Summary
Background. To investigate the therapeutic consequences of restricting the CSF dynamic evaluation to a lumbar infusion test (LIT), as opposed to our formerly applied intraventricular assessment (VIT), in patients with communicating hydrocephalus (CH).
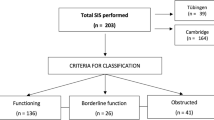
Method. All patients over 18 years of age referred with clinical and radiological indication of treatment-requiring secondary CH (n = 50) or idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus (INPH, n = 33) were subjected to a LIT. Subsequently, a combination of the results of the LIT (mainly the resistance to CSF outflow) and the clinical presentation determined whether to proceed with (a) VIT before a decision about shunt surgery, (b) shunt surgery or (c) no further diagnostic investigation or surgery.
Findings. In 88 percent of the patients with secondary CH and 80 percent of the patients with INPH the decision on shunt surgery was made after performing exclusively a LIT. The shunting success rate was 90 percent in patients with secondary CH and 82 percent in patients with INPH, which however in the latter group decreased to 76 percent, when including the patients undergoing an additional VIT. The achieved shunt success rates are equal or better, compared to the results from previous studies using intraventricular assessment.
Conclusions. LIT and VIT are equally reliable for selecting shunt responsive patients with CH, using clinical improvement rate as the main criterion for comparison. The practical and economic consequences are substantial: the LIT can be performed in an outpatient setting, whereas VIT necessitates hospitalisation for 1–2 days including occupation of the neurosurgical theatre and postoperative neuro-intensive monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RA Bech G Waldemar F Gjerris L Klinken M Juhler (1999) ArticleTitleShunting effects in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus; correlation with cerebral and leptomeningeal biopsy findings. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141 633–639 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007010050353
R Bech-Azeddine G Waldemar GM Knudsen P Hogh P Bruhn G Wildschiodtz F Gjerris OB Paulson M Juhler (2001) ArticleTitleIdiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: evaluation and findings in a multidisciplinary memory clinic. Eur J Neurol 8 601–611 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1468-1331.2001.00291.x Occurrence Handle11784345
EC Benzel AL Pelletier PG Levy (1990) ArticleTitleCommunicating hydrocephalus in adults: prediction of outcome after ventricular shunting procedures. Neurosurgery 26 655–660 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199004000-00015 Occurrence Handle2330088
B Beyerl PM Black (1984) ArticleTitlePosttraumatic hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 15 257–261 Occurrence Handle6384812
AJ Boon JT Tans EJ Delwel SM Egeler-Peerdeman PW Hanlo HA Wurzer CJ Avezaat DA de Jong RH Gooskens J Hermans (1997) ArticleTitleDutch normal-pressure hydrocephalus study: prediction of outcome after shunting by resistance to outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurosurg 87 687–693 Occurrence Handle9347976
AJ Boon JT Tans EJ Delwel SM Egeler-Peerdeman PW Hanlo HA Wurzer J Hermans (1999) ArticleTitleDutch Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Study: the role of cerebrovascular disease. J Neurosurg 90 221–226 Occurrence Handle9950492
SE Børgesen (1984) ArticleTitleConductance to outflow of CSF in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 71 1–45 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01401149
SE Børgesen MJ Albeck F Gjerris M Czosnyka P Laniewski (1992) ArticleTitleComputerized infusion test compared to steady pressure constant infusion test in measurement of resistance to CSF outflow. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 119 12–16 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01541775
SE Børgesen F Gjerris (1982) ArticleTitleThe predictive value of conductance to outflow of CSF in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain 105 65–86 Occurrence Handle7066675
WG Bradley AR Whittemore AS Whatanabe SJ Davis LM Teresi M Homyak (1991) ArticleTitleAssociation of deep white matter infarction with chronic communicating hydrocephalus: Implications regarding the possible etiology of normal pressure hydrocephalus. AJNR 12 31–39 Occurrence Handle1899515
ER Cardoso S Galbraith (1985) ArticleTitlePosttraumatic hydrocephalus – a retrospective review. Surg Neurol 23 261–264 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0090-3019(85)90092-8 Occurrence Handle3975808
HA Crockard K Hanlon EE Duda JF Mullan (1977) ArticleTitleHydrocephalus as a cause of dementia: evaluation by computerised tomography and intracranial pressure monitoring. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40 736–740 Occurrence Handle925692
M Czosnyka H Whitehouse P Smielewski S Simac JD Pickard (1996) ArticleTitleTesting of cerebrospinal compensatory reserve in shunted and non-shunted patients: a guide to interpretation based on an observational study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 60 549–558 Occurrence Handle8778261
Czosnyka M, Wollk-Laniewski D, Darwaj P, Duda M, Batorski L, Zaworski W (1989) Software for neurosurgery intensive care. In: Hoff JT, Betz AL (eds) Intracranial pressure VII. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 84–87
Fedders O, Schmidt JF, Albeck MJ, Gjerris F (1989) Comparison of resistance to CSF outflow (Rout) by ventricular and lumbar perfusion. In: Hoff JT, Betz AL (eds) Intracranial pressure VII. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 359–361
MF Folstein SE Folstein PR McHugh (1975) ArticleTitleMini-mental state; A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12 189–198 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6 Occurrence Handle1202204
RP Friedland (1989) ArticleTitleNormal-pressure hydrocephalus and the saga of the treatable dementias. JAMA 262 2577–2581 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.262.18.2577 Occurrence Handle2535659
F Gjerris SE Børgesen (1992) ArticleTitleCurrent concepts of measurement of cerebrospinal fluid absorption and biomechanics of hydrocephalus. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg 19 147–177
Gjerris F, Børgesen SE (2000) Pathophysiology of the CSF Circulation. In: Crockard A, Hayward RD, Hoff JT (eds) Neurosurgery – the scientific basis of clinical practice. Blackwell Science, Boston, pp 147–168
F Gjerris SE Børgesen PS Sørensen F Boesen K Schmidt A Harmsen J Lester (1987) ArticleTitleResistance to cerebrospinal fluid outflow and intracranial pressure in patients with hydrocephalus after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 88 79–86 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01404142
NR Graff-Radford JC Godersky MP Jones (1989) ArticleTitleVariables predicting surgical outcome in symptomatic hydrocephalus in the elderly. Neurology 39 1601–1604 Occurrence Handle2586777
NR Graff-Radford J Torner HP Adams SuffixJr NF Kassell (1989) ArticleTitleFactors associated with hydrocephalus after subarachnoid hemorrhage. A report of the cooperative aneurysm study. Arch Neurol 46 744–752 Occurrence Handle2742543
JO Greenberg HA Shenkin R Adam (1977) ArticleTitleIdiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus – a report of 73 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40 336–341 Occurrence Handle874511
AO Hebb MD Cusimano (2001) ArticleTitleIdiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a systematic review of diagnosis and outcome. Neurosurgery 49 1166–1184 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200111000-00028 Occurrence Handle11846911
B Kahlon G Sundbarg S Rehncrona (2002) ArticleTitleComparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73 721–726 Occurrence Handle10.1136/jnnp.73.6.721 Occurrence Handle12438477
A Larsson C Wikkelsø M Bilting H Stephensen (1991) ArticleTitleClinical parameters in 74 consecutive patients shunt operated for normal pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurol Scand 84 475–482 Occurrence Handle1792852
J Malm B Kristensen T Karlsson M Fagerlund J Elfverson J Ekstedt (1995) ArticleTitleThe predictive value of cerebrospinal fluid dynamic tests in patients with the idiopathic adult hydrocephalus syndrome. Arch Neurol 52 783–789 Occurrence Handle7639630
J Malm B Kristensen B Stegmayr M Fagerlund LO Koskinen (2000) ArticleTitleThree-year survival and functional outcome of patients with idiopathic adult hydrocephalus syndrome. Neurology 55 576–578 Occurrence Handle10953197
EM Massicotte MR Del Bigio (1999) ArticleTitleHuman arachnoid villi response to subarachnoid hemorrhage: possible relationship to chronic hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 91 80–84 Occurrence Handle10389884
U Meier FS Zeilinger D Kintzel (1999) ArticleTitleSigns, symptoms and course of normal pressure hydrocephalus in comparison with cerebral atrophy. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141 1039–1048 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007010050480
O Motohashi M Suzuki N Shida K Umezawa T Ohtoh Y Sakurai T Yoshimoto (1995) ArticleTitleSubarachnoid haemorrhage induced proliferation of leptomeningeal cells and deposition of extracellular matrices in the arachnoid granulations and subarachnoid space. Immunohistochemical study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 136 88–91 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01411441
RC Petersen B Mokri ER Laws SuffixJr (1985) ArticleTitleSurgical treatment of idiopathic hydrocephalus in elderly patients. Neurology 35 307–311 Occurrence Handle3974888
Pickard JD, Teasdale G, Matheson M, Lindsay K, Galbraith S, Wyper D, Macpherson P (1980) Intraventricular pressure waves – the best predictive test for shunting in normal pressure hydrophalus. In: Shulman K, Marmarou A, Miller JD, Becker DP, Hochwald GM, Brock M (eds) Intracranial pressure IV. Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 498–500
P Reilly (2001) ArticleTitleIn normal pressure hydrocephalus, intracranial pressure monitoring is the only useful test. J Clin Neurosci 8 66–67 Occurrence Handle10.1054/jocn.2000.0781 Occurrence Handle11322125
B Reisberg SH Ferris M de Leon T Crook (1982) ArticleTitleThe global deterioration scale for assessment of primary degenerative dementia. Am J Psychiatry 139 1136–1139 Occurrence Handle7114305
JV Rosenfeld S Siraruj (2001) ArticleTitleIn normal pressure hydrocephalus, intracranial pressure monitoring is the only useful test. J Clin Neurosci 8 68–69 Occurrence Handle10.1054/jocn.2000.0803 Occurrence Handle11322127
JP Sheehan RS Polin JM Sheehan MK Baskaya NF Kassell (1999) ArticleTitleFactors associated with hydrocephalus after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 45 1120–1127 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199911000-00021 Occurrence Handle10549928
FH Sklar CW Beyer SuffixJr M Ramanathan WK Clark (1980) ArticleTitleServo-controlled lumbar infusions in children. A quantitative approach to the problem of arrested hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 52 87–98 Occurrence Handle7350284
LM Tang (1990) ArticleTitleVentriculoperitoneal shunt in cryptococcal meningitis with hydrocephalus. Surg Neurol 33 314–319 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0090-3019(90)90198-X Occurrence Handle2330532
Tans JT, Poortvliet DCJ (1993) Comparison of lumbar and ventricular constant flow and bolus infusions in hydrocephalus. In: Avezaat CJ, Eijndhoven JHM, Maas AIR, Tans JT (eds) Intracranial pressure VIII. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 749–752
J Vanneste P Augustijn C Dirven WF Tan ZD Goedhart (1992) ArticleTitleShunting normal pressure hydrocephalus: do the benefits outweigh the risks? Neurology 42 54–59
J Vanneste P Augustijn WF Tan C Dirven (1993) ArticleTitleShunting normal pressure hydrocephalus: the predictive value of combined clinical and CT data. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56 251–256 Occurrence Handle8459240
R Walchenbach E Geiger RT Thomeer JA Vanneste (2002) ArticleTitleThe value of temporary external lumbar CSF drainage in predicting the outcome of shunting on normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72 503–506
MA Williams AY Razumovsky DF Hanley (1998) ArticleTitleEvaluation of shunt function in patients who are never better, or better than worse after shunt surgery for NPH. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 71 368–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bech-Azeddine, R., Gjerris, F., Waldemar, G. et al. Intraventricular or lumbar infusion test in adult communicating hydrocephalus? Practical consequences and clinical outcome of shunt operation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147, 1027–1036 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0589-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0589-0