Abstract
Background and objective
Contrary to what happens in adult–onset multiple sclerosis (MS), in a previous preliminary magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study we showed only subtle normal–appearing brain tissue changes in patients with earlyonset MS. Our objective was to evaluate the presence and extent of tissue damage in the brain normalappearing white matter (NAWM) and gray matter (GM) from a larger population of patients with earlyonset MS.
Methods
Using diffusion tensor (DT) and magnetization transfer (MT) MRI, we obtained DT and MT ratio (MTR) maps of the NAWM and GM from 23 patients with early–onset MS and 16 sex– and age–matched healthy volunteers.
Results
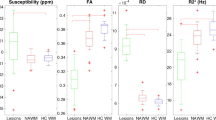
Compared with healthy volunteers, patients with early–onset MS had significantly increased average MD (p = 0.02) and FA peak height (p = 0.007) and decreased average FA (p <0.0001) of the NAWM.Brain dual–echo lesion load was significantly correlated with average FA (r = –0.48, p = 0.02) and with FA peak height (r = 0.45, p = 0.03) of the NAWM. No MTR and diffusion changes were detected in the GM.
Conclusions
This study confirms the paucity of the ‘occult’ brain tissue damage in patients with earlyonset MS. It also suggests that in these patients GM is spared by the disease process and that NAWM changes are likely to be secondary to Wallerian degeneration of fibers passing through macroscopic lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen IV, McKeown SR (1979) A histological, histochemical and biochemical study of the macroscopically normal white matter in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 41:81–91
Evangelou N, Esiri MM, Smith S, et al. (2000) Quantitative pathological evidence for axonal loss in normal appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 47:391–395
Bjartmar C, Kinkel RP, Kidd G, et al. (2001) Axonal loss in normal–appearing white matter in a patient with acute MS. Neurology 57:1248–1252
Brownell B, Hughes JT (1962) Distribution of plaques in the cerebrum in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 25:315–320
Kidd D, Barkhof F, McConnell R, et al. (1999) Cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Brain 122:17–26
Peterson JW, Bo L, Mork S, Chang A, Trapp BD (2001) Transected neurites, apoptotic neurons, and reduced inflammation in cortical multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol 50:389–400
Miller DH, Thompson AJ, Filippi M (2003) Magnetic resonance studies of abnormalities in the normal appearing white matter and gray matter in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 250:1407–1419
Filippi M, Rocca MA, Comi G (2003) The use of quantitative magnetic–resonance– based techniques to monitor the evolution of multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 2:337–346
Oreja–Guevara C, Rovaris M, Iannucci G, et al. (2005) Progressive gray matter damage in patients with relapsing remitting MS: a longitudinal diffusion tensor MRI study. Arch Neurol 62:578–584
Simone IL, Carrara D, Tortorella C, et al. (2002) Course and prognosis in early–onset MS: comparison with adult–onset forms. Neurology 59: 1922–1928
Mezzapesa DM, Rocca MA, Falini A, et al. (2004) A preliminary diffusion tensor and magnetization transfer magnetic resonance imaging study of early–onset multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 61:366–368
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurological impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
Cercignani M, Bozzali M, Iannucci G, Comi G, Filippi M (2001) Magnetisation transfer ratio and mean diffusivity of normal appearing white and grey matter from patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70:311–317
Rovaris M, Filippi M, Calori G, et al. (1997) Intra–observer reproducibility in measuring new putative MR markers of demyelination and axonal loss in multiple sclerosis: a comparison with conventional T2–weighted images. J Neurol 244:266–270
Studholme C, Hill DLG, Hawkes DJ (1996) Automated three–dimensional registration of magnetic resonance and positron emission tomography brain images by multiresolution optimization of voxel similarity measures. Med Phys 24:25–35
Ashburner J, Friston K (1997) Multimodal image coregistration and partitioning– a unified framework. Neuro Image 6:209–217
Smith S, Zhang Y, Jenkinson M, et al. (2002) Accurate, robust and automated longitudinal and cross–sectional brain change analysis. Neuro Image 17:479–489
Sastre–Garriga J, Ingle GT, Chard DT, et al. (2004) Gray and white matter atrophy in early clinical stages of primary progressive multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage 22:353–359
Amato MP, Bartolozzi ML, Zipoli V, et al. (2004) Neocortical volume decrease in relapsing–remitting MS patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 63:89–93
Chard DT, Griffin CM, McLean MA, et al. (2002) Brain metabolite changes in cortical gray and normal–appearing white matter in clinically early relapsing– remitting multiple sclerosis. Brain 125:2342–2352
Rovaris M, Bozzali M, Iannucci G, et al. (2002) Assessment of normal–appearing white and gray matter in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 59:1406–1412
Ge Y, Grossman RI, Udupa JK, et al. (2002) Magnetization transfer ratio histogram analysis of normal–appearing gray matter and normal appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:62–68
Dehmeshki J, Chard DT, Leary SM, et al. (2003) The normal appearing gray matter in primary progressive multiple sclerosis: a magnetisation transfer imaging study. J Neurol 250:67–74
Bozzali M, Cercignani M, Sormani MP, et al. (2002) Quantification of brain gray matter damage in different MS phenotypes by use of diffusion tensor MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:985–988
Audoin B, Ranjeva JP, Duong MV, et al. (2004) Voxel–based analysis of MTR images: a method to locate gray matter abnormalities in patients at the earliest stage of multiple sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:765–771
Chard DT, Griffin CM, Rashid W, et al. (2004) Progressive grey matter atrophy in clinically early relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 10:387–391
Davies GR, Altmann DR, Hadjiprocopis A, et al. (2005) Increasing normal– appearing grey and white matter magnetisation transfer ratio abnormality in early relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 252:1037–1044
Rovaris M, Gallo A, Valsasina P, et al. (2005) Short–term accrual of gray matter pathology in patients with progressive multiple sclerosis: an in vivo study using diffusion tensor MRI. NeuroImage 24:1139–1146
Sastre–Garriga J, Ingle GT, Chard DT, et al. (2005) Grey and white matter volume changes in early primary progressive multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal study. Brain 128:1454–1460
Dalton CM, Chard DT, Davies GR, et al. (2004) Early development of multiple sclerosis is associated with progressive gray matter atrophy in patients presenting with clinically isolated syndromes. Brain 127:1101–1107
Rovaris M, Iannucci G, Falautano M, et al. (2002) Cognitive dysfunction in patients with mildly disabling relapsing– remitting MS: an exploratory study with diffusion tensor MR imaging. J Neurol Sci 195:103–109
Benedetti B, Rovaris M, Judica E, et al. (2005) Diffusion tensor MRI–detectable grey matter damage predicts the medium–term clinical evolution of primary progressive MS patients. Mult Scler (in press) (Abstract, accepted for presentation at the ECTRIMS/ACTRIMS 2005)
Balassy C, Bernert G, Wober–Bingol C, et al. (2001) Long–term MRI observations of childhood–onset relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Neuropediatrics 32:28–37
Confavreux C, Vukusic S, Adeleine P (2003) Early clinical predictors and progression of irreversible disability in multiple sclerosis: an amnesic process. Brain 126:770–782
Miller DH, Barkhof F, Frank JA, et al. (2002) Measurement of atrophy in multiple sclerosis: pathological basis, methodological aspects and clinical relevance. Brain 125:1676–1695 (Review)
Filippi M, Rovaris M, Inglese M, et al. (2004) Reduced brain tissue loss during randomized study of interferon beta–1a in patients at presentation with syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis. Lancet 364:1489–1496
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tortorella, P., Rocca, M.A., Mezzapesa, D.M. et al. MRI quantification of gray and white matter damage in patients with early–onset multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 253, 903–907 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0129-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0129-8