Abstract
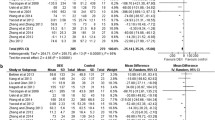
Objective: To evaluate the literature regarding antiinflammatory actions of cytokines, evaluate randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of supranormal oxygen delivery, and suggest alternative mechanism(s) for possible beneficial effects of supranormal oxygen delivery in critically ill surgical patients.¶Design: Literature review using Medline and review of selected illustrative studies.¶Main results: Catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, isoproterenol, and dopamine) in general inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) production and may enhance interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-10 production. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors also inhibit TNF and may enhance IL-10. All studies used models (cell, animal, or humans infused with endotoxin) of sepsis. RCTs of supranormal oxygen delivery show decreased mortality in high-risk surgical patients; however, prevention or reversal of tissue hypoxia may not be the mechanism of benefit. Antiinflammatory effects of catecholamines are a potential and, to date, unexplored mechanism of the benefit of supranormal oxygen delivery in critically ill surgical patients.¶Conclusions: Catecholamines may modulate cytokine response beneficially and could be a mechanism of decreased morbidity and mortality of supranormal oxygen delivery in high-risk surgical patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 April 1999/Final revision received: 19 August 1999/Accepted: 27 October 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uusaro, A., Russell, J. Could anti-inflammatory actions of catecholamines explain the possible beneficial effects of supranormal oxygen delivery in critically ill surgical patients?. Intensive Care Med 26, 299–304 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340051153
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340051153