Summary
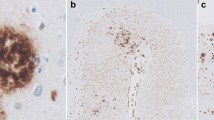
The nature of senile plaques (SP) in 27 cases of diffuse Lewy body disease (LBD) was investigated using immunocytochemistry and antibodies to beta amyloid protein synthetic peptides (BetaSP), ubiquitin (UBQ), paired helical filaments (PHF; Ab39) and a 68-kDa protein in Alzheimer brains (Alz50). Lewy bodies were present in widespread areas of the neocortex of all cases and were more easily detected with ubiquitin immunocytochemistry than with conventional stains. All cases had neocortical SP, but only six cases had neocortical neurofibrillary tangles (NFT). SP were very numerous in most cases and were usually “pale”, “diffuse” or “very primitive” plaques with thioflavin S fluorescent microscopy. SP in diffuse LBD were immunostained with BetaSP. Several cases had extensive amyloid angiopathy that was also immunoreactive with BetaSP. SP in diffuse LBD were characterized by amyloid deposits with few or no neuritic elements that could be detected with thioflavin S, Bielschowsky's stain or double staining with BetaSP and Bodian's silver stain. They differed from plaques in Alzheimer's disease by lack of PHF-type neurites that could be stained with Ab39. In diffuse LBD, SP contained PHF-type neurites only in areas coexistent with NFT. Some SP had round, granular neurites that were immunoreactive with UBQ, but weakly argyrophilic with Bodian's stain and nonfluorescent with thioflavin S. Diffuse LBD lacked significant neuritic change in the neuropil that could be detected with UBQ, Ab39 and Alz50. The latter finding is a characteristic feature that distinguishes Alzheimer's disease from diffuse LBD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bancher C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Jellinger K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Wisniewski HM (1989) An antigenic profile of Lewy bodies: immunocytochemical indication for protein phosphorylation and ubiquitination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 48:81–93
Beal MF, Mazurek MF, Martin JB (1986) Somatostatin immunoreactivity is reduced in Parkinson's disease dementia with Alzheimer changes. Brain Res 397:386–388
Braak H, Braak E, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (1986) Occurence of neuropil threads in the senile human brain and in Alzheimer's disease: a third location of paired helical filaments outside of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques. Neurosci Lett 65:351–355
Burkhardt CR, Filley CM, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, de la Monte S, Norenberg MD, Schneck SA (1988) Diffuse Lewy body disease and progressive dementia. Neurology 38:1520–1528
Byrne EJ, Lowe J, Godwin-Austen RB, Arie T, Jones R (1987) Dementia and Parkinson's disease associated with diffuse cortical Lewy bodies. Lancet I:501
Candy JM, Perry EK, Perry RH, Court JA, Oakley AE, Edwardson JA (1986) The current status of the cortical cholinergic system in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 70:105–130
Crystal H, Dickson D, Fuld P, Masur D, Scott R, Mehler M, Masdeu F, Kawas C, Aronson M, Wolfson L (1988) Clinico-pathologic studies in dementia: nondemented subjects with pathologically confirmed Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 38:1682–1687
Crystal H, Davies P, Dickson DW (1988) Neuropsychological characteristics of subjects with and without Alz50 immunoreactivity. Alzheimer Related Dis Assoc J 2:171
Dickson DW, Kress Y, Crowe A, Yen S-H (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. II. Demonstration of a common antigenic determinant between ANT and neurofibrillay degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy. Am J Pathol 120:292–302
Dickson DW, Yen S-H, Suzuki KI, Davies P, Garcia JH, Hirano A (1986) Ballooned neurons in select neurodegenerative disease contain phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 71:216–223
Dickson DW, Davies P, Mayeux R, Crystal H, Horoupian DS, Thompson A, Goldman JE (1987) Diffuse Lewy body disease: neuropathological and biochemical studies of six patients. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75:8–15
Dickson DW, Farlo J, Davies P, Crystal H, Fuld P, Yen SHC (1988) Alzheimer's disease: a double-labeling immunohistochemical study of senile plaques. Am J Pathol 132:86–101
Dickson DW, Farlo J, Yen SH, Crystal H, Fuld P, Davies P (1988) Clinicopathologic and immunocytochemical studies on demented and nondemented individuals distinguishes two classes of senile plaques. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:381 [abstr]
Ditter SM, Mirra SS (1987) Neuropathologic and clinical features of Parkinson's disease in Alzheimer's disease patients. Neurology 37:754–760
Epelbaum J, Ruberg M, Moyse E, Javoy-Agid F, Dubois B, Agid Y (1983) Somatostatin and dementia in Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 278:376–379
Forno LS (1969) Concentric hyalin intraneuronal inclusions of Lewy type in the brains of elderly persons (50 incidental cases): relationship to Parkinsonism. J Am Geriatr Soc 17:557–575
Forno LS, Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH, Strefling AM, Swanson K, Eng LF (1986) Reaction of Lewy bodies with antibodies to phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated neurofilaments. Neurosci Lett 64:253–258
Fuld PA, Dickson DW, Crystal H, Aronson MK (1987) Primitive plaques and memory dysfunction in normal and impaired elderly. N Engl Med 316:756
Galloway PG, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Perry G (1988) Lewy bodies contain epitopes both shared and distinct from Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:654–663
Gibb WRG (1986) Idiopathic Parkinson's disease and the Lewy body disorders. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 12:223–234
Gibb WRG, Luthert PJ, Janota I, Lantos PL (1989) Cortical Lewy body dementia: clinical features and classification. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:185–192
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752
Gibb WRG, Esiri MM, Lees AJ (1987) Clinical and pathological features of diffuse cortical Lewy body disease (Lewy body dementia). Brain 110:1131–1153
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120:885–890
Goldman JE, Yen S-H, Chiu F-C, Peress NS (1983) Lewy bodies of Parkinson's disease contain neurofilament antigens. Science 221:1082–1084
Hyman BT, VanHoesen GW, Wolozin BI, Davies P, Kromer LJ, Damasio AR (1988) Alz50: recognition of Alzheimerrelated neuronal changes that precede neurofibrillary tangle formation. Ann Neurol 23:371–379
Ikeda S-I, Allsop D, Glenner GG (1989) Morphology and distribution of plaque and related deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's disease and control cases. Lab Invest 60:113–122
Jellinger K (1986) Overview of morphological changes in Parkinson's disease. Adv Neurol 45:1–18
Jolkkonen J, Soininen H, Halonen T, Ylinen A, Laulumaa V, Laakso M, Riekkinen P (1986) Somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson's disease and its relation to dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:1374–1377
Kitamoto T, Ogomori K, Tateishi J, Prusiner SB (1987) Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest 57:230–236
Kosaka K, Yoshimura M, Ikeda K, Budka H (1984) Diffuse type of Lewy body disease: progressive dementia with abundant cortical Lewy bodies and senile changes of varying degree — a new disease? Clin Neuropathol 3:185–192
Kosaka K, Tsuchiya K, Yoshimura M (1988) Lewy body disease with and without dementia: a clinicopathologic study of 35 cases. Clin Neuropathol 7:299–305
Kuroda S, Otsuki S, Hayashi Y (1987) Diffuse Lewy body disease: an autopsy case. Acta Med Okayama 41:133–139
Ksiezak-Reding H, Davies P, Yen S-H (1988) Alz50, a monoclonal antibody to Alzheimer's disease antigen, crossreacts with tau proteins from bovine and normal human brain. J Biol Chem 263:7943–7947
Kuzuhara S, Mori H, Izumiyama N, Yoshimura M, Ihara Y (1988) Lewy bodies are ubiquitinated: a light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75:345–353
Lee S, Park YD, Yen S-H, Ksiezak-Reding H, Goldman JE, Dickson DW (1989) Infantile motor neuron disease: a case report with electron microscopic and ubiquitin and neurofilament immunohistochemical studies. Neuropediatrics 20:107–111
Lennox G, Lowe J, Morrell K, Landon M, Mayer RJ (1989) Anti-ubiquitin immunocytochemistry is more sensitive than conventional techniques in the detection of diffuse Lewy body disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:67–71
Leverenz J, Sumi M (1986) Parkinson's disease in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 43:662–664
Manetto V, Perry G, Tabaton M, Mulvihill P, Fried VA, Smith HT, Gambetti P, Autillo-Gambetti L (1988) Ubiquitin is associated with abnormal cytoplasmic filaments characteristic of neurodegenerative disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4501–4505
Okazaki H, Lipkin LE, Aronson SM (1961) Diffuse intracytoplasmic ganglionic inclusions (Lewy type) associated with progressive dementia and quadriparesis in flexion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 3:237–243
Ogomori K, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J, Sato Y, Suetsugu M, Abe M (1989) Beta-protein amyloid is widely distributed in the central nervous system of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 134:243–251
Pappolla MA (1986) Lewy bodies of Parkinson's disease. Immune electron microscopic demonstration of neurofilament antigens in constituent filaments. Arch Pathol Lab Med 110:1160–1163
Perry EK, Curtis M, Dick DJ, Candy JM, Atack JR, Bloxham CA, Blessed G, Fairbairn A, Tomlinson BE, Perry RH (1985) Cholinergic correlates of cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: comparisons with Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:413–421
Perry G, Manetto V, Mulvihill P (1987) Ubiquitin in Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative disease. In: Perry G (ed) Alterations in the neuronal cytoskeleton in Alzheimer disease. Plenum, New York, pp 53–59
Rosenblum WI, Ghatak NR (1979) Lewy bodies in the presence of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 36:170–171
Sima AAF, Clark AW, Sternberger NA, Sternberger LA (1986) Lewy body dementia without Alzheimer changes. Can J Neurol Sci 13:490–497
Schwartz P (1970) Amyloidosis: cause and manifestation of senile deterioration. Thomas, Springfield, Ill, pp 43–61
Ulrich J (1985) Alzheimer changes in nondemented patients younger than sixty-five. A possible early stage of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol 17:273–277
Wolozin BL, Davies P (1987) Alzheimer-related neuronal protein A68: specificity and distribution. Ann Neurol 22:521–526
Wolozin BL, Pruchnicki A, Dickson DW, Davies P (1986) A neuronal antigen in the brain of Alzheimer patients. Science 232:648–650
Wolozin B, Scicutella A, Davies P (1988) Reexpression of a developmentally regulated antigen in Down's syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6202–6206
Yamaguchi H, Hirai S, Morimatsu M, Shogji M, Ihara Y (1988) A variety of cerebral amyloid deposits in the brain of the Alzheimer type dementia demonstrated by beta protein immunostaining. Acta Neuropathol 76:541–549
Yamamoto T, Imai T (1988) A case of diffuse Lewy body and Alzheimer's disease with periodic synchronous discharges. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:536–548
Yen S-H, Crowe A, Dickson DW (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. I. Identification of polypeptides. Am J Pathol 120:282–291
Yen S-H, Dickson DW, Peterson C, Goldman JE (1986) Cytoskeletal abnormalities in neuropathology. Prog neuropathol 6:63–90
Yoshimura N, Yoshimura I, Asada M, Hayashi S, Fukushima Y, Sato T, Kudo H (1988) Juvenile Parkinson's disease with widespread Lewy bodies in the brain. Acta Neuropathol 77:213–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grant NIA AG06803
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dickson, D.W., Crystal, H., Mattiace, L.A. et al. Diffuse Lewy body disease: light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of senile plaques. Acta Neuropathol 78, 572–584 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691284
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691284