Abstract
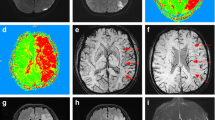
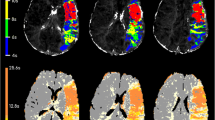
There are many reports on acute cerebral infarcts diagnosed by diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI), but few describe brain-stem infarcts diagnosed by this method. Using the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), we studied 18 consecutive patients with brain-stem infarcts who underwent DWI during the acute phase. We calculated and compared the ADC ratio (lesion ADC/contralateral ADC) in 10 patients with brain-stem and 23 with supratentorial cortical infarcts examined within 24 h of the onset of stroke. Ischaemic brain-stem lesions were detected in all 15 patients who underwent DWI more than 3h after the onset, but not in two who had DWI within 3 h of the onset; their ADC ratio was more than 0.95. ADC ratios in patients with brain-stem infarcts decreased as the interval between onset and DWI increased; the decrease was slower than in patients with supratentorial cortical infarcts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
González RG, Schaefer PW, Buonanno FS, et al (1999) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging: diagnostic accuracy in patients imaged within 6 hours of stroke symptom onset. Radiology 210: 155–162
Lovblad KO, Laubach HJ, Baird AE, et al (1998) Clinical experience with diffusion-weighted MR in patients with acute stroke. AJNR 19: 1061–1066
Uno M, Harada M, Yoneda K, Matsubara S, Sato S, Nagahiro S (2002) Can diffusion- and perfusion- weighted MRI evaluate the efficacy of acute thrombolysis in patients with ICA or MCA occlusion? Neurosurgery 50: 28–35
Yoneda Y, Tokui K, Hanihara T, Kitagaki H, Tabuchi M, Mori E (1999) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: detection of ischemic injury 39 minutes after onset in a stroke patient. Ann Neurol 45: 794–797
Bryan RN, Levy LM, Whitlow WD, Killian JM, Preziosi TJ, Rosario JA (1991) Diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction: comparison of CT and MR imaging. AJNR 12: 611–620
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42: 288–292
Schlaug G, Siewert B, Benfield A, Edelman RR, Warach S (1997) Time course of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) abnormality in human stroke. Neurology 49: 113–119
Hirai S (1993) Brainstem infarction. -frequency, background factors and pathogenesis-. Nippon Rinsho 51 [Suppl] 722–727 (Japanese)
Tazaki Y (1990) Clinical aspects of brainstem infarction. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 30: 1291–1300 (Japanese)
Oppenheim C, Stanescu R, Dormont D, et al (2000) False-negative diffusion-weighted MR findings in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR 21: 1434–1440
Busza AL, Allen KL, King MD, van Bruggen N, Williams SR, Gadian DG (1992) Diffusion-weighted imaging studies of cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Potential relevance to energy failure. Stroke 23: 1602–1612
Minematsu K, Li L, Sotak CH, Davis MA, Fisher M (1992) Reversible focal ischemic injury demonstrated by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in rats. Stroke 23: 1304–1311
Minematsu K, Li L, Fisher M, Sotak CH, Davis MA, Fiandaca MS (1992) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: rapid and quantitative detection of focal brain ischemia. Neurology 42: 235–240
Moseley ME, Cohen Y, Mintorovitch J, et al (1990) Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: comparison of diffusion and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 14: 330–346
Benveniste H, Laurence WH, Johnson A (1992) Mechanism of detection of acute cerebral ischemia in rats by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance microscopy. Stroke 23: 746–754
Becker K, Purcell LL, Hacke W, Hanley D (1996) Vertebrobasilar thrombosis: diagnosis, management, and the use of intra-arterial thrombolysis. Crit Care Med 24: 1729–1742
Matsumoto K, Satoh K (1991) Topical intra-arterial urokinase infusion for acute stroke. In: Hacke W, del Zoppo GJ, Hirschberg M (eds) Thrombolytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 207–212
Oriaandi G, Moscato G, Padolecchia R, Sartucci F (2001) Early thrombolysis in stroke due to basilar artery occlusion. Neurol Sci 22: 399–402
Bogousslavsky J, Regli F, Maeder P, Meuli R, Nader J (1993) The etiology of posterior circulation infarcts: a prospective study using magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography. Neurology 43: 1528–1533
Neumann-Haefelin T, Wittsack HJ, Wenserski F, et al (1999) Diffusion-and perfusion weighted MRI. The DWI/PWI mismatch region in acute stroke. Stroke 30: 1591–1597
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toi, H., Uno, M., Harada, M. et al. Diagnosis of acute brain-stem infarcts using diffusion-weighed MRI. Neuroradiology 45, 352–356 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-002-0897-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-002-0897-5