Summary
Background. External ventricular drainage (EVD) is frequently used in neurosurgery for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage in patients with raised intracranial pressure. The major complication of this procedure is an EVD-related infection, i.e., meningitis or ventriculitis. The purpose of the present retrospective single centre study is to assess the possible causes of these infections.
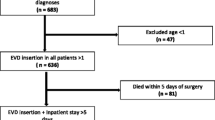
Patients and methods. Two hundred and twenty-eight patients were included in the period from January 1993 until April 2005. Patient and disease demographics, as well as EVD data, and the occurrence of infection were reviewed, compared, and included in a risk-analysis study.
Results. The population’s mean age was 56 ± 15 years and the sexes were equally distributed. Most frequently, the indication for EVD was hydrocephalus due to intraventricular haemorrhage (48.2%). An infection was documented in 23.2% of all patients. Duration of EVD drainage appeared to be a risk factor for infection (>11 days: OR 4.1; 95% CI 1.8–9.2, p = 0.001). CSF sampling frequency was also a significant risk-factor (no sampling: OR 0.2, 95% CI 0.2–0.5, p = 0.003).
Conclusions. We found a relatively high percentage of EVD-related infections. After multivariate analysis there appears to be a relation with duration of drainage and frequent CSF sampling. As a result, a new EVD protocol is proposed in our institution that we believe will decrease the number of EVD-related infections to a minimum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CH Alleyne SuffixJr M Hassan JM Zabramski (2000) ArticleTitleThe efficacy and cost of prophylactic and perioprocedural antibiotics in patients with external ventricular drains Neurosurgery 47 1124–1127 Occurrence Handle11063105 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200011000-00020
Y Arabi ZA Memish HH Balkhy C Francis A Ferayan A Al Shimemeri MA Almuneef (2005) ArticleTitleVentriculostomy-associated infections: incidence and risk factors Am J Infect Control 33 137–143 Occurrence Handle15798667 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ajic.2004.11.008
P Gerner-Smidt E Stenager C Kock-Jensen (1988) ArticleTitleTreatment of ventriculostomy-related infections Acta Neurochir (Wien) 91 47–49 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01400527 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c3nvFWjsw%3D%3D
KL Holloway T Barnes S Choi R Bullock LF Marshall HM Eisenberg JA Jane JD Ward HF Young A Marmarou (1996) ArticleTitleVentriculostomy infections: the effect of monitoring duration and catheter exchange in 584 patients J Neurosurg 85 419–424 Occurrence Handle8751626 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28zltVaiug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.3171/jns.1996.85.3.0419
TC Horan RP Gaynes (2004) Surveillance of nosocomial infections CG Mayhall (Eds) Hospital epidemiology and infection control Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Philadelphia 1659–1702
RK Khanna ML Rosenblum JP Rock GM Malik (1995) ArticleTitleProlonged external ventricular drainage with percutaneous long-tunnel ventriculostomies J Neurosurg 83 791–794 Occurrence Handle7472544 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28%2Fislylsg%3D%3D
DK Kim D Uttley BA Bell HT Marsh AJ Moore (1995) ArticleTitleComparison of rates of infection of two methods of emergency ventricular drainage J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 58 444–446 Occurrence Handle7738551 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M3ls1ylsg%3D%3D
AM Korinek M Reina AL Boch AO Rivera D De Bels L Puybasset (2005) ArticleTitlePrevention of external ventricular drain-related ventriculitis Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147 39–45 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00701-004-0416-z
CH Lo D Spelman M Bailey DJ Cooper JV Rosenfeld JE Brecknell (2007) ArticleTitleExternal ventricular drain infections are independent of drain duration: an argument against elective revision J Neurosurg 106 378–383 Occurrence Handle17367058 Occurrence Handle10.3171/jns.2007.106.3.378
AP Lozier RR Sciacca MF Romagnoli ES Connolly SuffixJr (2002) ArticleTitleVentriculostomy-related infections: a critical review of the literature Neurosurgery 51 170–181 Occurrence Handle12182415 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200207000-00024
MA Lucey JA Myburgh (2003) ArticleTitleAntibiotic prophylaxis for external ventricular drains in neurosurgical patients: an audit of compliance with a clinical management protocol Crit Care Resusc 5 182–185 Occurrence Handle16573480 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD287otVWktw%3D%3D
KE Lyke OO Obasanjo MA Williams M O’Brien R Chotani TM Perl (2001) ArticleTitleVentriculitis complicating use of intraventricular catheters in adult neurosurgical patients Clin Infect Dis 33 2028–2033 Occurrence Handle11712094 Occurrence Handle10.1086/324492 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnmsFGksw%3D%3D
CG Mayhall NH Archer VA Lamb AC Spadora JW Baggett JD Ward RK Narayan (1984) ArticleTitleVentriculostomy-related infections. A prospective epidemiologic study N Engl J Med 310 553–559 Occurrence Handle6694707 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2c7hslChsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM198403013100903
JK Ohrstrom JK Skou T Ejlertsen M Kosteljanetz (1989) ArticleTitleInfected ventriculostomy: bacteriology and treatment Acta Neurochir (Wien) 100 67–69 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01405277 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3c%2Flt1Orsw%3D%3D
CG Paramore DA Turner (1994) ArticleTitleRelative risks of ventriculostomy infection and morbidity Acta Neurochir (Wien) 127 79–84 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01808552 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M%2FivVKlsg%3D%3D
P Park HJ Garton MJ Kocan BG Thompson (2004) ArticleTitleRisk of infection with prolonged ventricular catheterisation Neurosurgery 55 594–599 Occurrence Handle15335426 Occurrence Handle10.1227/01.NEU.0000134289.04500.EE
W Pfisterer M Muhlbauer T Czech A Reinprecht (2003) ArticleTitleEarly diagnosis of external ventricular drainage infection: results of a prospective study J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74 929–932 Occurrence Handle12810782 Occurrence Handle10.1136/jnnp.74.7.929 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s3otlOitQ%3D%3D
RP Schade J Schinkel FW Roelandse RB Geskus LG Visser MC Van Dijk JH Voormolen H Van Pelt EJ Kuijper (2006) ArticleTitleLack of value of routine analysis of cerebrospinal fluid for prediction and diagnosis of external drainage-related bacterial meningitis J Neurosurg 104 101–108 Occurrence Handle16509153 Occurrence Handle10.3171/jns.2006.104.1.101
RP Schade J Schinkel LG Visser JM Van Dijk JH Voormolen EJ Kuijper (2005) ArticleTitleBacterial meningitis caused by the use of ventricular or lumbar cerebrospinal fluid catheters J Neurosurg 102 229–234 Occurrence Handle15739549
E Stenager P Gerner-Smidt C Kock-Jensen (1986) ArticleTitleVentriculostomy-related infections – an epidemiological study Acta Neurochir (Wien) 83 20–22 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01420503 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s%2Fps1GksA%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Correspondence: Daphna Hoefnagel, Erasmus Medical Centre, Department of Neurosurgery, ‘s Gravendijkwal 230, PO Box 2040, 3000 CA Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoefnagel, D., Dammers, R., Ter Laak-Poort, M. et al. Risk factors for infections related to external ventricular drainage. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150, 209–214 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1458-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1458-9