Abstract
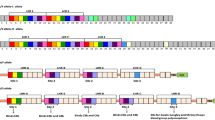
The amyloid-beta peptide (Aβ) cascade hypothesis posits that Aβ accumulation is the fundamental initiator of Alzheimer's disease (AD), and mounting evidence suggests that impaired Aβ clearance rather than its overproduction is the major pathogenic event for AD. Recent genetic studies have identified cluster of differentiation 33 (CD33) as a strong genetic locus linked to AD. As a type I transmembrane protein, CD33 belongs to the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins, mediating the cell–cell interaction and inhibiting normal functions of immune cells. In the brain, CD33 is mainly expressed on microglial cells. The level of CD33 was found to be increased in the AD brain, which positively correlated with amyloid plaque burden and disease severity. More importantly, CD33 led to the impairment of microglia-mediated clearance of Aβ, which resulted in the formation of amyloid plaques in the brain. In this article, we review the recent epidemiological findings of CD33 that related with AD and discuss the levels and pathogenic roles of CD33 in this disease. Based on the contributing effects of CD33 in AD pathogenesis, targeting CD33 may provide new opportunities for AD therapeutic strategies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297(5580):353–356. doi:10.1126/science.1072994
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE, Bateman RJ (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Science 330(6012):1774. doi:10.1126/science.1197623
Bertram L, Lange C, Mullin K, Parkinson M, Hsiao M, Hogan MF, Schjeide BM, Hooli B, Divito J, Ionita I, Jiang H, Laird N, Moscarillo T, Ohlsen KL, Elliott K, Wang X, Hu-Lince D, Ryder M, Murphy A, Wagner SL, Blacker D, Becker KD, Tanzi RE (2008) Genome-wide association analysis reveals putative Alzheimer's disease susceptibility loci in addition to APOE. Am J Hum Genet 83(5):623–632. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.10.008
Naj AC, Jun G, Beecham GW, Wang LS, Vardarajan BN, Buros J, Gallins PJ, Buxbaum JD, Jarvik GP, Crane PK, Larson EB, Bird TD, Boeve BF, Graff-Radford NR, De Jager PL, Evans D, Schneider JA, Carrasquillo MM, Ertekin-Taner N, Younkin SG, Cruchaga C, Kauwe JS, Nowotny P, Kramer P, Hardy J, Huentelman MJ, Myers AJ, Barmada MM, Demirci FY, Baldwin CT, Green RC, Rogaeva E, St George-Hyslop P, Arnold SE, Barber R, Beach T, Bigio EH, Bowen JD, Boxer A, Burke JR, Cairns NJ, Carlson CS, Carney RM, Carroll SL, Chui HC, Clark DG, Corneveaux J, Cotman CW, Cummings JL, DeCarli C, DeKosky ST, Diaz-Arrastia R, Dick M, Dickson DW, Ellis WG, Faber KM, Fallon KB, Farlow MR, Ferris S, Frosch MP, Galasko DR, Ganguli M, Gearing M, Geschwind DH, Ghetti B, Gilbert JR, Gilman S, Giordani B, Glass JD, Growdon JH, Hamilton RL, Harrell LE, Head E, Honig LS, Hulette CM, Hyman BT, Jicha GA, Jin LW, Johnson N, Karlawish J, Karydas A, Kaye JA, Kim R, Koo EH, Kowall NW, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Lieberman AP, Lopez OL, Mack WJ, Marson DC, Martiniuk F, Mash DC, Masliah E, McCormick WC, McCurry SM, McDavid AN, McKee AC, Mesulam M, Miller BL, Miller CA, Miller JW, Parisi JE, Perl DP, Peskind E, Petersen RC, Poon WW, Quinn JF, Rajbhandary RA, Raskind M, Reisberg B, Ringman JM, Roberson ED, Rosenberg RN, Sano M, Schneider LS, Seeley W, Shelanski ML, Slifer MA, Smith CD, Sonnen JA, Spina S, Stern RA, Tanzi RE, Trojanowski JQ, Troncoso JC, Van Deerlin VM, Vinters HV, Vonsattel JP, Weintraub S, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Williamson J, Woltjer RL, Cantwell LB, Dombroski BA, Beekly D, Lunetta KL, Martin ER, Kamboh MI, Saykin AJ, Reiman EM, Bennett DA, Morris JC, Montine TJ, Goate AM, Blacker D, Tsuang DW, Hakonarson H, Kukull WA, Foroud TM, Haines JL, Mayeux R, Pericak-Vance MA, Farrer LA, Schellenberg GD (2011) Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet 43(5):436–441. doi:10.1038/ng.801
Hollingworth P, Harold D, Sims R, Gerrish A, Lambert JC, Carrasquillo MM, Abraham R, Hamshere ML, Pahwa JS, Moskvina V, Dowzell K, Jones N, Stretton A, Thomas C, Richards A, Ivanov D, Widdowson C, Chapman J, Lovestone S, Powell J, Proitsi P, Lupton MK, Brayne C, Rubinsztein DC, Gill M, Lawlor B, Lynch A, Brown KS, Passmore PA, Craig D, McGuinness B, Todd S, Holmes C, Mann D, Smith AD, Beaumont H, Warden D, Wilcock G, Love S, Kehoe PG, Hooper NM, Vardy ER, Hardy J, Mead S, Fox NC, Rossor M, Collinge J, Maier W, Jessen F, Ruther E, Schurmann B, Heun R, Kolsch H, van den Bussche H, Heuser I, Kornhuber J, Wiltfang J, Dichgans M, Frolich L, Hampel H, Gallacher J, Hull M, Rujescu D, Giegling I, Goate AM, Kauwe JS, Cruchaga C, Nowotny P, Morris JC, Mayo K, Sleegers K, Bettens K, Engelborghs S, De Deyn PP, Van Broeckhoven C, Livingston G, Bass NJ, Gurling H, McQuillin A, Gwilliam R, Deloukas P, Al-Chalabi A, Shaw CE, Tsolaki M, Singleton AB, Guerreiro R, Muhleisen TW, Nothen MM, Moebus S, Jockel KH, Klopp N, Wichmann HE, Pankratz VS, Sando SB, Aasly JO, Barcikowska M, Wszolek ZK, Dickson DW, Graff-Radford NR, Petersen RC, van Duijn CM, Breteler MM, Ikram MA, DeStefano AL, Fitzpatrick AL, Lopez O, Launer LJ, Seshadri S, Berr C, Campion D, Epelbaum J, Dartigues JF, Tzourio C, Alperovitch A, Lathrop M, Feulner TM, Friedrich P, Riehle C, Krawczak M, Schreiber S, Mayhaus M, Nicolhaus S, Wagenpfeil S, Steinberg S, Stefansson H, Stefansson K, Snaedal J, Bjornsson S, Jonsson PV, Chouraki V, Genier-Boley B, Hiltunen M, Soininen H, Combarros O, Zelenika D, Delepine M, Bullido MJ, Pasquier F, Mateo I, Frank-Garcia A, Porcellini E, Hanon O, Coto E, Alvarez V, Bosco P, Siciliano G, Mancuso M, Panza F, Solfrizzi V, Nacmias B, Sorbi S, Bossu P, Piccardi P, Arosio B, Annoni G, Seripa D, Pilotto A, Scarpini E, Galimberti D, Brice A, Hannequin D, Licastro F, Jones L, Holmans PA, Jonsson T, Riemenschneider M, Morgan K, Younkin SG, Owen MJ, O'Donovan M, Amouyel P, Williams J (2011) Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet 43(5):429–435. doi:10.1038/ng.803
Carrasquillo MM, Belbin O, Hunter TA, Ma L, Bisceglio GD, Zou F, Crook JE, Pankratz VS, Sando SB, Aasly JO, Barcikowska M, Wszolek ZK, Dickson DW, Graff-Radford NR, Petersen RC, Passmore P, Morgan K, Younkin SG (2011) Replication of EPHA1 and CD33 associations with late-onset Alzheimer's disease: a multi-centre case–control study. Mol Neurodegener 6(1):54. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-6-54
Chung SJ, Lee JH, Kim SY, You S, Kim MJ, Lee JY, Koh J (2012) Association of GWAS top hits with late-onset Alzheimer disease in Korean population. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 27(3):250–257. doi:10.1097/WAD.0b013e31826d7281
Deng YL, Liu LH, Wang Y, Tang HD, Ren RJ, Xu W, Ma JF, Wang LL, Zhuang JP, Wang G, Chen SD (2012) The prevalence of CD33 and MS4A6A variant in Chinese Han population with Alzheimer's disease. Hum Genet 131(7):1245–1249. doi:10.1007/s00439-012-1154-6
Tan L, Yu JT, Zhang W, Wu ZC, Zhang Q, Liu QY, Wang W, Wang HF, Ma XY, Cui WZ (2013) Association of GWAS-linked loci with late-onset Alzheimer's disease in a northern Han Chinese population. Alzheimer's Dement J Alzheimer's Assoc 9(5):546–553. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.08.007
Yuan Q, Chu C, Jia J (2012) Association studies of 19 candidate SNPs with sporadic Alzheimer's disease in the North Chinese Han population. Neurol Sci 33(5):1021–1028. doi:10.1007/s10072-011-0881-0
Reitz C, Jun G, Naj A, Rajbhandary R, Vardarajan BN, Wang LS, Valladares O, Lin CF, Larson EB, Graff-Radford NR, Evans D, De Jager PL, Crane PK, Buxbaum JD, Murrell JR, Raj T, Ertekin-Taner N, Logue M, Baldwin CT, Green RC, Barnes LL, Cantwell LB, Fallin MD, Go RC, Griffith P, Obisesan TO, Manly JJ, Lunetta KL, Kamboh MI, Lopez OL, Bennett DA, Hendrie H, Hall KS, Goate AM, Byrd GS, Kukull WA, Foroud TM, Haines JL, Farrer LA, Pericak-Vance MA, Schellenberg GD, Mayeux R (2013) Variants in the ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCA7), apolipoprotein E 4, and the risk of late-onset Alzheimer disease in African Americans. JAMA 309(14):1483–1492. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.2973
Crocker PR, Paulson JC, Varki A (2007) Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 7(4):255–266. doi:10.1038/nri2056
Griciuc A, Serrano-Pozo A, Parrado AR, Lesinski AN, Asselin CN, Mullin K, Hooli B, Choi SH, Hyman BT, Tanzi RE (2013) Alzheimer's disease risk gene CD33 inhibits microglial uptake of amyloid beta. Neuron 78(4):631–643. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.014
Karch CM, Jeng AT, Nowotny P, Cady J, Cruchaga C, Goate AM (2012) Expression of novel Alzheimer's disease risk genes in control and Alzheimer's disease brains. PloS One 7(11):e50976. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050976
Bradshaw EM, Chibnik LB, Keenan BT, Ottoboni L, Raj T, Tang A, Rosenkrantz LL, Imboywa S, Lee M, Von Korff A, Morris MC, Evans DA, Johnson K, Sperling RA, Schneider JA, Bennett DA, De Jager PL (2013) CD33 Alzheimer's disease locus: altered monocyte function and amyloid biology. Nat Neurosci 16(7):848–850. doi:10.1038/nn.3435
Malpass K (2013) Alzheimer disease: functional dissection of CD33 locus implicates innate immune response in Alzheimer disease pathology. Nat Rev Neurol 9(7):360. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2013.119
Varki A, Angata T (2006) Siglecs—the major subfamily of I-type lectins. Glycobiology 16(1):1R–27R. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwj008
von Gunten S, Bochner BS (2008) Basic and clinical immunology of Siglecs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1143:61–82. doi:10.1196/annals.1443.011
Ravetch JV, Lanier LL (2000) Immune inhibitory receptors. Science 290(5489):84–89
Walter RB, Raden BW, Zeng R, Hausermann P, Bernstein ID, Cooper JA (2008) ITIM-dependent endocytosis of CD33-related Siglecs: role of intracellular domain, tyrosine phosphorylation, and the tyrosine phosphatases, Shp1 and Shp2. J Leukoc Biol 83(1):200–211. doi:10.1189/jlb.0607388
Andrews RG, Torok-Storb B, Bernstein ID (1983) Myeloid-associated differentiation antigens on stem cells and their progeny identified by monoclonal antibodies. Blood 62(1):124–132
Griffin JD, Linch D, Sabbath K, Larcom P, Schlossman SF (1984) A monoclonal antibody reactive with normal and leukemic human myeloid progenitor cells. Leuk Res 8(4):521–534
Jandus C, Simon HU, von Gunten S (2011) Targeting Siglecs—a novel pharmacological strategy for immuno- and glycotherapy. Biochem Pharmacol 82(4):323–332. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.05.018
Vimr E, Lichtensteiger C (2002) To sialylate, or not to sialylate: that is the question. Trends Microbiol 10(6):254–257
Ricart AD (2011) Antibody-drug conjugates of calicheamicin derivative: gemtuzumab ozogamicin and inotuzumab ozogamicin. Clin Cancer Res 17(20):6417–6427. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0486
Crocker PR, Redelinghuys P (2008) Siglecs as positive and negative regulators of the immune system. Biochem Soc Trans 36(Pt 6):1467–1471. doi:10.1042/BST0361467
Lajaunias F, Dayer JM, Chizzolini C (2005) Constitutive repressor activity of CD33 on human monocytes requires sialic acid recognition and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mediated intracellular signaling. Eur J Immunol 35(1):243–251. doi:10.1002/eji.200425273
Gonzalez Y, Herrera MT, Soldevila G, Garcia-Garcia L, Fabián G, Pérez-Armendariz EM, Bobadilla K, Guzmán-Beltran S, Sada E, Torres M (2012) High glucose concentrations induce TNF-alpha production through the down-regulation of CD33 in primary human monocytes. BMC Immunol 13:19. doi:10.1186/1471-2172-13-19
Vitale C, Romagnani C, Falco M, Ponte M, Vitale M, Moretta A, Bacigalupo A, Moretta L, Mingari MC (1999) Engagement of p75/AIRM1 or CD33 inhibits the proliferation of normal or leukemic myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(26):15091–15096
Balaian L, Zhong RK, Ball ED (2003) The inhibitory effect of anti-CD33 monoclonal antibodies on AML cell growth correlates with Syk and/or ZAP-70 expression. Exp Hematol 31(5):363–371
Lin PI, Vance JM, Pericak-Vance MA, Martin ER (2007) No gene is an island: the flip-flop phenomenon. Am J Hum Genet 80(3):531–538. doi:10.1086/512133
Allen M, Cox C, Belbin O, Ma L, Bisceglio GD, Wilcox SL, Howell CC, Hunter TA, Culley O, Walker LP, Carrasquillo MM, Dickson DW, Petersen RC, Graff-Radford NR, Younkin SG, Ertekin-Taner N (2012) Association and heterogeneity at the GAPDH locus in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 33(1):203.e25–203.e33. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.08.002
Cameron B, Landreth GE (2010) Inflammation, microglia, and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 37(3):503–509. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.10.006
Tahara K, Kim HD, Jin JJ, Maxwell JA, Li L, Fukuchi K (2006) Role of toll-like receptor signalling in Abeta uptake and clearance. Brain: J Neurol 129(Pt 11):3006–3019. doi:10.1093/brain/awl249
Simard AR, Rivest S (2004) Bone marrow stem cells have the ability to populate the entire central nervous system into fully differentiated parenchymal microglia. FASEB J 18(9):998–1000. doi:10.1096/fj.04-1517fje
Hickman SE, El Khoury J (2013) The neuroimmune system in Alzheimer's disease: the glass is half full. J Alzheimer's Dis 33(Suppl 1):S295–S302. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-129027
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K (2009) Siglec receptors and hiding plaques in Alzheimer's disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 87(7):697–701. doi:10.1007/s00109-009-0472-1
Yu JT, Tan L (2012) The role of clusterin in Alzheimer's disease: pathways, pathogenesis, and therapy. Mol Neurobiol 45(2):314–326. doi:10.1007/s12035-012-8237-1
Bu G (2009) Apolipoprotein E and its receptors in Alzheimer's disease: pathways, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(5):333–344. doi:10.1038/nrn2620
Ariga T, McDonald MP, Yu RK (2008) Role of ganglioside metabolism in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease—a review. J Lipid Res 49(6):1157–1175. doi:10.1194/jlr.R800007-JLR200
Selkoe DJ (2000) Toward a comprehensive theory for Alzheimer's disease. Hypothesis: Alzheimer's disease is caused by the cerebral accumulation and cytotoxicity of amyloid beta-protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci 924:17–25
Wang YJ, Zhou HD, Zhou XF (2006) Clearance of amyloid-beta in Alzheimer's disease: progress, problems and perspectives. Drug Discov Today 11(19–20):931–938. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2006.08.004
Legrand O, Perrot JY, Baudard M, Cordier A, Lautier R, Simonin G, Zittoun R, Casadevall N, Marie JP (2000) The immunophenotype of 177 adults with acute myeloid leukemia: proposal of a prognostic score. Blood 96(3):870–877
Sievers EL (2001) Efficacy and safety of gemtuzumab ozogamicin in patients with CD33-positive acute myeloid leukaemia in first relapse. Expert Opin Biol Ther 1(5):893–901. doi:10.1517/14712598.1.5.893
Paulson JC, Macauley MS, Kawasaki N (2012) Siglecs as sensors of self in innate and adaptive immune responses. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1253:37–48. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06362.x
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81000544 and 81171209), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (ZR2010HQ004 and ZR2011HZ001), and the Shandong Provincial Outstanding Medical Academic Professional Program.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, T., Yu, JT., Hu, N. et al. CD33 in Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Neurobiol 49, 529–535 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8536-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8536-1