Summary
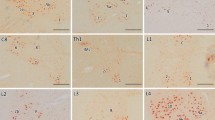
The spinal cord and the thoracic and lumbar posterior root ganglia (PRGs) of 14 HIV-positive men and 7 age- and sex-matched controls were studied by routine histology, morphometric analysis of the number of nodules of Nageotte (nN) and the diameters of sensory ganglion cells, immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. In 7 patients (2 of whom had evidence of cytomegalovirus ganglionitis) there were increased numbers of nN and diffuse, mild infiltration with CD45R+ T lymphocytes; no B lymphocytes were observed. Macrophages were increased in number in all cases. Whenever more than one ganglion was examined from the same patient, the appearances were similar in all. There was no alteration in the distribution of ganglion cell diameters. Changes in the spinal cord included vacuolar myelopathy (5 cases), HIV myelitis (1 case), microglial nodules (3 cases) and pallor of the gracile tracts (GTP) in 7 cases, in 6 of whom it co-existed with increased numbers of nN. Seven cases had no abnormalities, except the increase in number of macrophages in PRGs. In spite of a correlation between sensory nerve cell loss and GTP our findings suggest that other mechanisms, such as ‘dying back’ may contribute to the pathogenesis of GTP. Moreover, sensory disturbances were found most commonly in association with nerve cell loss; however, loss of sensory ganglion cells was not necessarily associated with evidence of sensory impairment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger JR, Raffanti S, Svenningsson A, McArthy M, Snodgrass S, Resnick (1991) The role of HTLV in HIV-1 neurologic disease. Neurology 41:197–202
Chung K, Coggeshall R (1984) The ratio of dorsal root ganglion cells to dorsal root axons in sacral segments of the cat. J Comp Neurol 225:24–30
Clatch RJ, Melvold RW, Miller SD, Lipton HL (1985) Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis (TMEV)-induced disease in mice is influenced by the H-2D region: correlation with TMEV-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol 135:1408–1414
Cornblath DR, McArthur JC, Kennedy PGE, Witte AS, Griffin JW (1987) Inflammatory demyelinating peripheral neuropathies associated with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III infection. Ann Neurol 21:32–40
Cristina S, Budka H, Schmidbauer M, Antonacci CM, Boldorini R, Berta L (1990) Pathology of spinal ganglia in unselected AIDS autopsies. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol [Suppl] 3:79–82
Dal Canto M (1989) AIDS and the nervous system: current status and future perspectives. Hum Pathol 20:410–418
Daniel SE, Love S, Scaravilli F, Harding AE (1985) Encephalomyeloneuropathy in the absence of a detectable neoplasm. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 66:311–317
Elder G, Dalakas M, Pezeshkpour G, Sever J (1986) Ataxic neuropathy due to ganglioneuronitis after probable acute human immunodeficiency virus infection. Lancet II:1275–1276
Esiri MM, Reading MC (1989) Macrophages, lymphocytes and major histocompatibility complex (HLA) class II antigens in adult human sensory and sympathetic ganglia. J Neuroimmunol 23:187–193
Fuller GN, Jacobs JM, Guiloff RJ (1989) Association of painful peripheral neuropathy in AIDS with cytomegalovirus infection. Lancet II:937–941
Fuller GN, Jacobs JM, Guiloff RJ (1991) Subclinical peripheral nerve involvement in AIDS: an electrophysiological and pathological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 54: 318–324
Gherardi R, Lebargy F, Gaulard P, Mhiri C, Bernaudin JF, Gray F (1989) Necrotizing vasculitis and HIV replication in peripheral nerves. N Engl J Med 321:685–686
Giulian D, Vaca K, Noonan CA (1990) Secretion of neurotoxin by mononuclear phagocytes infected with HIV-1. Science 250:1593–1596
Goldstick L, Mandybur TI, Bode R (1985) Spinal cord degeneration in AIDS. Neurology 35:103–106
Grafe MR, Wiley CA (1989) Spinal cord and peripheral nerve pathology in AIDS: the roles of cytomegalovirus and human immunodeficiency virus. Ann Neurol 25:561–566
Hénin D, Masson C, Ratinahirana H, Chaunu M-P, Duyckaerts C. Leger J-M (1990) Morphometric and immunohistochemical study of the L5 posterior root ganglia. Correlation with superficial peroneal nerve abnormalities in 26 cases of AIDS. Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Neuromuscular Disease, Munich, vol 98 [Suppl.] p 158
Ho DD, Rota TR, Schooley RT, Kaplan JC, Allan JD, Groopman JE, Resnick L, Felstenstein D, Andrews CA, Hirsch MS (1985) Isolation of HTLV-III from cerebrospinal fluid and neural tissues of patients with neurologic syndromes related to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med 313:1493–1497
Johnson RT, McArthur JC (1987) Myelopathies and retroviral infections. Editorial. Ann Neurol 21:115–118
Kunsch C, Hartle HT, Wigdahl B (1989) Infection of human fetal dorsal root ganglion glial cells with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 involves an entry mechanism independent of the CD4 T4A epitope. J Virol 12:5054–5061
Mahieux F, Gray F, Fenelon G, Gherardi R, Adams D, Guillard A, poirier J (1989) Acute myeloradiculitis due to cytomegalovirus as the initial manifestation of AIDS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 52:270–274
McArthur JC (1987) Neurologic manifestations of AIDS. Medicine 66:407–437
Miller RG, Storey JR, Greco CM (1990) Ganciclovir in the treatment of progressive AIDS-related polyradiculopathy. Neurology 40:569–574
Monte SM de la, Gabuzda DH, Ho DD, Brown RH, Hedley-White ET, Schooley RT, Hirsch MS, Bhan AK (1988) Peripheral neuropathy in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol 23:485–492
Navia BA, Price RW (1987) The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia complex as the presenting or sole manifestation of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Neurol 44:65–69
Navia BA, Jordan BD, Price RW (1986) The AIDS dementia complex. I. Clinical features. Ann Neurol 19:517–524
Navia BA, Cho ES, Petito CK, Price RW (1986) The AIDS dementia complex. II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol 19:525–535
Petito CK, Navia BA, Cho E-S, Jordan BD, George DC, Price RW (1985) Vacuolar myelopathy pathologically resembling subacute combined degeneration in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med 312:874–879
Petito CK, Cho ES, Lemann W, Navia BA, Price RW (1986) Neuropathology of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): an autopsy review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:635–646
Price RW, Brew B, Siditis J, Rosenblum M, Scheck AC, Cleary P (1988) The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science 239:586–592
Rance NE, McArthur JC, Cornblath DR, Landstrom DL, Griffin JW, Price DL (1988) Gracile tract degeneration in patients with sensory neuropathy and AIDS. Neurology 38:265–271
Robert ME, Geraghty JJ, Miles SA, Miles SA, Cornford ME, Vinters HV (1989) Severe neuropathy in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome: evidence for widespread cytomegalovirus infection of peripheral nerve and human immunodeficiency virus-like immunoreactivity of anterior horn cells. Acta Neuropathol 79:255–261
Robert-Guroff M, Weiss SH, Giron JA, Jennings AM, Ginzburg HM, Margolis IB, Blattner WA, Gallo RC (1986) Prevalence and antibodies to HTLV-I, II, III in intravenous drug abusers from an AIDS endemic region. JAMA 255:3133–3137
Said G, Lacroix-Ciaudo C, Fujimara H, Blas C, Faux N (1988) The peripheral neuropathy of necrotizing arteritis: a clinicopathological study. Ann Neurol 23:461–465
Scaravilli F (1988) Changes in neuronal structure and cell population with ageing. In: Thomas PK (ed) Peripheral nerve changes in the elderly. New Issues in Neurosciences. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, pp 95–107
Scaravilli F, Giometto B, Chimelli L, Sinclair E (1991) Macrophages in human sensory ganglia: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. J Neurocytol 20:609–624
Schmidbauer M, Budka H, Ambros P (1988) Comparison of in situ hybridization (ISH) and immunocytochemistry for diagnosis of herpes simplex virus (HSV) encephalitis in tissue. Virchows Arch [A] 414:39–43
Singh BM, Levine S, Yarrish RL, Hyland MJ, Jeanty D, Wormser GP (1986) Spinal cord syndromes in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand 73:590–598
Smith SH, Brown MH, Rowe D, Callard RE, Beverley PC (1986) Functional subset of human helper-inducer cells defined by a new monoclonal antibody UCHL1. Immunology 58:63–70
Snider WD, Simpson DM, Nielsen S, Gold JWM, Metroka CE, Posner JB (1983) Neurological complications of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: analysis of 50 patients. Ann Neurol 14:403–418
Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH (1976) Central-peripheral distal axonopathy: the pathology of dying-back polyneuropathies. Prog Neuropathol 3:253–295
Thomas PK, Landon DN, King RHM (1984) Diseases of the peripheral nerves. In: Adams JH, Duchen LW, Corsellis JAN (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology. Edward Arnold, London, pp 807–920
Weiser B, Peress N, LaNeve D (1990) Human immunodeficiency virus expression in the central nervous system correlates directly with extent of disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3997–4001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Medical Research Council (MRC); and by the Royal Society and the Wellcome Trust (FS)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scaravilli, F., Sinclair, E., Arango, J.C. et al. The pathology of the posterior root ganglia in AIDS and its relationship to the pallor of the gracile tract. Acta Neuropathol 84, 163–170 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00311390
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00311390