Abstract
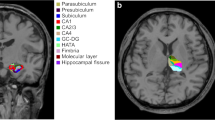
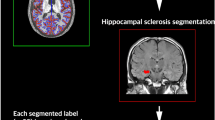
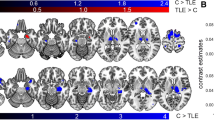
Hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is often associated with hippocampal atrophy. This study assessed whether such atrophy is correlated with loss of gray matter volume in other brain regions. In 16 patients with TLE and clear magnetic resonance imaging–based evidence of hippocampal sclerosis, hippocampal volumes were determined manually and the local gray matter (LGM) amount was estimated throughout the entire brain using voxel–based morphometry. Voxelwise correlations between the volume of the sclerotic hippocampus and LGM were computed. The pattern of voxels whose LGM correlated with hippocampal volume outlined remarkably well the anatomy of the extended limbic system and included the parahippocampal region, cingulate gyrus throughout its extent, basal forebrain, thalamic nuclei, medial orbitofrontal areas and the insula. These correlations emerged mainly on the side ipsilateral to the affected hippocampus but were also found contralaterally. No such correlations were found in a group of 16 healthy controls. The present data show that hippocampal volume loss in TLE is associated with a widespread limbic systems atrophy. These findings are helpful to better understand the functional deficit and reorganization often found in temporal lobe epilepsy and will also provide a basis to assess neural plasticity in the limbic system for those patients who will undergo curative temporal lobe surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi N, Alarcon G, Binnie CD, Elwes RD, Polkey CE, Reynolds EH (1998) Predictive value of interictal epileptiform discharges during non-REM sleep on scalp EEG recordings for the lateralization of epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 39:682–632
Andermann F (2003) Why study mesial temporal atrophy in patients with intractable temporal lobe epilepsy? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1606–1607
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxelbased morphometry–the methods. Neuroimage 11:805–821
Barbas H, Blatt GJ (1995) Topographically specific hippocampal projections target functionally distinct prefrontal areas in the rhesus monkey. Hippocampus 5:511–533
Bentivoglio M,Aggleton JP,Mishkin M (1997) The Thalamus and Memory Formation. In: M Steriade EGJ, McCormick DA (ed) Thalamus, Experimental and Clinical Aspects. Amsterdam-Lausanne, pp 869–711
Bernasconi N, Bernasconi A, Caramanos Z, Andermann F, Dubeau F, Arnold DL (2000) Morphometric MRI analysis of the parahippocampal region in temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 911:495–500
Binnie CD, Stefan H (1999) Modern electroencephalography: its role in epilepsy management. Clin Neurophysiol 110:1671–1697
Blatt GJ, Rosene DL (1998) Organization of direct hippocampal efferent projections to the cerebral cortex of the rhesus monkey: projections from CA1, prosubiculum, and subiculum to the temporal lobe. J Comp Neurol 392:92–114
Bonilha L, Kobayashi E, Rorden C, Cendes F, Li LM (2003) Medial temporal lobe atrophy in patients with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1627–1630
Duzel E, Kaufmann J, Guderian S, Szentkuti A, Schott B, Bodammer N, Hopf M, Kanowski M, Tempelmann C, Heinze HJ (2004) Measures of hippocampal volumes, diffusion and 1H MRS metabolic abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy provide partially complementary information. Eur J Neurol 11:195–205
Fernandez G, Effenberger O, Vinz B, Steinlein O, Elger CE, Dohring W, Heinze HJ (1998) Hippocampal malformation as a cause of familial febrile convulsions and subsequent hippocampal sclerosis. Neurology 50:909–917
Ferreira NF, de Oliveira V, Amaral L, Mendonça R, Lima SS (2003) Analysis of parahippocampal gyrus in 115 patients with hippocampal sclerosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 61:707–711
French SJ, Totterdell S (2002) Hippocampal and prefrontal cortical inputs monosynaptically converge with individual projection neurons of the nucleus accumbens. J Comp Neurol 446:151–165
French SJ, Totterdell S (2003) Individual nucleus accumbens-projection neurons receive both basolateral amygdala and ventral subicular afferents in rats. Neuroscience 119:19–31
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 14:21–36
Guerreiro C, Cendes F, Li LM, Jones-Gotman M, Andermann F, Dubeau F, Piazzini A, Feindel W (1999) Clinical patterns of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and pure amygdalar atrophy. Epilepsia 40:453–461
Helmstaedter C, Brosch T, Kurthen M, Elger CE (2004) The impact of sex and language dominance on materialspecific memory before and after left temporal lobe surgery. Brain 127: 1518–1525
Helmstaedter C, Grunwald T, Lehnertz K, Gleissner U, Elger CE (1997) Differential involvement of left temporolateral and temporomesial structures in verbal declarative learning and memory: evidence from temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Cogn 35:110–131
Helmstaedter C, Kurthen M, Linke DB, Elger CE (1994) Right hemisphere restitution of language and memory functions in right hemisphere language- dominant patients with left temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 117 (Pt 4):729–737
Insausti R, Herrero MT, Witter MP (1997) Entorhinal cortex of the rat: cytoarchitectonic subdivisions and the origin and distribution of cortical efferents. Hippocampus 7:146–183
Jokeit H, Ebner A, Holthausen H, Markowitsch HJ, Moch A, Pannek H, Schulz R, Tuxhorn I (1997) Individual prediction of change in delayed recall of prose passages after left-sided anterior temporal lobectomy. Neurology 49:481–487
Jones EG, Powell TPS (1970) An anatomical study of converging sensory pathways within the cerebral cortex of the monkey. Brain 93:793–820
Keller SS, Mackay CE, Barrick TR, Wieshmann UC, Howard MA, Roberts N (2002) Voxel-based morphometric comparison of hippocampal and extrahippocampal abnormalities in patients with left and right hippocampal atrophy. Neuroimage 16:23–31
Keller SS, Wieshmann UC, Mackay CE, Denby CE, Webb J, Roberts N (2002) Voxel based morphometry of grey matter abnormalities in patients with medically intractable temporal lobe epilepsy: effects of side of seizure onset and epilepsy duration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:648–655
Knecht S (2004) Does language lateralization depend on the hippocampus? Brain 127:1217–1218
Kuzniecky RI, Bilir E, Gilliam F, Faught E, Palmer C, Morawetz R, Jackson G (1997) Multimodality MRI in mesial temporal sclerosis: relative sensitivity and specificity. Neurology 49:774–778
Liegeois F, Connelly A, Cross JH, Boyd SG, Gadian DG, Vargha-Khadem F, Baldeweg T (2004) Language reorganization in children with early-onset lesions of the left hemisphere: an fMRI study. Brain 127:1229–1236
Liegeois F, Connelly A, Salmond CH, Gadian DG, Vargha-Khadem F, Baldeweg T (2002) A direct test for lateralization of language activation using fMRI: comparison with invasive assessments in children with epilepsy. Neuroimage 17:1861–1867
MacLean PD (1955) The limbic system (‘visceral brain’) and emotional behavior. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 73:130–134
Meiners LC, Witkamp TD, de Kort GA, van Huffelen AC, van der Graaf Y, Jansen GH, van der Grond J, van Veelen CW (1999) Relevance of temporal lobe white matter changes in hippocampal sclerosis. Magnetic resonance imaging and histology. Invest Radiol 34:38–45
Merschhemke M, Mitchell TN, Free SL, Hammers A, Kinton L, Siddiqui A, Stevens J, Kendall B, Meencke HJ, Duncan JS (2003) Quantitative MRI detects abnormalities in relatives of patients with epilepsy and malformations of cortical development. Neuroimage 18:642–649
Moran NF, Lemieux L, Kitchen ND, Fish DR, Shorvon SD (2001) Extrahippocampal temporal lobe atrophy in temporal lobe epilepsy and mesial temporal sclerosis. Brain 124:167–175
Morris R, Petrides M, Pandya DN (1999) Architecture and connections of retrosplenial area 30 in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Eur J Neurosci 11:2506–2518
Natsume J, Bernasconi N, Andermann F, Bernasconi A (2003) MRI volumetry of the thalamus in temporal, extratemporal, and idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Neurology 60:1296–1300
Oikawa H, Sasaki M, Tamakawa Y, Kamei A (2001) The circuit of Papez in mesial temporal sclerosis: MRI. Neuroradiology 43:205–210
Pandya DN, Van Hoesen GW, Mesulam MM (1981) Efferent connections of the cingulate gyrus in the rhesus monkey. Exp Brain Res 42:319–330
Pruessner JC, Li LM, Serles W, Pruessner M, Collins DL, Kabani N, Lupien S, Evans AC (2000) Volumetry of hippocampus and amygdala with highresolution MRI and three-dimensional analysis software: minimizing the discrepancies between laboratories. Cereb Cortex 10:433–442
Rockland KS, Van Hoesen GW (1999) Some temporal and parietal cortical connections converge in CA1 of the primate hippocampus. Cereb Cortex 9:232–237
Ruggieri PM, Najm IM (2001) MR imaging in epilepsy. Neurol Clin 19:477–489
Sandok EK, O’Brien TJ, Jack CR, So EL (2000) Significance of cerebellar atrophy in intractable temporal lobe epilepsy: a quantitative MRI study. Epilepsia 41:1315–1320
Springer JA, Binder JR, Hammeke TA, Swanson SJ, Frost JA, Bellgowan PS, Brewer CC, Perry HM, Morris GL, Mueller WM (1999) Language dominance in neurologically normal and epilepsy subjects: a functional MRI study. Brain 122(Pt 11):2033–2046
Suzuki WA, Amaral DG (1994) Perirhinal and parahippocampal cortices of the macaque monkey: cortical afferents. J Comp Neurol 350:497–533
Szentkuti A, Guderian S, Schiltz K, Kaufmann J, Munte TF, Heinze HJ, Duzel E (2004) Quantitative MR analyses of the hippocampus: Unspecific metabolic changes in aging. J Neurol 251:1345–1353
Van Hoesen GW (1982) The parahippocampal gyrus: new observations regarding its cortical connections in the monkey. Trends Neurosci 5:345–350
von Oertzen J, Urbach H, Blumcke I, Reuber M, Traber F, Peveling T, Menzel C, Elger CE (2002) Time-efficient T2 relaxometry of the entire hippocampus is feasible in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 58:257–264
Wilke M, Kassubek J, Ziyeh S, Schulze-Bonhage A, Huppertz HJ (2003) Automated detection of gray matter malformations using optimized voxel-based morphometry: a systematic approach. Neuroimage 20:330–343
Wormann FG (2001) The value of neuroimaging in diagnosis of epilepsy. Ther Umsch 58:645–649
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Düzel, E., Schiltz, K., Solbach, T. et al. Hippocampal atrophy in temporal lobe epilepsy is correlated with limbic systems atrophy. J Neurol 253, 294–300 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0981-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0981-y