Abstract.
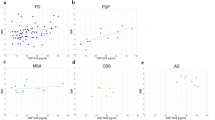
We used SPECT and the tracer 123I-Ioflupane to measure dopamine transporter (DAT) binding in the caudate nucleus and the putamen of 70 patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), 10 with multiple system atrophy (MSA-P type), and 10 with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Data were compared with 12 age-matched control subjects. We found significant reductions in mean striatal values in all three forms of parkinsonism. However, decrements were significantly greater in PSP (0.51±0.39, p<0.01) compared with MSA-P (0.70±0.33) and PD (0.95±0.38). No differences were found between MSA and PD. Putamen/caudate ratios were greater in PSP (0.83±0.12, p<0.01) than in PD (0.51±0.11), suggesting a more-uniform involvement of dopamine nerve terminals in both caudate nucleus and putamen. Our results confirm that DAT binding can provide an accurate and highly sensitive measure of dopamine degeneration. PSP patients may show a different pattern of neuronal loss compared with MSA and PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonini, A., Benti, R., De Notaris, R. et al. 123I-Ioflupane/SPECT binding to striatal dopamine transporter (DAT) uptake in patients with Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurol Sci 24, 149–150 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-003-0103-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-003-0103-5