Summary
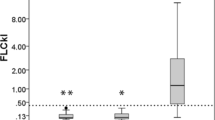
Immunoglobulin (Ig) concentrations were investigated in white matter samples of two adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD), threee multiple sclerosis (MS), two systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), one rheumatoid arthritis, and three control brains obtained at autopsy. “Free” Igs were extracted at pH 7.4; subsequently, bound Igs were extracted at pH 2.5 and 10.8, respectively. Igs were quantified by radial immunodiffusion. In ALD material there was an increase of free IgG and IgA, in one sample also of IgM, as compared to controls. No significant amounts of Igs were detected in the pH 2.5 and 10.8 extracts of ALD brain. Similarly to ALD, an increase of free IgG and IgA was a characteristic finding in MS brain; in contrast to ALD and control material, significant amounts of bound Igs (IgG) extractable at acid or alkaline pH, respectively, were present in MS tissue. In both SLE brains increase of free IgM was conspicuous. Preliminary studies on binding of Igs extracted at pH 7.4 from brain to frozen sections of normal human and bovine brain tissue revealed different binding properties of Igs from ALD, MS, SLE, and control brains. Immunochemical findings in ALD indicating pathologic accumulation of Igs in brain tissue were paralleled by immunocytochemical observations demonstrating accumulation of lymphoid cells staining for IgG, IgA, and IgM, respectively, mainly in areas of recent demyelination. Participation of Igs in the pathogenesis of ALD lesions may be considered but needs further confirmation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarli JA, Aparicio SR, Lumsden CE, Tönder O (1975) Binding of normal human IgG to myelin sheaths, glia and neurons. Immunology 28:171–185
Askanas V, McLaughlin J, Engel WK, Adornato BT (1979) Abnormalities in cultured muscle and peripheral nerve of a patient with adrenomyeloneuropathy. N Engl J Med 301:588–591
Auff E, Budka H (1980) Immunhistologische Methoden in der Neuropathologie. In: Jellinger K, Gross H (eds) Current topics in neuropathology, vol 6. Facultas, Wien, pp 21–29
Bernheimer H, Budka H (1982) Central nervous system immunoglobulins in adrenoleuk odystrophy. In: Peeters H (ed) Protides of the biological fluids, Colloquium 30. Pergamon Press, Oxford (in press)
Blaw ME (1970) Melanodermic type leukodystrophy (adrenoleukodystrophy). In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 10, chap 8. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 128–133
Britton DE, Houff SA, Eiben RM, Madden DL, Sever JL (1977) Studies of viral antibodies, oligoclonal IgG, in situ central nervous system IgG production and lymphocyte rosetting in sex-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Neurology (NY) 27:396
Budka H (1981) Brain pathology in the collagen vascular diseases. Angiology 32:365–372
Budka H (1982) Immunohistological demonstration of serum proteins, structural and viral antigens in paraffin sections of nervous tissues. Ann NY Acad Sci (in press)
Budka H, Molzer B, Bernheimer H, Lassmann H, Pilz P, Toifl K (1982) Clinical, morphological and neurochemical findings in adrenoleukodystrophy and its variants. Neuropathology (Tokyo) (in press)
Budka H, Popow-Kraupp Th (1981) Rabies and herpes simplex virus encephalitis. An immunohistological study on site and distribution of viral antigens. Virchows Arch [Pathol Anat] 390:353–364
Budka H, Sluga E, Heiss WD (1976) Spastic paraplegia associated with Addison's disease — Adult variant of adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurol 213:237–250
Esiri MM (1977) Immunoglobulin-containing cells in multiplesclerosis plaques. Lancet 2:478–480
Esiri MM (1980) Multiple sclerosis: a quantitative and qualitative study of immunoglobulin-containing cells in the central nervous system. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 6:9–21
Griffin JW, Goren E, Schaumburg H, Engel WK, Loriaux L (1977) Adrenomyeloneuropathy — A probable variant of adrenoleukodystrophy. Part 1: Clinical and endocrinological aspects. Neurology (NY) 27:1107–1113
Igarashi M, Schaumburg HH, Powers J, Kishimoto Y, Kolodny E, Suzuki K (1976a) Fatty acid abnormality in adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurochem 26:851–860
Igarashi M, Belchis D, Suzuki K (1976b) Brain gangliosides in adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurochem 27:327–328
Kawamura N, Moser AB, Moser HW, Ogino T, Suzuki K, Schaumburg H, Milunsky A, Murphy J, Kishimoto Y (1978) High concentration of hexacosanoate in cultured skin fibroblast lipids from adrenoleukodystrophy patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 82:114–120
Link H (1972) Oligoclonal immunoglobulin G in multiple sclerosis brains. J Neurol Sci 16:103–114
Lisak RP (1980) Multiple sclerosis: Evidence for immunopathogenesis. Neurology (NY) 30:99–105
Mehta PD, Frisch S, Thormar H, Tourtellotte WW, Wisniewski HM (1981) Bound antibody in multiple sclerosis brains. J Neurol Sci 49:91–98
Mobley WC, White C, Gale AD, Clark AW, Tennekoon G, Moser HW (1982) Adrenoleukodystrophy — Biochemical and morphological features of a case with neonatal onset. Abstracts of the IXth International Congress of Neuropathology, Vienna, September 5–10, 1982
Molzer B, Bernheimer H, Toifl K (1981a) Fatty acid patterns in brain, fibroblast, leukocyte and body fluid lipids in adrenoleukodystrophy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) [Suppl] VII:211–214
Molzer B, Bernheimer H, Budka H, Pilz P, Toifl K (1981b) Accumulation of very long chain fatty acids is common to 3 variants of adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD). “Classical” ALD, atypical ALD (female patient) and adrenomyeloneuropathy. J Neurol Sci 51:301–310
Molzer B, Bernheimer H, Heller R, Toifl K, Vetterlein M (1982) Detection of adrenoleukodystrophy by increased C26:0 fatty acid levels in leukocytes. Clin Chim Acta 125:299–305
Moser HW, Moser AB, Kawamura N, Murphy J, Suzuki K, Schaumburg H, Kishimoto Y (1980) Adrenoleukodystrophy-Elevated C26 fatty acid in cultured skin fibroblasts. Ann Neurol 7:542–549
Moser HW, Moser AB, Freyer KK, Chen W, Schulmann JD, O'Neill P, Kishimoto Y (1981) Adrenoleukodystrophy: Increased plasma content of saturated very long chain fatty acids. Neurology (NY) 31:1241–1249
Mussini JM, Hauw JJ, Escourolle R (1977) Immunofluorescence studies of intra cytoplasmatic immunoglobulin binding lymphoid cells (CILS) in the central nervous system. Report of 32 cases including 19 multiples sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 40:227–232
Pilz P, Schiener P (1973) Kombination von Morbus Addison und Morbus Schilder bei einer 43-jährigen Frau. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 26:357–360
Powers JM, Schaumburg HH, Johnson AB, Raine CS (1980) A correlative study of the adrenal cortex in adreno-leukodystrophy — evidence for a fatal intoxication with very long chain saturated fatty acids. Invest Cell Pathol 3:353–376
Prineas JW, Raine CS (1976) Electron microscopy and immunoperoxidase studies of early multiple sclerosis lesions. Neurlogy (NY) 26:29–32
Schaumburg HH, Powers JM, Raine CS, Suzuki K, Richardson EP (1975) Adrenoleukodystrophy — A clinical and pathological study of 17 cases. Arch Neurol 32:577–591
Schaumburg HH, Powers JM, Raine CS, Spencer PS, Griffin JW, Prineas JW, Boehme DM (1977) Adrenomyeloneuropathy — a probable variant of adrenoleukodystrophy, part 2: General pathologic, neuropathologic and biochemical aspects. Neurology (NY) 27:1114–1119
Sindic CJM, Cambiaso CL, Masson PL, Laterre EC (1980) The elution of IgG from subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and multiple sclerosis brains. Clin Exp Immunol 41:8–12
Singh I, Moser HW, Moser AB, Kishimoto Y (1981) Adrenoleukodystrophy: Impaired oxidation of long chain fatty acids in cultured skin fibroblasts and adrenal cortex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 102:1223–1229
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto
Tourtellotte WW, Parker JA (1967) Multiple sclerosis: Brain immunoglobulin-G and albumin. Nature 214:683–686
Ulrich J, Herschkowitz N, Heitz P, Sigrist T, Baerlocher P (1978) Adrenoleukodystrophy — Preliminary report of a connatal case. Light- and electronmicroscopical, immunohistochemical and biochemical findings. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 43:77–83
Vandvik B, Reske-Nielsen E (1972) Immunochemical and immunohistochemical studies of brain tissue in subacute panencephalitis and multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand [Suppl 51] 48:413–416
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Austrian Science Research Fund, project no. S-25/04 and by Seegen-Stiftung
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernheimer, H., Budka, H. & Müller, P. Brain tissue immunoglobulins in adrenoleukodystrophy: A comparison with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Neuropathol 59, 95–102 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691593
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691593