564
Rothrock JF, Lim V, Press G, Gosink B (1989) Serial magnetic resonance and carotid duplex examinations in the management of carotid dissection. Neurology 39: 686–692
Frank E, Brown BM, Wilson DF (1989) Asymptomatic fusiform aneurysm of the petrous carotid artery in a patient with von Recklinghausen's neurofibromatosis. Surg Neurol 32: 75–78
Shimoji T, Bando K, Nakajima K, Ito K (1984) Dissecting aneurysm of the vertebral artery: report of seven cases and angiographic findings. J Neurosurg 61: 1038–1046
Shokunbi MT, Vinters HV, Kaufman JCE (1988) Fusiform intracranial aneurysms: clinicopathologic features. Surg Neurol 29: 263–270
Akins EW, Hill JA, Carmichael MJ (1987) MR imaging of blood pool signal variation with cardiac phase in aortic dissection. J Comput Assist Tomogr 11: 543–545
Rumancik WM, Naidich DP, Chandra R, Kowalski HM, McCauley DI, Megibow AJ, Hernanz-Schulman M, Genieser NB (1988) Cardiovascular disease: evaluation with MR phase imaging. Radiology 166: 63–68
Bradley WG, Waluch V, Lai K, Fernandez EJ, Spalter C (1984) The appearance of rapidly flowing blood on magnetic resonance images. AJR 143: 1167–1174
Bradley WG, Waluch V (1985) Blood flow: magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology 154: 443–450
Von Schulthess GK, Higgins CB (1985) Blood flow imaging with MR: spin-phase phenomena. Radiology 157: 687–695
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1985) Intracranial hematomas: imaging by high-field MR. Radiology 157: 87–93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwama, T., Andoh, T., Sakai, N. et al. Dissecting and fusiform aneurysms of vertebro-basilar systems. Neuroradiology 32, 272–279 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00593045
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00593045