Abstract
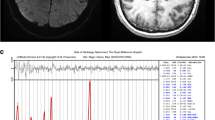
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy has proved to be useful for monitoring a number of metabolites in cerebral infarction. Combined magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy investigations were carried out in 14 patients with a recent ischaemic stroke (< 1 week); follow-up examinations were performed from day 28 to day 252 after stroke. The aim of this study was to assess the correlation between the changes ofN-acetyl-aspartate, choline, creatine-phosphocreatine, lactate and clinical evolution measured by the Scandinavian Neurological Scale (SNS). Initially the lactate magnetic resonance signal was present in all patients and the other metabolite contents were significantly reduced (P < 0.001; unpairedt-test) as compared with those on the contralateral side. Spearman's rank correlation test showed a positive correlation between the initial reduction ofN-acetyl-aspartate content and the SNS (P < 0.05), and between the finalN-acetyl-aspartate content and the SNS (P < 0.001). Our results suggest that serial examination in stroke patients may provide further prognostic information and encourage controlled clinical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkelbach van der Sprenkel JW, Luyten PR, Rijen PC van, Tulleken CAF, Hollander JA den (1988) Cerebral lactate detected by regional proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a patient with cerebral infarction. Stroke 19:1556–1560
Bryan RN, Levy LM, Writlow WD, Kilian JM, Preziosi TJ, Rosario JA (1991) Diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction: comparison of CT and MR imaging. AJNR 12:611–620
Davie CA, Hawkins CP, Barker GJ, Brennan A, Tofts PS, Miller DH, McDonald WI (1994) Serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in acute multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 117:49–58
De Haan R, Horn J, Limburg M, Van Der Meulen J, Bossuyt P (1993) A comparison of five stroke scales with measures of disability, handicap and quality of life. Stroke 24:1178–1181
Duijn JH, Matson GB, Maudsley AA, Hugg JW, Weiner MW (1992) Human brain infarction: proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 183:711–718
Federico F, Conte C, Simone IL, Giannini P, Liguori M, Picciola E, Tortorella C, Ferrari E (1994) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with ischemic stroke. Ital J Neurol Sci 15:413–420
Felber SR, Aichner FT, Sauter R, Gerstenbrand F (1992) Combined magnetic resonance imaging and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of patients with acute stroke. Stroke 23:1106–1110
Fenstermacher MJ, Narayana PA (1990) Serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of ischemic brain injury in humans. Invest Radiol 25:1034–1039
Fisher M, Sotak CH, Minematsu K, Li L (1992) New magnetic resonance techniques for evaluating cerebrovascular disease. Ann Neurol 32:115–122
Ford CC, Griffey RH, Matwyoff NA, Rosenberg GA (1992) Multivoxel1H-MRS of stroke. Neurology 42:1408–1412
Frahm J, Merboldt KD, Hanicke W (1987) Localized proton spectroscopy using stimulated echoes: initial applications. J Magn Reson 72:502–508
Frahm J, Bruhn H, Gyngell ML, Merboldt KD, Hanicke W, Sauter R (1989) Localizated high-resolution proton NMR spectroscopy using stimulated echoes: initial applications to human brain in vivo. Magn Reson Med 9:79–93
Frahm J, Bruhn H, Gyngell ML, Merboldt KD, Hanicke W, Sauter R (1989) Localized H-NMR spectroscopy in different regions of the human brain in vivo: relaxation times and concentrations of cerebral metabolites. Magn Reson Med 11:47–63
Frahm J, Michaelis T, Merboldt KD, Hanicke W, Gyngell ML, Bruhn H (1991) On theN-Acetyl methyl resonance in localized1 H-NMR spectra of human brain in vivo. NMR Biomed 4:201–204
Gideon P, Henriksen O, Sperling B, Christiansen P, Olsen TS, Jorgensen HS, Arlien-Soborg P (1992) Early time course ofN-Acetyl-Aspartate, Creative and Phosphocreatine, and compounds containing Choline in the brain after acute stroke. A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Stroke 23:1566–1572
Gideon P, Sperling B, Arlien-Soborg P, Olsen TS, Henriksen O (1994) Long-term follow up of cerebral infarctions patients with proton magnetic resonance spectrocopy. Stroke 25:867–973
Graham GD, Blamire AM, Howseman AM, Rothman DL, Fayad PB, Brass LM, Petroff OAC, Shulman RG, Prichard JW (1992) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of cerebral lactate and other metabolites in stroke patients. Stroke 23:333–340
Graham GD, Blamire AM, Rothman DL, Brass LM, Fayad PB, Petroff OAC, Prichard JW (1993) Temporal variation of cerebral metabolites after human stroke. A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Stroke 24:1891–1896
Graham GD, Kalvach P, Blamire A, Brass LM, Fayad PB, Prichard JW (1995) Clinical correlates of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy findings after acute cerebral infarctions. Stroke 26:225–229
Houkin K, Kamada K, Kamiyama H, Iwasaki Y, Abe H, Kashiwaba T (1993) Longitudinal changes in proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in cerebral infarction. Stroke 24:1316–1321
Hugg JW, Duijn JH, Matson GB, Maudsley AA, Tsuruda JS, Gelinas DF, Weiner MW (1992) Elevated lactate and alkalosis in chronic human brain infarction observed by H and P MR spectroscopy imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 12:734–744
Koller KJ, Zaczek R, Coyle JT (1984)N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate: regional levels in rate brain and the effects of brain lesions as determined by a new HPLC method. J Neurochem 43:1136–1142
Michaelis T, Merboldt KD, Hanicke W, Gyngell M, Bruhn H, Frahm J (1991) On the identification of cerebral metabolites in localized1H-NMR spectra of human brain in vivo. NMR Biomed 4:90–98
Miller BL (1991) A review of chemical issues in1H-NMR spectroscopy:N-Acetyl-L-Aspartate, Creatine and Choline. NMR Biomed 4:47–52
Nadler JV, Cooper JR (1972)N-Acetyl-L-Aspartic acid content of human neural tumours and bovine peripheral nervous tissues. J Neurochem 19:213–219
Narayana PA, Fotedar LK, Jackson EF, Bohan TP, Butler IL, Wolinski JS (1989) Regional in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of brain. J Magn Reson 83:44–52
Scandinavian Stroke Study Group (1985) Multicentre trial of hemodilution in ischemic stroke. Background and study protocol. Stroke 16:885–890
Veech RL (1991) The metabolism of lactate. NMR Biomed 4:53–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Federico, F., Simone, I.L., Conte, C. et al. Prognostic significance of metabolic changes detected by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in ischaemic stroke. J Neurol 243, 241–247 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868521
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868521