Abstract
Introduction
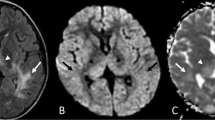
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) is usually a monophasic illness characterized by multiple lesions involving gray and white matter. Quantitative MR techniques were used to characterize and stage these lesions.
Methods
Eight patients (seven males and one female; mean age 19 years, range 5 to 36 years) were studied using conventional MRI (T2- and T1-weighted and FLAIR sequences), diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values and MRS ratios were calculated for the lesion and for normal-appearing white matter (NAWM). Three patients were imaged in the acute stage (within 7 days of the onset of neurological symptoms) and five in the subacute stage (after 7 days from the onset of symptoms).
Results
ADC values in NAWM were in the range 0.7–1.24×10−3 mm/s2 (mean 0.937 ± 0.17 mm/s2). ADC values of ADEM lesions in the acute stage were in the range 0.37–0.68×10−3 mm/s2 (mean 0.56 ± 0.16 mm/s2) and 1.01–1.31×10−3 mm/s2 (mean 1.24 ± 0.13 mm/s2) in the subacute stage. MRS ratios were obtained for all patients. NAA/Cho ratios were in the range 1.1–3.5 (mean 1.93 ± 0.86) in the NAWM. NAA/Cho ratios within ADEM lesions in the acute stage were in the range 0.63–1.48 (mean 1.18 ± 0.48) and 0.29–0.84 (mean 0.49 ± 0.22) in the subacute stage. The ADC values, NAA/Cho and Cho/Cr ratios were significantly different between lesions in the acute and subacute stages (P < 0.001, P < 0.027, P < 0.047, respectively). ADC values were significantly different between lesions in the acute (P < 0.009) and subacute stages (P < 0.005) with NAWM. In addition, NAA/Cho and Cho/Cr ratios were significantly different between lesions in the subacute stage and NAWM (P < 0.006, P < 0.007, respectively).
Conclusion
ADEM lesions were characterized in the acute stage by restricted diffusion and in the subacute stage by free diffusion and a decrease in NAA/Cho ratios. Restricted diffusion and progressive decrease in NAA/Cho ratios may help in staging the disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garg RK (2003) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: review. Postgrad Med J 79:11–17
Hynson JL, Kornberg AJ, Coleman LT, Shield L, Harvey AS, Kean MJ (2001) Clinical and neuroradiologic features of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children. Neurology 56:1308–1312
Schwarz S, Mohr A, Knauth M, Wildemann B, Storch-Hagenlocher B (2001) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. A follow-up study of 40 adult patients. Neurology 56:1313–1318
Caldemeyer KS, Smith RR, Harris TM, Edwards MK (1994) MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neuroradiology 36:216–220
Singh S, Alexander M, Korah IP (1999) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: MR imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:1101–1107
Baum PA, Barkovich AJ, Koch TK, Berg BO (1994) Deep gray matter involvement in children with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1275–1283
Cercignani M, Iannucci G, Rocca MA, Comi G, Horsfield MA, Filippi M (2000) Pathologic damage in MS assessed by diffusion-weighted and magnetization transfer MRI. Neurology 54:1139–1144
Werring DJ, Brassat D, Droogan AG, et al (2000) The pathogenesis of lesions and normal-appearing white matter changes in multiple sclerosis: a serial diffusion MRI study. Brain 123:1667–1676
Cohen J (ed) (1988) Statistical power analysis for behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Earlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 20–26
Dale RC, De Sousa C, Chong WK, Cox TCS, Harding B, Neville BGR (2000) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, multiphasic disseminated encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis in children. Brain 123:2407–2422
Tenembaum S, Chamoles N, Fejerman N (2002) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. A long-term follow-up study of 84 pediatric patients. Neurology 59:1224–1231
Honkaniemi J, Dastidar P, Kähärä V, Haapasalo H (2001) Delayed MR imaging changes in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1117–1124
Harada M, Hisaoka S, Mori K, Yoneda K, Noda S, Nishitani H (2000) Differences in water diffusion and lactate production in two different types of postinfectious encephalopathy. J Magn Reson Imaging 11:559–563
Kuker W, Ruff J, Gaertner S, Mehnert F, Madder I, Nagele T (2004) Modern MRI tools for the characterization of acute demyelinating lesions: value of chemical shift and diffusion weighted imaging. Neuroradiology 46:421–426
Rovira A, Pericot I, Alonso J, Rio J, Grivé E, Montalban X (2002) Serial diffusion-weighted MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy of acute large demyelinating brain lesions: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:989–994
Bizzi A, Ulug AM, Crawford TO, Passe T, Bugiani M, Bryan RN, Barker PB (2001) Quantitative proton MR spectroscopic imaging in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1125–1130
Gabis LV, Panasci DJ, Andriola MR, Huang W (2004) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: an MRI/MRS longitudinal study. Pediatr Neurol 30:324–329
Mader I, Wolff M, Nagele T, Niemann G, Grodd W, Kuker W (2005) MRI and proton MR spectroscopy in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Childs Nerv Syst 21:566–572
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. D.K. Thennarasu, Associate Professor, Department of Biostatistics, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasubramanya, K.S., Kovoor, J.M.E., Jayakumar, P.N. et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging and proton MR spectroscopy in the characterization of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neuroradiology 49, 177–183 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0164-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0164-2