Abstract
Background
Rest tremor is a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD), but its pathogenesis remains incompletely understood. Nigro-striatal dopamine deficiency correlates best with bradykinesia, but not with tremor. Oscillating neurons in one or multiple localizations within the basal gangliathalamo-cortical loop may cause rest tremor, and an active contribution of the cerebellum and the cerebello-thalamo-cortical projections has been postulated.
Objective
To compare the pattern of grey matter volume in PD patients with and without tremor to identify structural correlates of rest tremor.
Methods
Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) of a high-resolution 3 Tesla, T1-weighted MR images, pre-processed according to an optimized protocol using SPM2, was performed in 24 patients with mild to moderate PD comparing local grey matter volume in patients with (n = 14) and without rest tremor (n = 10).
Results
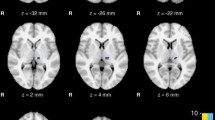
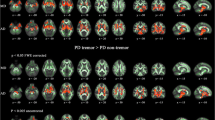
Grey matter volume is decreased in the right quadrangular lobe and declive of the cerebellum in PD with tremor compared to those without (PFDR < 0.05).
Conclusions
These results demonstrate for the first time morphological changes in the cerebellum in PD patients with rest tremor and highlight the involvement of the cerebellum and cerebello- thalamo-cortical circuit in the pathogenesis of parkinsonian rest tremor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarsland D, Andersen K, Larsen JP, Lolk A, Kragh-Sorensen P (2003) Prevalence and characteristics of dementia in Parkinson disease – An 8-year prospective study. Arch Neurol 60:387–392
Amunts K, Schlaug G, Schleicher A, Steinmetz H, Dabringhaus A, Roland PE, Zilles K (1996) Asymmetry in the human motor cortex and handedness. Neuroimage 3:216–222
Antonini A, Moeller JR, Nakamura T, Spetsieris P, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (1998) The metabolic anatomy of tremor in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 51:803–810
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelsohn M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571
Benabid AL, Pollak P, Gervason C, Hoffmann D, Gao DM, Hommel M, Perret JE, Derougemont J (1991) Long- Term Suppression of Tremor by Chronic Stimulation of the Ventral Intermediate Thalamic Nucleus. Lancet 337:403–406
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, De Vos RAI, Steur ENHJ, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Brenneis C, Seppi K, Schocke MF, Muller J, Luginger E, Bosch S, Loscher WN, Buchel C, Poewe W, Wenning GK (2003) Voxel-based morphometry detects cortical atrophy in the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 18:1132–1138
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, O’Brien JT (2005) Brain atrophy rates in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia using serial magnetic resonance imaging. Mov Disord 20:1571–1576
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Williams ED, O’Brien JT (2004) Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and controls. Brain 127:791–800
Caparros-Lefebvre D, Blond S, Vermersch P, Pecheux N, Guieu JD, Petit H (1993) Chronic Thalamic-Stimulation Improves Tremor and Levodopa Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson Disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56:268–273
Caparros-Lefebvre D, Ruchoux MM, Blond S, Petit H, Percheron G (1994) Long-Term Thalamic-Stimulation in Parkinsons-Disease – Postmortem Anatomoclinical Study. Neurology 44:1856–1860
Chapman LJ, Chapman JP (1987) The Measurement of Handedness. Brain and Cognition 6:175–183
Coffey CE, Lucke JF, Saxton JA, Ratcliff G, Unitas LJ, Billig B, Bryan RN (1998) Sex differences in brain aging – A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol 55:169–179
Daniels C, Peller M, Wolff S, Alfke K, Witt K, Gaser C, Jansen O, Siebner HR, Deuschl G (2006) Voxel-based morphometry shows no decreases in cerebellar gray matter volume in essential tremor. Neurology 67:1452–1456
Deiber MP, Pollak P, Passingham R, Landais P, Gervason C, Cinotti L, Friston K, Frackowiak R, Mauguiere F, Benabid AL (1993) Thalamic-Stimulation and Suppression of Parkinsonian Tremor – Evidence of A Cerebellar Deactivation Using Positron Emission Tomography. Brain 116:267–279
Deuschl G, Raethjen J, Baron R, Lindemann M, Wilms H, Krack P (2000) The pathophysiology of parkinsonian tremor: a review. J Neurol 247:33–48
Dissanayaka NN, Sellbach A, Matheson S, Marsh R, Silburn PA, O’Sullivan JD, Byrne GJ, Mellick GD (2007) Validity of Hamilton Depression Inventory in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22:399–403
Draganski B, Gaser C, Busch V, Schuierer G, Bogdahn U, May A (2004) Neuroplasticity: Changes in grey matter induced by training. Nature 427:311–312
Eidelberg D, Moeller JR, Dhawan V, Sidtis JJ, Ginos JZ, Strother SC, Cedarbaum J, Greene P, Fahn S, Rottenberg DA (1990) The Metabolic Anatomy of Parkinsons-Disease – Complementary [F-18] Fluorodeoxyglucose and [F-18] Fluorodopa Positron Emission Tomographic Studies. Mov Disord 5:203–213
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12(3):189–198
Foltynie T, Brayne C, Barker RA (2002) The heterogeneity of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 249:138–145
Fukuda M, Barnes A, Simon ES, Holmes A, Dhawan V, Giladi N, Fodstad H, Ma YL, Eidelberg D (2004) Thalamic stimulation for parkinsonian tremor: correlation between regional cerebral blood flow and physiological tremor characteristics. NeuroImage 21:608–615
Galaburda AM, LeMay M, Kemper TL, Geschwind N (1978) Right-left asymmetrics in the brain. Science 199:852–856
Genovese CR, Lazar NA, Nichols T (2002) Thresholding of Statistical Maps in Functional Neuroimaging Using the False Discovery Rate. Neuro- Image 15:870–878
Ghaemi M, Raethjen J, Hilker R, Rudolf J, Sobesky J, Deuschl G, Heiss WD (2002) Monosymptomatic resting tremor and Parkinson’s disease: A multitracer positron emission tomographic study. Mov Disord 17:782–788
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752
Goetz CG, Tanner CM, Stebbins GT, Buchman AS (1988) Risk-Factors for Progression in Parkinsons-Disease. Neurology 38:1841–1844
Goldenberg G, Podreka I, Muller C, Deecke L (1989) The relationship between cognitive deficits and frontal lobe function in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Behav Neurol 2:79–87
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RNA, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RSJ (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage 14:21–36
Guillard A, Chastang C (1978) Long- Term Prognostic Factors in Parkinsons- Disease. Rev Neurol 134:341–354
Guillard A, Chastang C, Fenelon G (1986) Parkinsons-Disease – A Long- Term Study of 416 Patients – Prognostic Factors and Implications for Treatment. Rev Neurol 142:207–214
Hamilton M (1960) A Rating Scale for Depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:56–62
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD (1967) Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 17(5):427–442
Inase M, Tanji J (1995) Thalamic Distribution of Projection Neurons to the Primary Motor Cortex Relative to Afferent Terminal Fields from the Globus-Pallidus in the Macaque Monkey. J Comp Neurol 353:415–426
Jankovic J, Kapadia AS (2001) Functional decline in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 58:1611–1615
Jankovic J, Mcdermott M, Carter J, Gauthier S, Goetz C, Golbe L, Huber S, Koller W, Olanow C, Shoulson I, Stern M, Tanner C, Weiner W (1990) Variable Expression of Parkinsons-Disease – A Base-Line Analysis of the Datatop Cohort. Neurology 40:1529–1534
Jankovic J, Schwartz KS, Ondo W (1999) Re-emergent tremor of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:646–650
Jellinger KA (1999) Post mortem studies in Parkinson’s disease – is it possible to detect brain areas for specific symptoms? J Neural Transm (Supplement):1–29
Jellinger KA (2002) Recent developments in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Supplement):347–376
Jellinger KA, Paulus W (1992) Clinicopathological correlations in Parkinsons- dtsease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 94:S86–S88
Josephs KA, Matsumoto JY, Ahlskog JE (2006) Benign Tremulous parkinsonism. Arch Neurol 63:354–357
Kassubek J, Juengling FD, Hellwig B, Spreer J, Lucking CH (2002) Thalamic gray matter changes in unilateral Parkinsonian resting tremor: a voxelbased morphometric analysis of 3- dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosci Lett 323:29–32
Kelly RM, Strick PL (2003) Cerebellar loops with motor cortex and prefrontal cortex of a nonhuman primate. J Neurosci 23:8432–8444
Koller W, Pahwa R, Busenbark K, Hubble J, Wilkinson S, Lang A, Tuite P, Sime E, Lazano A, Hauser R, Malapira T, Smith D, Tarsy D, Miyawaki E, Norregaard T, Kormos T, Olanow CW (1997) High-frequency unilateral thalamic stimulation in the treatment of essential and parkinsonian tremor. Ann Neurol 42:292–299
Lee MS, Rinne JO, Marsden CD (2000) The pedunculopontine nucleus: Its role in the genesis of movement disorders. Yonsei Med J 41:167–184
Lenz FA, Kwan HC, Martin RL, Tasker RR, Dostrovsky JO, Lenz YE (1994) Single-unit analysis of the human ventral thalamic nuclear group – Tremor-related activity in functionally identified cells. Brain 117:531–543
Limousin P, Speelman JD, Gielen F, Janssens M, study c (1999) Multicentre European study of thalamic stimulation in parkinsonian and essential tremor. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 66:289–296
Marras C, Rochon P, Lang AE (2002) Predicting motor decline and disability in Parkinson disease – A systematic review. Arch Neurol 59:1724–1728
Mori F, Piao YS, Hayashi S, Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Yoshimoto M, Iwatsubo T, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2003) alpha-Synuclein accumulates in Purkinje cells in Lewy body disease but not in multiple system atrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:812–819
Nagano-Saito A, Washimi Y, Arahata Y, Kachi T, Lerch JP, Evans AC, Dagher A, Ito K (2005) Cerebral atrophy and its relation to cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64:224–229
Otsuka M, Ichiya Y, Kuwabara Y, Hosokawa S, Sasaki M, Yoshida T, Fukumura T, Masuda K, Kato M (1996) Differences in the reduced F-18-Dopa uptakes of the caudate and the putamen in Parkinson’s disease: Correlations with the three main symptoms. J Neurol Sci 136:169–173
Pahapill PA, Lozano AM (2000) The pedunculopontine nucleus and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 123:1767–1783
Paulus W, Jellinger K (1991) The Neuropathologic Basis of Different Clinical Subgroups of Parkinsons-Disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 50:743–755
Piao YS, Mori F, Hayashi S, Tanji K, Yoshimoto M, Kakita A, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2003) alpha-synuclein pathology affecting Bergmann glia of the cerebellum in patients with alphasynucleinopathies. Acta Neuropathol 105:403–409
Price S, Paviour D, Scahill R, Stevens J, Rossor M, Lees A, Fox N (2004) Voxelbased morphometry detects patterns of atrophy that help differentiate progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage 23:663–669
Ramirez-Ruiz B, Marti MJ, Tolosa E, Bartres-Faz D, Summerfield C, Salgado-Pineda P, Gomez-Anson B, Junque C (2005) Longitudinal evaluation of cerebral morphological changes in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. J Neurol 252:1345–1352
Rye DB (1997) Contributions of the pedunculopontine region to normal and altered REM sleep. Sleep 20(9):757–788
Smith AM, Bourbonnais D (1981) Neuronal-Activity in Cerebellar Cortex Related to Control of Prehensile Force. J Neurophysiol 45:286–303
Snyder PJ, Bilder RM, Wu HW, Bogerts B, Lieberman JA (1995) Cerebellar volume asymmetries are related to handedness: a quantitative MRI study. Neuropsychologia 33:407–419
Spreen O, Strauss E (1998) A compendium of neuropsychological tests. Oxford: University Press
Stein JF, Aziz TZ (1999) Does imbalance between basal ganglia and cerebellar outputs cause movement disorders? Curr Opin Neurol 12:667–669
Summerfield C, Junque C, Tolosa E, Salgado-Pineda P, Gomez-Anson B, Marti M, Ramirez-Ruiz B, Mercader J (2005) Structural brain changes in Parkinson disease with dementia. Arch Neurol 62:281–285
Thach WT, Goodkin HP, Keating JG (1992) The cerebellum and the adaptive coordination of movement. Annu Rev Neurosci 15:403–442
Timmermann L, Gross J, Dirks M, Volkmann J, Freund HJ, Schnitzler A (2003) The cerebral oscillatory network of parkinsonian resting tremor. Brain 126:199–212
Vingerhoets FJ, Schulzer M, Calne DB, Snow BJ (1997) Which clinical sign of Parkinson’s disease best reflects the nigrostriatal lesion? Ann Neurol 41:58–64
Visser M, Leentjens AFG, Marinus J, Stiggelbout AM, van Hilten JJ (2006) Reliability and validity of the Beck Depression Inventory in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 21:668–672
Zetusky WJ, Jankovic J, Pirozzolo FJ (1985) The heterogeneity of Parkinsons- disease – Clinical and prognostic implications. Neurology 35:522–526
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benninger, D.H., Thees, S., Kollias, S.S. et al. Morphological differences in Parkinson’s disease with and without rest tremor. J Neurol 256, 256–263 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-0092-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-0092-2