Abstract
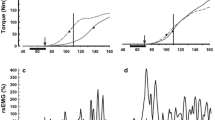
We investigated maximal isometric force and electromyographic (EMG) activity of the biceps brachii muscle during rapid bilateral (BL) and unilateral (UL) elbow flexion in 11 right-handed subjects. The BL exhibited a deficit in force for both arms and more so for the right than the left arm during the rising phase of force generation. The EMG of the left biceps brachii muscle was similar during UL and BL, but for the right arm EMG was lower during BL than during UL for the rising phase of force generation. The BL to UL ratio of mean power frequency of the EMG was lower for the right than for the left arm. The data would suggest that the relatively small BL strength was associated with a equally small EMG and a shift to a lower mean power frequency especially for the fast motor units of the dominant muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grimby L, Hannerz J (1977) Firing rate and recruitment order of toe extensor motor units in different modes of voluntary contraction. J Physiol 264:865–879
Henry FM, Smith LE (1961) Simultaneous vs separate bilateral muscular contractions in relation to neural overflow theory and neuromoter specificity. Res Q 32:42–46
Kanda K, Burke RE, Walmsley B (1977) Differential control of fast and slow twitch motor units in the decerebrate cat. Exp Brain Res 29:57–74
Koh TJ, Grabiner MD, Clough CA (1993) Bilateral deficit is larger for step than for ramp isometric contractions. J Appl Physiol 74:1200–1205
Kroll W (1965) Isometric cross-transfer effects under conditions of central facilitation. J Appl Physiol 20:297–300
Moritani T, Muro M (1987) Motor unit activity and surface electromyogram power spectrum during increasing force of contraction. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:260–265
Moritani T, Gaffiney FD, Carmichael T, Hargis J (1985) Interrelationships among muscle fiber types, electromyogram, and blood pressure during fatiguing isometric contraction. In: Winter DA (ed) Biomechanics IX-A. Human Kinetic, Champaign, Ill., pp 287–292
Moritani T, Muro M, Nagata A (1986) Intermuscular and surface electromyogram changes during muscle fatigue. J Appl Physiol 60:1179–1185
Moritani T, Muramatsu S, Muro M (1988) Activity of motor units during concentric and eccentric contractions. Am J Phys Med 66:338–350
Moritani T, Oddsson L, Thorstensson A (1991) Activation patterns of the soleus and gastrocnemius muscle during different motor tasks. Electromyogr Kinesiol 2:81–88
Muro M, Nagata A, Moritani T (1983) Analysis of myoelectric signals during dynamic and isometric contractions. In: Matsui H, Kobayashi K (eds) Biomechanics VIII-A. Human Kinetics, Champaign, Ill., pp 432–439
Ohtsuki T (1981) Decrease in grip strength induced by simultaneous bilateral exertion with reference to finger strength. Ergonomics 24:37–48
Ohtsuki T (1983) Decrease in human voluntary isometric arm strength induced by simultaneous bilateral exertion. Behav Brain Res 7:165–178
Rube N, Secher NH (1981) Paradoxical influence of encouragement on muscle fatigue. Eur J Appl Physiol 46:1–7
Schantz PG, Moritani T, Karlson E, Johansson E, Lundh A (1989) Maximal voluntary force of bilateral and unilateral leg extension. Act Physiol Scand 136:185–192
Secher NH, Rørsgaard S, Secher O (1978) Contralateral influence on recruitment of curarized muscle fibres during maximal voluntary extension of the legs. Acta Physiol Scand 103:456–462
Secher NH, Rube N, Secher O (1983) Effect of tubocurarine and decamethonium on voluntary muscle contractions in man. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 27:480–483
Secher NH, Rube N, Elers J (1988) Strength of two- and one-leg extension in man. Acta Physiol Scand 134:333–339
Vandervoot AA, Sale DG, Moroz J (1984) Comparison of motor unit activation during unilateral and bilateral leg extension. J Appl Physiol 56:46–51
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oda, S., Moritani, T. Maximal isometric force and neural activity during bilateral and unilateral elbow flexion in humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 69, 240–243 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01094795
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01094795