Abstract
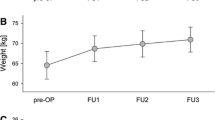
Patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and essential tremor (ET) tend to lose weight progressively over years. Weight gain following deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) for treatment of PD has been documented in several studies that were limited by small sample size and exclusive focus on PD patients with STN stimulation. The current study was undertaken to examine weight change in a large sample of movement disorder patients following DBS. A retrospective review was undertaken of 182 patient charts following DBS of the STN, ventralis intermedius nucleus of the thalamus (VIM), and globus pallidus internus (GPi). Weight was collected preoperatively and postoperatively up to 24 months following surgery. Data were adjusted for baseline weight and multivariate linear regression was performed with repeated measures to assess weight change. Statistically significant mean weight gain of 1.8 kg (2.8% increase from baseline, p = 0.0113) was observed at a rate of approximately 1 kg per year up to 24 months following surgery. This gain was not predicted by age, gender, diagnosis, or stimulation target in a multivariate model. Significant mean weight gain of 2.3 kg (p = 0.0124) or 4.2% was observed in our PD patients. Most patients with PD and ET gain weight following DBS, and this gain is not predicted by age, gender, diagnosis, or stimulation target.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- ET:
-
Essential tremor
- DBS:
-
Deep brain stimulation
- STN:
-
Subthalamic nucleus
- GPi:
-
Globus pallidus internus
- VIM:
-
Ventralis intermedius nucleus of the thalamus
References
Beyer PL, Palarino MY, Michalek D, Busenbark K, Koller WC (1995) Weight change and body composition in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Am Diet Assoc 95(9):979–983
Chen H, Zhang SM, Hernan MA, Willett WC, Ascherio A (2003) Weight loss in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53(5):676–679
Palhagen S, Lorefalt B, Carlsson M, Ganowiak W, Toss G, Unosson M, Granerus AK (2005) Does l-dopa treatment contribute to reduction in body weight in elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease? Acta Neurol Scand 111(1):12–20
Louis ED, Marder K, Jurewicz EC, Watner D, Levy G, Mejia-Santana H (2002) Body mass index in essential tremor. Arch Neurol 59(8):1273–1277
Moro E, Scerrati M, Romito LM, Roselli R, Tonali P, Albanese A (1999) Chronic subthalamic nucleus stimulation reduces medication requirements in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 53(1):85–90
Barichella M, Marczewska AM, Mariani C, Landi A, Vairo A, Pezzoli G (2003) Body weight gain rate in patients with Parkinson’s disease and deep brain stimulation. Mov Disord 18(11):1337–1340
Romito LM, Scerrati M, Contarino MF, Bentivoglio AR, Tonali P, Albanese A (2002) Long-term follow up of subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 58(10):1546–1550
Bannier S, Montaurier C, Derost PP, Ulla M, Lemaire JJ, Boirie Y et al (2009) Overweight after deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease: long-term follow-up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80(5):484–488
Gironell B, Pascual-Sedano P, Otermin Kulisevsky J (2002) Weight gain after functional surgery for Parkinsons disease. Neurologia 17(6):310–316
Walker HC, Lyerly M, Cutter G et al (2009) Weight changes associated with unilateral STN DBS and advanced PD. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15(9):709–711
Montaurier C, Morio B, Bannier S et al (2007) Mechanisms of body weight gain in patients with Parkinson’s disease after subthalamic stimulation. Brain 130:1808–1818
Macia F, Perlemoine C, Coman I et al (2004) Parkinson’s disease patients with bilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation gain weight. Mov Disord 19(2):206–212
Perlemoine C, Macia F, Tison F et al (2005) Effects of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation and levodopa on energy production rate and substrate oxidation in Parkinson’s disease. Br J Nutr 93(2):191–198
Lipp A, Tank J, Trottenberg T, Kupsch A, Arnold G, Jordan J (2005) Sympathetic activation due to deep brain stimulation in the region of the STN. Neurology 65:774–775
Diamond A, Kenney C, Almaguer M, Jankovic J (2007) Hyperhidrosis due to deep brain stimulation in a patient with essential tremor. Case report. J Neurosurg 107(5):1036–1038
Ashkan K, Blomstedt P, Zrinzo L et al (2007) Variability of the subthalamic nucleus: the case for direct MRI guided targeting. Br J Neurosurg 21(2):197–200
Grafton ST, Turner RS, Desmurget M, Bakay R, Delong M, Vitek J et al (2006) Normalizing motor-related brain activity: subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 66:1192–1199
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strowd, R.E., Cartwright, M.S., Passmore, L.V. et al. Weight change following deep brain stimulation for movement disorders. J Neurol 257, 1293–1297 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5509-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5509-4