Abstract
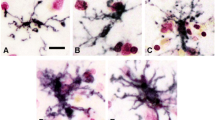
Previous investigations demonstrated that the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients contains antibodies that recognize specific neuronal populations in the adult rat central nervous system (CNS). These findings suggest a pathogenic role for immunological aberrations in this disorder. To determine if antibodies may provide a means to differentially diagnose the dementias, CSF from a diversified dementia population was screened against the developing rat CNS and a cell culture system. Markings produced by AD CSF were distinctly different from those of vascular dementias (VAD) against the developing rat CNS. More importantly, some AD CSF recognized amoeboid microglia. The recognition of amoeboid microglia by antibodies in AD CSF is particularly interesting since these cells proliferate in response to nervous system disease and also engulf debris. A cell culture technique was developed to allow the rapid screening of CSF antibodies. Patient CSF produced five different types of markings in the cell culture: microglia, glioblasts, fibers, nonspecific, or negative. Correlations with these structures and the diagnosis of four different dementia populations revealed that, in comparison to the other groups, AD CSF displayed remarkable selectivity toward microglial cells. Cortical biopsies from patients suspected to have AD were incubated with the patient's own CSF and that of confirmed AD patients. Both CSF samples recognized microglial cells in the patient's cortical biopsy. The same CSF samples incubated against normal human cortical autopsy or a biopsy from a 3-mo-old child displayed negative immunoreactivity. These three approaches suggest that the presence of CSF microglial antibodies may be a means to distinguish AD patients from other dementias. The results add further support to the widely growing concept that inflammation and similar immune mechanisms may contribute to AD pathogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Werkle H. C., Linington H., Lassmann H., and Meyermann R. (1986)TINS 9, 271.
Rogers J., Luber-Narod J., Styren S., and Civin H. (1988)Neurobiol. Aging 9, 339.
McGeer P. and Rogers J. (1992)Neurology 42, 447.
Glenner G. G. and Wong C. W. (1984)Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1(20), 885.
Kemper T. (1984) inClinical Neurology of Aging (Albert M. L., ed.), Oxford, New York, p. 9.
Selkoe D., Ihara Y., and Salazar F. J. (1982)Science 215, 1243.
Haga S., Akai K., and Ishii T. (1989)Acta Neuropathol. 77, 569.
Perlmutter L., Barron E., and Chang Chui H. (1990)Neurosci. Letts. 119, 32.
McGeer P., Itagaki S., Tago H., and McGeer E. (1987)Neurosci. Lett. 79, 194.
Cras P., Kawai M., Siedlak S., and Perry G. (1991)Brain Res. 558, 312.
Schechter R., Yen S. H., and Terry R. D. (1981)J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 40, 95.
Kozlowski P., Wisniewski H. M., Moretz R. C., and Lossinsky A. S. (1981).Ann. Neurol. 10, 517.
Itagaki S., McGeer P., and Akiyama H. (1988)Neurosci. Letts. 91, 259
McGeer P., Akiyama H., Itagaki S., and McGeer E. (1989)Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 16, 516.
Luber-Narod J. and Rogers J. (1988)Neurosci. Letts. 94, 17.
Griffin S., Stanley L., Ling C., White L., Macleod V., Perrot L., White C. L. III, and Araoz C. (1989)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7611.
Bauer J., Strauss S., Schreiter-Gasser U., Ganter U., Schlegel P., Witt I., Yolk B., and Berger M. (1991)FEBS Letts. 285, 111.
Ishii T. and Haga S. (1976)Acta Neuropathol. 36, 243.
Eikelenboom P. and Stam F. C. (1982)Acta Neuropathol. 57, 239–242.
Ishii T. and Haga S. (1984)Acta Neuropathol. 63, 296.
McGeer P., Akiyama H., Itagaki S., and McGeer E. (1989)Neurosci. Letts. 197, 341.
Schabel J. (1993)Science 260, 1719.
Bauer J., König G., Strauss S., Jonas U., Ganter U., Weidemann A., Möning U., Masters C., Volk B., Berger M., and Beyreuther K. (1991)FEBS Letts. 282, 335.
Wiegiel J. and Wisniewski H. M. (1990)Acta Neuropathol. 81, 116.
Singh V. (1990)Prog. Drug Res. 34, 384.
Fudenberg H. H. and Singh V. (1988)Drug Dev. Res. 15, 165.
McRae A., Blennon K., Gottfries C. G., Walin A., and Dahlstrom A. (1990) inBiological Markers in Dementia of Alzheimer Type (Fowler C. J., Carlson L. A., Gottfries C. G., and Winblad B., eds.) Smith-Gordon, London, pp. 135–148.
McRae A. and Dahlstrom A. (1992)Rev. Neurosci. 3, 79.
McRae A., Ling E. A., Polinsky R., Goffries C. G., and Dahlstrom A. (1991)Neuroscience 41, 739.
St. George-Hyslop P., Tanzi R. E., Polinsky R. J., Haines J. L., Nee L., Watkins, et al. (1987).Science 235, 885–890.
Shu S., Ju G., and Fan L. (1988)Neurosci. Lett. 85, 169.
Wigander A., Lundmark K., McRae A., Mölne J., Nilsson O., Haglid K., Dahlstrom A., and Ahlman H. (1991)Acta Physiol. Scand. 141, 107.
Perry V. H. and Gordon S. (1988)11, 273.
Ling E. A. and Wong W. C. (1993)Glia 7, 9.
Tseng C. Y., Ling E. A., and Wong W. C. (1983)J. Anat. 136, 251.
Skalickova O., Jezkova Z., and Slavickova V. (1962)Czech. Psych. 58, 1.
Tavolato B. and Argentiero V. (1980)J. Neurol. Sci. 46, 325.
Whittingham S., Lennon V., Mackay I. E., Vernon-Davies G., and Davies B. (1970)Brit. J. Psychiat. 116, 447.
Watts H., Kennedy P. G. E., and Thomas M. (1981)J. Neuroimmunol. 1, 107.
Nandy K. (1972).J. Geronotol. 27, 173.
Mayer P. P., Chughtai M. A., and Cape R. D. T. (1976)Age Aging 5, 164.
Felsenfeld O. and Wolf R. H. (1972)J. Med. Primatol. 1, 287.
Ingram C. R., Phegan K. J., and Blumenthal H. T. (1974).J. Geront. 29, 20.
Baldinger S. and Blumenthal H. T. (1982) inGeriatrics (Platt D., ed.) Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp. 283–299.
Nandy K. (1978) inAging, vol. 7 (Katzman R. D., Terry R. D., and Bick K. L., eds.) Raven, New York, pp. 503–512.
Bahmanyar S., Gadjusek C. D., Sotelo J., and Gibbs C. J. (1982)J. Neurosci. 53, 85.
Lal H. and Forster M. J. (1988)Neurobiol. Aging 9, 733.
Chapman J., Korczyn A. D., Hareuveni M., and Michaelson D. M. (1986) inAlzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases: Strategies for Research and Development (Fisher A., Hanin I., and Lachman C., eds.), Plenum, New York, pp. 329–333.
McRae-Degueurce A., Booj S., Haglid K., Rosengren L., Karlsson J. E., Karlsson I., Wallin A., Svennerholm L., Gottfries C. G., and Dahlstrom A. (1987)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 9214.
Fillit H. M., Luine V. N., Reisberg B., Amador R., McEwen B., and Zabriskie J. B. (1985) inSenile Dementia (Hutton J. T. and Kenny A. D., eds.) Liss, New York, pp. 307–318.
Gaskin F., Kingsley B. S., and Fu S. M. (1987).J. Exp. Med. 165, 245.
McRae-Degueurce A., Haglid K., Rosengren L., Wallin A., Blennow K., Gotffries C. G., and Dahlstrom A. (1988)Drug Devel. Res. 15, 153.
Fillit H. M., Kemeny E., Luine V., Weksler M. E., and Zabriskie J. B. (1987)J. Geronotol. 42, 180.
Foley P., Bradford H., Docherty M., Fillit H., Luine V., McEwen B., Bucht G., Wimblad B., and Hardy J. (1988)J. Neurol. 235, 466.
Chapman J., Alroy G., Weiss Z., Faigon M., Feldon J., and Michaelson D. (1991)Neuroscience 40, 297.
Ito H., Goto S., Hirano A., Shu-Hui M. D., and Yen C. (1991)J. Geriat. Psych. Neurol. 4, 134.
Snow A. D., Mar H., Nochlin D., Sekiguichi R. T., Kimata K., Koike Y., and Wight T. N. (1990)Am. J. Pathol. 137, 1253.
Probst A., Brunnschweiler H., Lautenshalager C., and Ulrich J. (1987)Acta Neuropath. 74, 133.
Rio-Hortega P. del. (1932) inCytology and Cellular Pathology of the Nervous System, vol. 2 (Penfield W., ed.) Hoeber, New York, pp. 481–584.
Guilian D. (1987)J. Neurosci. Res. 18, 155.
Streit W. J., Graeber M. B., and Kreutzberg G. W. (1988)Glia 1, 301.
Ling E. A., Kaur C., and Wong W. C. (1992)Histol. Histopath. 7, 93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahlström, A., McRae, A., Polinsky, R. et al. Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid antibodies display selectivity for microglia. Mol Neurobiol 9, 41–54 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816104
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816104