Abstract
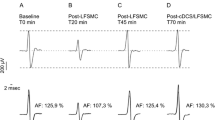
Recent evidence suggests a role for cerebellum in pathophysiology of dystonia. Here we explored, the cerebellar modulation of motor cortex in patients with focal upper limb dystonia. Eight patients and eight controls underwent a transcranial magnetic stimulation protocol to study the cerebellar-brain-inhibition (CBI): a conditioning cerebellar stimulus (CCS) was followed 5 ms after by the contralateral motor cortex stimulation (test stimulus: TS). We explored the effects of CBI on MEP amplitude, short intracortical inhibition (SICI) and intracortical facilitation (ICF) measures. At baseline no differences in TS-MEP amplitude, SICI or ICF were found between patients and controls. Cerebellar-conditioning significantly reduced TS-MEP amplitude, increased ICF, and decreased SICI in control subjects. In contrast, no changes in these neurophysiological measures were observed in the motor cortex of patients, regardless of which side was tested. If further confirmed, these findings suggest a reduced cerebellar modulation of motor cortex excitability in patients with focal dystonia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell DB, North JB, Hess EJ (1999) Tottering mouse motor dysfunction is abolished on the Purkinje cell degeneration (PCD) mutant background. Exp Neurol 160:268–278
Carbon M, Kingsley PB, Su S, Smith GS, Spetsieris P, Bressman S, Eidelberg D (2004) Microstructural white matter changes in carriers of the DYT1 gene mutation. Ann Neurol 56:283
Chen R, Wassermann EM, Caños M, Hallett M (1997) Impaired inhibition in writer’s cramp during voluntary muscle activation. Neurology 49:1054–1059
Daskalakis ZJ, Paradiso JO, Christensen BK, Fitzgerald PB, Gunraj C, Chen R (2004) Exploring the connectivity between the cerebellum and motor cortex in humans. J Physiol 557:689–700
De Fazio G, Berardelli A, Hallett M (2007) Do primary adult-onset focal dystonias share aetiological factors. Brain 130:1183–1193
Delmaire C, Vidaihet M, Elbaz A et al (2007) Structural abnormalities in the cerebellum and sensori-motor circuit in writer’ s cramp. Neurology 69:376–380
Di Lazzaro V, Restuccia D, Nardone R, Leggio MG, Oliviero A, Profice P, Tonali P, Molinari M (1995) Motor cortex changes in a patient with hemicerebellectomy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 97:259–263
Eidelberger D, Moeller JR, Antonini A (1998) Functional brain networks in DTY1 dystonia. Ann Neurol 44:303–312
Fierro B, Giglia G, Palermo A, Pecoraro C, Scalia S, Brighina F (2007) Modulatory effects of 1 Hz rTMS over the cerebellum on motor cortex excitability. Exp Brain Res 176:440–447
Le Ber I, Clot F, Vecueil L et al (2006) Predominant diystonia with marked cerebellar atrophy: a raree phenotype in familial dystonia. Neurology 67:1769–1773
Manto MU (2005) The wide spectrum of spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs). Cerebellum 4:2–6
Mink JW (2003) The basal ganglia and involuntary movements: impaired inhibition of competing motor patterns. Arch Neurol 60:1365–1368
Murase N, Rothwell JC, Kaji R, Urushihara R, Nakamura K, Murayama N, Igasaki T, Sakata-Igasaki M, Mima T, Ikeda A, Shibasaki H (2005) Subthreshold low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the premotor cortex modulates writer’s cramp. Brain 128:104–115
Oliveri M, Koch G, Torriero S, Caltagirone C (2005) Increased facilitation of the primary motor cortex following 1 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the contralateral cerebellum in normal humans. Neurosci Lett 376:188–193
Peller M, Zeuner KE, Munchau A, Quartarone A, Weiss M, Knutzen A, Hallett M, Deuschl G, Siebner HR (2006) The basal ganglia are hyperactive during the discrimination of tactile stimuli in writer’s cramp. Brain 129:2697–2708
Pizoli CE, Jinnah HA, Ml Billingsley, Hess EJ (2002) Abnormal cerebellar signaling induces dystonia in mice. J Neurosci 22:7825–7833
Quartarone A, Siebner HR, Rothwell JC (2006) Task-specific hand dystonia: can too much plasticity be bad for you? Trends Neurosci 29:192–199
Ridding MC, Sheean G, Rothwell JC, Inzelberg R, Kujirai T (1995) Changes in the balance between motor cortical excitation and inhibition in focal, task specific dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59:493–498
Romito LM, Franzini A, Perani D, Carella F, Marras C, Capus L, Garibotto V, Broggi G, Albanese A (2007) Fixed dystonia unresponsive to pallidal stimulation improved by motor cortex stimulation. Neurology 68:875–876
Rona S, Berardelli A, Vacca L, Inghilleri M, Manfredi M (1998) Alterations of motor cortical inhibition in patients with dystonia. Mov Disord 13:118–124
Ugawa Y, Uesaka Y, Terao Y, Hanajima R, Kanazawa I (1994) Magnetic stimulation of corticospinal pathways at the foramen magnum level in humans. Ann Neurol 36:618–624
Ugawa Y, Uesaka Y, Terao Y, Hanajima R, Kanazawa I (1995) Magnetic stimulation over the cerebellum in humans. Ann Neurol 37:703–713
Ugawa Y, Terao Y, Hanajima R, Sakai K, Furubayashi T, Machii K, Kanazawa I (1997) Magnetic stimulation over the cerebellum in patients with ataxia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 104:453–458
Wassermann EM (2002) Variation in the response to transcranial magnetic brain stimulation in the general population. Clin Neurophysiol 113:1165–1171
41st World Medical Assembly (1990) Declaration of Helsinki: recommendations guiding physicians in biomedical research, involving human subjects. Bulletin of the Pan American Health Organization 24:606–609
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brighina, F., Romano, M., Giglia, G. et al. Effects of cerebellar TMS on motor cortex of patients with focal dystonia: a preliminary report. Exp Brain Res 192, 651–656 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1572-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1572-9