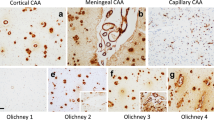
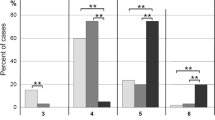
Abstract
Whereas the prevalence and impact of vascular pathology in Alzheimer diease (AD) are well established, the role of vascular and Alzheimer pathologies in the progression of neurodegeneration and cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease (PD) is under discussion. A retrospective clinico-pathologic study of 100 patients with autopsy proven PD (including 44 cases with dementia/PDD) and 20 cases of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) confirmed essential clinical (duration of illness, Mini-Mental State Examination/MMSE, age at death) and morphologic differences between these groups; Lewy body Braak scores and Alzheimer pathologies (neuritic Braak stage, cortical Aβ plaque load, and generalized cerebral amyloid angiopathy or CAA) were significantly higher/more severe in DLB and PDD than in PD without dementia. Duration of illness showed no association to any of the examined pathologic parameters, while there was a moderate association between LB scores and neuritic Braak stages, the latter significantly increasing with age. Significant association between cerebrovascular lesions and neuritic Braak stage was seen in PDD but not in PD subjects without dementia. These data suggest an influence of Alzheimer-related lesions on the progression of the neurodegenerative process and, in particular, on cognitive decline in both PDD and DLB. On the other hand, both these factors in PD and DLB appear to be largely independent from coexistent vascular pathology, except in cases with severe cerebrovascular lesions or those related to neuritic AD pathology. Assessment of ApoE genotype in a small number of cases showed no significant differences in the severity of Aβ plaque load and CAA except for much lower intensities in non-demented ε3/3 patients. Despite increasing evidence suggesting synergistic reactions between α-synuclein (αSyn), tau and Aβ-peptides, the major protein markers of both AD and Lewy body diseases, and of both vascular pathology and AD, the molecular background and pathophysiological impact of these pathologies on the progression of neurodegeneration and development of cognitive decline in PD await further elucidation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler CH, Grover AC, Sabbagh MN, Caviness JN, Connor DJ, Beach TG (2006) Clinical and pathologic findings in PD with LRRK2 mutations: 2 cases with mild cognitive impairment and small amplitude myoclonus. Mov Disord 21(Suppl 15):S538
Arai Y, Yamazaki M, Mori O, Muramatsu H, Asano G, Katayama Y (2001) Alpha-synuclein-positive structures in cases with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: morphology and its relationship to tau aggregation. Brain Res 888:287–296
Attems J (2005) Sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: pathology, clinical implications, and possible pathomechanisms. Acta Neuropathol 110:345–359
Attems J, Jellinger KA, Lintner F (2005) Alzheimer’s disease pathology influences severity and topographical distribution of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Acta Neuropathol 110:222–231
Attems J, Quass M, Jellinger KA, Lintner F (2007) Topographical distribution of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and its effect on cognitive decline are influenced by Alzheimer disease pathology. J Neurol Sci 257:49–55
Bailey TL, Rivara CB, Rocher AB, Hof PR (2004) The nature and effects of cortical microvascular pathology in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Res 26:573–578
Bancher C, Egensperger R, Kosel S, Jellinger K, Graeber MB (1997) Low prevalence of apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele in the neurofibrillary tangle predominant form of senile dementia. Acta Neuropathol 94:403–409
Barrachina M, Dalfo E, Puig B, Vidal N, Freixes M, Castano E, Ferrer I (2005) Amyloid-beta deposition in the cerebral cortex in Dementia with Lewy bodies is accompanied by a relative increase in AbetaPP mRNA isoforms containing the Kunitz protease inhibitor. Neurochem Int 46:253–260
Bertrand E, Lewandowska E, Pasennik E, Stepien T, Szpak GM, Dymecki J, Wierzba-Bobrowicz T (2007) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol (in press)
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rub U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318:121–134
Braak H, Rub U, Jansen Steur EN, Del Tredici K, de Vos RA (2005) Cognitive status correlates with neuropathologic stage in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64:1404–1410
Braak H, Bohl JR, Muller CM, Rub U, de Vos RA, Del Tredici K (2006) Stanley Fahn Lecture 2005: The staging procedure for the inclusion body pathology associated with sporadic Parkinson’s disease reconsidered. Mov Disord 21:2042–2051
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Williams ED, O’Brien JT (2004) Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and controls. Brain 127:791–800
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Firbank MJ, O’Brien JT (2006) Progression of white matter hyperintensities in Alzheimer disease, dementia with lewy bodies, and Parkinson disease dementia: a comparison with normal aging. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 14:842–849
Camicioli R, Moore MM, Kinney A, Corbridge E, Glassberg K, Kaye JA (2003) Parkinson’s disease is associated with hippocampal atrophy. Mov Disord 18:784–790
de la Torre JC (2002) Alzheimer disease as a vascular disorder: nosological evidence. Stroke 33:1152–1162
Del Ser T, Hachinski V, Merskey H, Munoz DG (2001) Clinical and pathologic features of two groups of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies: effect of coexisting Alzheimer-type lesion load. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 15:31–44
Deramecourt V, Bombois S, Maurage CA, Ghestem A, Drobecq H, Vanmechelen E, Lebert F, Pasquier F, Delacourte A (2006) Biochemical staging of synucleinopathy and amyloid deposition in dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:278–288
Desai BS, Monahan AJ, Carvey PM, Hendey B (2007) Blood–brain barrier pathology in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: implications for drug therapy. Cell Transplant 16:285–299
Dickson DW (2000) Alzheimer–Parkinson disease overlap: neuropathology. In: Clark CM, Trojanowski JQ (eds) Neurodegenerative dementias. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 247–259
Duka T, Rusnak M, Drolet RE, Duka V, Wersinger C, Goudreau JL, Sidhu A (2006) Alpha-synuclein induces hyperphosphorylation of Tau in the MPTP model of parkinsonism. FASEB J 20:2302–2312
Galasko D, Salmon D (2000) The Alzheimer–Parkinson’s disease connection. In: Clark CM, Trojanowski JQ (eds) Neurodegenerative dementias. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 229–246
Galpern WR, Lang AE (2006) Interface between tauopathies and synucleinopathies: a tale of two proteins. Ann Neurol 59:449–458
Galvin JE, Pollack J, Morris JC (2006) Clinical phenotype of Parkinson disease dementia. Neurology 67:1605–1611
Geddes JW (2005) Alpha-synuclein: a potent inducer of tau pathology. Exp Neurol 192:244–250
Giasson BI, Forman MS, Higuchi M, Golbe LI, Graves CL, Kotzbauer PT, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2003) Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein. Science 300:636–640
Giasson BI, Covy JP, Bonini NM, Hurtig HI, Farrer MJ, Trojanowski JQ, Van Deerlin VM (2006) Biochemical and pathological characterization of Lrrk2. Ann Neurol 59:315–322
Greenberg SM, Gurol ME, Rosand J, Smith EE (2004) Amyloid angiopathy-related vascular cognitive impairment. Stroke 35:2616–2619
Guerini F, Frisoni GB, Bellwald C, Rossi R, Bellelli G, Trabucchi M (2004) Subcortical vascular lesions predict functional recovery after rehabilitation in patients with l-dopa refractory parkinsonism. J Am Geriatr Soc 52:252–256
Hamilton RL (2000) Lewy bodies in Alzheimer’s disease: a neuropathological review of 145 cases using alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry. Brain Pathol 10:378–384
Hansen L, Salmon D, Galasko D, Masliah E, Katzman R, DeTeresa R, Thal L, Pay MM, Hofstetter R, Klauber M, Rice V, Butters N, Alford M (1990) The Lewy body variant of Alzheimer’s disease: a clinical and pathologic entity. Neurology 40:1–8
Hansen LA (1997) The Lewy body variant of Alzheimer disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 51:83–93
Haugarvoll K, Aarsland D, Wentzel-Larsen T, Larsen JP (2005) The influence of cerebrovascular risk factors on incident dementia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 112:386–390
Hughes TA, Ross HF, Mindham RH, Spokes EG (2004) Mortality in Parkinson’s disease and its association with dementia and depression. Acta Neurol Scand 110:118–123
Iseki E, Marui W, Kosaka K, Ueda K (1999) Frequent coexistence of Lewy bodies and neurofibrillary tangles in the same neurons of patients with diffuse Lewy body disease. Neurosci Lett 265:9–12
Iseki E, Togo T, Suzuki K, Katsuse O, Marui W, de Silva R, Lees A, Yamamoto T, Kosaka K (2003) Dementia with Lewy bodies from the perspective of tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol 105:265–270
Ishizawa T, Mattila P, Davies P, Wang D, Dickson DW (2003) Colocalization of tau and alpha-synuclein epitopes in Lewy bodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:389–397
Jellinger KA (1996) Parkinsonism due to Binswanger’s subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy. Mov Disord 11:461–462
Jellinger KA (2003) Prevalence of vascular lesions in dementia with Lewy bodies. A postmortem study. J Neural Transm 110:771–778
Jellinger KA (2003) Prevalence of cerebrovascular lesions in Parkinson’s disease. A postmortem study. Acta Neuropathol 105:415–419
Jellinger KA, Attems J (2003) Incidence of cerebrovascular lesions in Alzheimer’s disease: a postmortem study. Acta Neuropathol 105:14–17
Jellinger KA, Mitter-Ferstl E (2003) The impact of cerebrovascular lesions in Alzheimer disease––a comparative autopsy study. J Neurol 250:1050–1055
Jellinger KA, Seppi K, Wenning GK (2003) Neuropathologic changes in Parkinson disease with late onset of dementia. Arch Neurol 60:452–453 author reply 453–454
Jellinger KA (2004) Lewy body-related alpha-synucleinopathy in the aged human brain. J Neural Transm 111:1219–1235
Jellinger KA, Attems J (2005) Prevalence and pathogenic role of cerebrovascular lesions in Alzheimer disease. J Neurol Sci 229–230:37–41
Jellinger KA (2006) The morphological basis of mental dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 248:167–172
Jellinger KA, Attems J (2006) Prevalence and impact of cerebrovascular pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and parkinsonism. Acta Neurol Scand 114:38–46
Jellinger KA (2007) The enigma of vascular cognitive disorder and vascular dementia. Acta Neuropathol 113:349–388
Jellinger KA, Attems J (2007) Neuropathological evaluation of mixed dementia. J Neurol Sci 257:80–87
Jellinger KA, Attems J (2008) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Lewy body disease. J Neural Transm. doi:10.1007/S00702-00007.00856.00708
Jendroska K, Lees AJ, Poewe W, Daniel SE (1996) Amyloid beta-peptide and the dementia of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 11:647–653
Junque C, Ramirez-Ruiz B, Tolosa E, Summerfield C, Marti MJ, Pastor P, Gomez-Anson B, Mercader JM (2005) Amygdalar and hippocampal MRI volumetric reductions in Parkinson’s disease with dementia. Mov Disord 20:540–544
Kallhoff V, Peethumnongsin E, Zheng H (2007) Lack of alpha-synuclein increases amyloid plaque accumulation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 2:6
Kempster PA, Williams DR, Selikhova M, Holton J, Revesz T, Lees AJ (2007) Patterns of levodopa response in Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study. Brain 130:2123–2128
Kumaran R, Kingsbury A, Coulter I, Lashley T, Williams D, de Silva R, Mann D, Revesz T, Lees A, Bandopadhyay R (2007) DJ-1 (PARK7) is associated with 3R and 4R tau neuronal and glial inclusions in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurobiol Dis 28:122–132
Lashley T, Holton JL, Gray E, Kirkham K, O’Sullivan SS, Hilbig A, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Revesz T (2008) Cortical alpha-synuclein load is associated with amyloid-beta plaque burden in a subset of Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-00007-00336-00400
Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2006) Mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease linked to pathological alpha-synuclein: new targets for drug discovery. Neuron 52:33–38
Lewis J, Dickson DW, Lin WL, Chisholm L, Corral A, Jones G, Yen SH, Sahara N, Skipper L, Yager D, Eckman C, Hardy J, Hutton M, McGowan E (2001) Enhanced neurofibrillary degeneration in transgenic mice expressing mutant tau and APP. Science 293:1487–1491
Lippa CF (2004) Synaptophysin immunoreactivity in Pick’s disease: comparison with Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 19:341–344
Lippa SM, Lippa CF, Mori H (2005) Alpha-Synuclein aggregation in pathological aging and Alzheimer’s disease: the impact of beta-amyloid plaque level. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 20:315–318
Mandal PK, Pettegrew JW, Masliah E, Hamilton RL, Mandal R (2006) Interaction between Abeta peptide and alpha synuclein: molecular mechanisms in overlapping pathology of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s in dementia with Lewy body disease. Neurochem Res 31:1153–1162
Maries E, Dass B, Collier TJ, Kordower JH, Steece-Collier K (2003) The role of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: insights from animal models. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:727–738
Mark MH, Sage JI, Walters AS, Duvoisin RC, Miller DC (1995) Binswanger’s disease presenting as levodopa-responsive parkinsonism: clinicopathologic study of three cases. Mov Disord 10:450–454
Marshall GA, Shchelchkov E, Kaufer DI, Ivanco LS, Bohnen NI (2006) White matter hyperintensities and cortical acetylcholinesterase activity in parkinsonian dementia. Acta Neurol Scand 113:87–91
Marti MJ, Tolosa E, de la Cerda A (2007) Dementia in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 254(Suppl):41–48
Marui W, Iseki E, Ueda K, Kosaka K (2000) Occurrence of human alpha-synuclein immunoreactive neurons with neurofibrillary tangle formation in the limbic areas of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 174:81–84
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Sagara Y, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Mucke L (2001) Beta-amyloid peptides enhance alpha-synuclein accumulation and neuronal deficits in a transgenic mouse model linking Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12245–12250
Mastaglia FL, Masters CL, Beyreuther K, Kakulas BA (1989) Deposition of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid (A4) protein in the cerebral cortex in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Clin Biol Res 317:475–484
Mastaglia FL, Johnsen RD, Kakulas BA (2002) Prevalence of stroke in Parkinson’s disease: a postmortem study. Mov Disord 17:772–774
Mastaglia FL, Johnsen RD, Byrnes ML, Kakulas BA (2003) Prevalence of amyloid-beta deposition in the cerebral cortex in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18:81–86
McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA, Salmon DP, Lowe J, Mirra SS, Byrne EJ, Lennox G, Quinn NP, Edwardson JA, Ince PG, Bergeron C, Burns A, Miller BL, Lovestone S, Collerton D, Jansen EN, Ballard C, de Vos RA, Wilcock GK, Jellinger KA, Perry RH (1996) Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 47:1113–1124
McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J, Emre M, O’Brien JT, Feldman H, Cummings J, Duda JE, Lippa C, Perry EK, Aarsland D, Arai H, Ballard CG, Boeve B, Burn DJ, Costa D, Del Ser T, Dubois B, Galasko D, Gauthier S, Goetz CG, Gomez-Tortosa E, Halliday G, Hansen LA, Hardy J, Iwatsubo T, Kalaria RN, Kaufer D, Kenny RA, Korczyn A, Kosaka K, Lee VM, Lees A, Litvan I, Londos E, Lopez OL, Minoshima S, Mizuno Y, Molina JA, Mukaetova-Ladinska EB, Pasquier F, Perry RH, Schulz JB, Trojanowski JQ, Yamada M (2005) Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 65:1863–1872
Mikolaenko I, Pletnikova O, Kawas CH, O’Brien R, Resnick SM, Crain B, Troncoso JC (2005) Alpha-synuclein lesions in normal aging, Parkinson disease, and Alzheimer disease: evidence from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:156–162
Mrak RE, Griffin WS (2007) Common inflammatory mechanisms in Lewy body disease and Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:683–686
Nagano-Saito A, Washimi Y, Arahata Y, Kachi T, Lerch JP, Evans AC, Dagher A, Ito K (2005) Cerebral atrophy and its relation to cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64:224–229
Neumann M, Muller V, Gorner K, Kretzschmar HA, Haass C, Kahle PJ (2004) Pathological properties of the Parkinson’s disease-associated protein DJ-1 in alpha-synucleinopathies and tauopathies: relevance for multiple system atrophy and Pick’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 107:489–496
Olichney JM, Hansen LA, Galasko D, Saitoh T, Hofstetter CR, Katzman R, Thal LJ (1996) The apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele is associated with increased neuritic plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body variant. Neurology 47:190–196
Olichney JM, Ellis RJ, Katzman R, Sabbagh MN, Hansen L (1997) Types of cerebrovascular lesions associated with severe cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 826:493–497
Papapetropoulos S, Lieberman A, Gonzalez J, Mash DC (2005) Can Alzheimer’s type pathology influence the clinical phenotype of Parkinson’s disease? Acta Neurol Scand 111:353–359
Parkkinen L, Soininen H, Alafuzoff I (2003) Regional distribution of alpha-synuclein pathology in unimpaired aging and Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:363–367
Pletnikova O, West N, Lee MK, Rudow GL, Skolasky RL, Dawson TM, Marsh L, Troncoso JC (2005) Abeta deposition is associated with enhanced cortical alpha-synuclein lesions in Lewy body diseases. Neurobiol Aging 26:1183–1192
Popescu A, Lippa CF, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2004) Lewy bodies in the amygdala: increase of a-synuclein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases with tau-based inclusions. Arch Neurol 61:1915–1919
Premkumar DR, Cohen DL, Hedera P, Friedland RP, Kalaria RN (1996) Apolipoprotein E-epsilon4 alleles in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and cerebrovascular pathology associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 148:2083–2095
Reitz C, Trenkwalder C, Kretzschmar K, Roesler A, Eckardstein VA, Berger K (2006) Relation of cerebral small-vessel disease and brain atrophy to mild Parkinsonism in the elderly. Mov Disord 21(11):1914–1919
Rogers J, Mastroeni D, Leonard B, Joyce J, Grover A (2007) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: are microglia pathogenic in either disorder? Int Rev Neurobiol 82:235–246
Saito Y, Kawashima A, Ruberu NN, Fujiwara H, Koyama S, Sawabe M, Arai T, Nagura H, Yamanouchi H, Hasegawa M, Iwatsubo T, Murayama S (2003) Accumulation of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein in aging human brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:644–654
Saito Y, Ruberu NN, Sawabe M, Arai T, Kazama H, Hosoi T, Yamanouchi H, Murayama S (2004) Lewy body-related alpha-synucleinopathy in aging. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:742–749
Schmidt ML, Martin JA, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1996) Convergence of Lewy bodies and neurofibrillary tangles in amygdala neurons of Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol 91:475–481
Shao CY, Crary JF, Rao C, Sacktor TC, Mirra SS (2006) Atypical protein kinase C in neurodegenerative disease II: PKCiota/lambda in tauopathies and alpha-synucleinopathies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:327–335
Thal DR, Rub U, Schultz C, Sassin I, Ghebremedhin E, Del Tredici K, Braak E, Braak H (2000) Sequence of Abeta-protein deposition in the human medial temporal lobe. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:733–748
Thanvi B, Lo N, Robinson T (2005) Vascular parkinsonism––an important cause of parkinsonism in older people. Age Ageing 34:114–119
Thomas A, Ballard C, Kenny RA, O’Brien J, Oakley A, Kalaria R (2005) Correlation of entorhinal amyloid with memory in Alzheimer’s and vascular but not Lewy body dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 19:57–60
Tian J, Shi J, Mann DM (2004) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy and dementia. Panminerva Med 46:253–264
Trembath D, Ervin JF, Broom L, Szymanski M, Welsh-Bohmer K, Pieper C, Hulette CM (2007) The distribution of cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease varies with ApoE genotype. Acta Neuropathol 113:23–31
Trembath Y, Rosenberg C, Ervin JF, Schmechel DE, Gaskell P, Pericak-Vance M, Vance J, Hulette CM (2003) Lewy body pathology is a frequent co-pathology in familial Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 105:484–488
Uchikado H, Lin WL, DeLucia MW, Dickson DW (2006) Alzheimer disease with amygdala Lewy bodies: a distinct form of alpha-synucleinopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:685–697
Wenning GK, Jellinger KA (2005) The role of alpha-synuclein and tau in neurodegenerative movement disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 18:357–362
Wirths O, Bayer TA (2003) Alpha-synuclein, Abeta and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:103–108
Wu E, Lipton RB, Dickson DW (1992) Amyloid angiopathy in diffuse Lewy body disease. Neurology 42:2131–2135
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uitti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Muller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44:601–607
Zlokovic BV (2004) Clearing amyloid through the blood–brain barrier. J Neurochem 89:807–811
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the colleagues of the clinical departments and Institute of Pathology of OWS Hospital (head: Prof. Dr. F. Lintner), Vienna, Austria, for the clinical and pathological data and the brain material; to Mrs. Veronika Rappelsberger for excellent laboratory work, and to Mr. Erich Mitter-Ferstl, Ph.D., for secretarial work. The study was supported in part by the Society for the Support of Research in Experimental Neurology, Vienna, Austria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of Professor Dr. Franz Seitelberger, a pioneer of modern neuropathology and neurosciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jellinger, K.A., Attems, J. Prevalence and impact of vascular and Alzheimer pathologies in Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 115, 427–436 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0347-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0347-5