Abstract
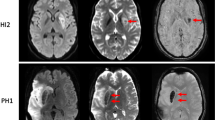
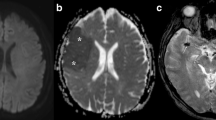
It is occasionally necessary to repeat diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) after giving intravenous contrast medium (CM). However, the effects of CM on DWI and apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) have not been fully examined. The aim of this prospective study was to investigate whether there are any diagnostically significant differences between echo-planar imaging (EPI)-DWI before and after intravenous CM. EPI-DWI was acquired twice in 203 consecutive patients before and after i.v. CM. Three blinded readers rated the diagnostic image quality. Quantitative ADC calculations were performed before and after CM in all 72 patients with lesions sufficiently large for quantification, and in 72 normal brain regions. Of the 203 patients, 127 had abnormalities on MRI, including ischaemic stroke (52), bleeding (nine), brain tumour with disturbed blood-brain barrier (BBB) (18) and other lesions (48). There were no significant signal differences on isotropic DWI before and after CM, even in lesions with definite disturbance of the BBB. No statistically significant difference between ADC of lesions and contralateral normal brain was observed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161: 401–407
Fitzek C, Tintera J, Muller-Forell W, et al (1998) Differentiation of recent and old cerebral infarcts by diffusion- weighted MRI. Neuroradiology 40: 778–782
Fiebach J, Jansen O, Schellinger P, et al (2001) Comparison of CT with diffusion-weighted MRI in patients with hyperacute stroke. Neuroradiology 43: 628–632
Urbach H, Flacke S, Keller E, et al (2000) Detectability and detection rate of acute cerebral hemisphere infarcts on CT and diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroradiology 42: 722–727
Wiener JI, King JT, Jr., Moore JR, Lewin JS (2001) The value of diffusion-weighted imaging for prediction of lasting deficit in acute stroke: an analysis of 134 patients with acute neurologic deficits. Neuroradiology 43: 435–441
Fitzek C, Mewes T, Fitzek S, Mentzel HJ, Hunsche S, Stoeter P (2002) Diffusion-weighted MRI of cholesteatomas of the petrous bone. J Magn Reson Imaging 15: 636–641
Hartmann M, Heiland S, Sartor K (2002) Functional MRI procedures in the diagnosis of brain tumours: Perfusion- and diffusion-weighted imaging. Rofo 174: 955–964
Chang SC, Lai PH, Chen WL, et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted MRI features of brain abscess and cystic or necrotic brain tumors: comparison with conventional MRI. Clin Imaging 26: 227–236
Tsuruda JS, Chew WM, Moseley ME, Norman D (1990) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain: value of differentiating between extraaxial cysts and epidermoid tumors. Am J Roentgenol 155: 1059–1068
Tzika AA, Zarifi MK, Goumnerova L, et al (2002) Neuroimaging in pediatric brain tumors: Gd-DTPA-enhanced, hemodynamic, and diffusion MR imaging compared with MR spectroscopic imaging. AJNR 23: 322–333
Hartmann M, Jansen O, Heiland S, Sommer C, Munkel K, Sartor K (2001) Restricted diffusion within ring enhancement is not pathognomonic for brain abscess. AJNR 22: 1738–1742
Fitzek C, Weissmann M, Speckter H, et al (2001) Anatomy of brain-stem white-matter tracts shown by diffusion-weighted imaging. Neuroradiology 43: 953–960
Tourbah A, Stievenart JL, Abanou A, Fontaine B, Cabanis EA, Lyon-Caen O (2001) Correlating multiple MRI parameters with clinical features: an attempt to define a new strategy in multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology 43: 712–720
Flacke S, Wullner U, Keller E, Hamzei F, Urbach H (2000) Reversible changes in echo planar perfusion- and diffusion-weighted MRI in status epilepticus. Neuroradiology 42: 92–95
Teixeira J, Zimmerman RA, Haselgrove JC, Bilaniuk LT, Hunter JV (2001) Diffusion imaging in pediatric central nervous system infections. Neuroradiology 43: 1031–1039
Inglese M, Salvi F, Iannucci G, Mancardi GL, Mascalchi M, Filippi M (2002) Magnetization transfer and diffusion tensor MR imaging of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. AJNR 23: 267–272
Liu AY, Maldjian JA, Bagley LJ, Sinson GP, Grossman RI (1999) Traumatic brain injury: diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings. AJNR 20: 1636–1641
Guo AC, MacFall JR, Provenzale JM (2002) Multiple sclerosis: diffusion tensor MR imaging for evaluation of normal-appearing white matter. Radiology 222: 729–736
Sener R (2002) Diffusion MRI in Rasmussen's encephalitis, herpes simplex encephalitis, and bacterial meningoencephalitis. Comput Med Imaging Graph 26: 327
Sener RN (2001) Herpes simplex encephalitis: diffusion MR imaging findings. Comput Med Imaging Graph 25: 391–397
Tsuchiya K, Katase S, Yoshino A, Hachiya J (1999) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of encephalitis. Am J Roentgenol 173: 1097–1099
Heiniger P, el-Koussy M, Schindler K, et al (2002) Diffusion and perfusion MRI for the localisation of epileptogenic foci in drug-resistant epilepsy. Neuroradiology 44: 475–480
Yamada K, Kubota H, Kizu O, et al (2002) Effect of intravenous gadolinium-DTPA on diffusion-weighted images: evaluation of normal brain and infarcts. Stroke 33: 1799–1802
Noguchi K, Watanabe N, Nagayoshi T, et al (1999) Role of diffusion-weighted echo-planar MRI in distinguishing between brain abscess and tumour: a preliminary report. Neuroradiology 41: 171–174
Brunberg JA, Chenevert TL, McKeever PE, et al (1995) In vivo MR determination of water diffusion coefficients and diffusion anisotropy: correlation with structural alteration in gliomas of the cerebral hemispheres. AJNR 16: 361–371
Lansberg MG, Thijs VN, O'Brien MW, et al (2001) Evolution of apparent diffusion coefficient, diffusion-weighted, and T2- weighted signal intensity of acute stroke. AJNR 22: 637–644.
Helenius J, Soinne L, Perkio J, et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in normal human brains in various age groups. AJNR 23: 194–199
Zhong J, Kennan RP, Fulbright RK, Gore JC (1998) Quantification of intravascular and extravascular contributions to BOLD effects induced by alteration in oxygenation or intravascular contrast agents. Magn Reson Med 40: 526–536
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitzek, C., Mentzel, H.J., Fitzek, S. et al. Echoplanar diffusion-weighted MRI with intravenous gadolinium-DTPA. Neuroradiology 45, 592–597 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-0965-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-0965-5