Summary
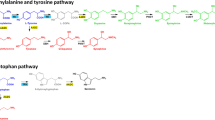
The concentrations of amino acids in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (n=20) and serum (n=20) taken from patients with essential tremor were measured by HPLC and compared with those of controls (n=10). Reduced concentrations of some amino acids (asparagine, glutamine, glycine, threonine, isoleucine, leucine) were observed in serum taken from patients with tremor. Significant increases were detected in the concentrations of glutamate (p < 0.001) and aspartate (p < 0.01). The general tendency of the changes in CSF and serum was similar; although the highest differences were observed in amino acid concentrations in the serum of patients with essential tremor. Opposite shifts of some amino acids were detected, in the concentrations of aspartate, serine, tyrosine, leucine, and isoleucine, which may indicate the independence of the changes in the serum from those in the CSF. This study raises the possibility that a genetically determined metabolic disorder is involved in the etiology of essential tremor that appears peripherally and, partly, centrally. The slight increase in the concentration of glutamate together with the reduced levels of GABA, glycine, and serine in CSF may form the neurochemical basis of the central oscillation observed in essential tremor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bain PG, Findley LJ, Thompson PD, Gresty MA, Rothwell JC, Harding AE, Marsden CD (1994) A study of hereditary essential tremor. Brain 117: 805–824
Barry J, Gombos G, Vizi ES (1989) Release of (3H)L-glutamate and (3H)L-glutamine in rat cerebellum slices: a comparison of the effect of veratridine and electrical stimulation. Biochem Res 14: 1053–1059
Colebatch JG, Findley LJ, Frackowiak RSJ, Marsden CD, Brooks DJ (1990) Preliminary report: activation of cerebellum in essential tremor. Lancet 336: 1028–1030
Hallett M, Dubinsky RM (1993) Glucose metabolism in the brain of patients with essential tremor. J Neurol Sci 114: 45–48
Hubble JP, Busenbarck KL, Koller WC (1989) Essential tremor. Clin Neuropharm 12: 453–482
Kornhuber ME, Balabanova S, Heiligensetzer GV, Kornhuber C, Zettlmeissl H, Kornhuber AW (1991) Stability of human blood serum aminoacids after storage at different pH and temperature conditions. Clin Chim Acta 197(3): 189–200
Lajtha A (1974) Amino acid transport in the brain in vivo and in vitro. Ciba Foundation Symposium 22. In: Aromatic amino acids in the brain. Elsevier Excerpta Medica, North Holland, pp 25–41
Larsson T, Sjögren T (1960) Essential tremor: a clinical and genetic population study. Acta Psych Neurol Scand 36 [Suppl 144]: 1–176
Málly J, Stone TW (1991) The effect of theophylline on essential tremor: the role of GABA. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39: 345–351
Metzger WS (1994) Essential tremor: an overview. J Ark Med Soc 90: 587–590
Rajput AH, Offord KP, Beard CM, Kurland LT (1984) Essential tremor in Rochester, Minnesota: a 45-year study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47: 466–470
Stone TW (1979) Glutamate as the neurotransmitter of cerebellar cells in the rat: electrophysiological evidence. Br J Pharmacol 66: 291–296
Toth E, Sershen H, Hashim A, Vizi ES, Lajtha A (1992) Effect of nicotine on extracellular levels of neurotransmitters assessed microdialysis in various brain regions: role of glutamic acid. Neurochem Res 17(7): 265–271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Málly, J., Baranyi, M. & Vizi, E.S. Change in the concentrations of amino acids in CSF and serum of patients with essential tremor. J. Neural Transmission 103, 555–560 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01273153
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01273153