Abstract
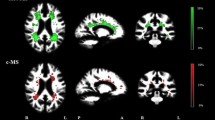
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory and degenerative disease of the central nervous system. In the last decade, pathological and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies have shown that a significant portion of inflammatory lesions are located in the grey matter, especially in the cerebral cortex, of MS patients. Cortical inflammatory lesions (CL) can be demonstrated in vivo in MS patients by double inversion recovery (DIR) MRI sequence. Neuropsychological deficits constitute a major clinical aspect of MS, being demonstrated in a percentage ranging from 40 to 65% of patients, and have been shown to be associated with cortical demyelination and atrophy. Recent DIR studies in MS patients having different clinical forms of the disease have disclosed that CL burden not only correlates with the severity of physical disability, but is also one of the major structural changes associated with disease-related cognitive impairment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato MP, Zipoli V, Portaccio E (2006) Multiple sclerosis-related cognitive changes: a review of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. J Neurol Sci 245(1–2):41–46
Chiaravalloti ND, DeLuca J (2008) Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 7(12):1139–1151
Rovaris M, Comi G, Filippi M (2006) MRI markers of destructive pathology in multiple sclerosis-related cognitive dysfunction. J Neurol Sci 245(1–2):111–116
Zivadinov R, Sepcic J, Nasuelli D et al (2001) A longitudinal study of brain atrophy and cognitive disturbances in the early phase of relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70(6):773–780
Sanfilipo MP, Benedict RH, Weinstock-Guttman B, Bakshi R (2006) Gray and white matter brain atrophy and neuropsychological impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 66(5):685–692
Sanchez MP, Nieto A, Barroso J, Martin V, Hernandez MA (2008) Brain atrophy as a marker of cognitive impairment in mildly disabling relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 15(10):1091–1099
Amato MP, Bartolozzi ML, Zipoli V et al (2004) Neocortical volume decrease in relapsing remitting MS patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 63(1):89–93
Morgen K, Sammer G, Courtney SM et al (2006) Evidence for a direct association between cortical atrophy and cognitive impairment in relapsing–remitting MS. Neuroimage 30(3):891–898
Peterson JW, Bö L, Mörk S et al (2001) Transected neurites, apoptotic neurons, and reduced inflammation in cortical multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol 50:389–400
Bø L, Vedeler CA, Nyland H et al (2003) Subpial demyelination in the cerebral cortex of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:723–732
Kidd D, Barkhof F, McConnell R et al (1999) Cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Brain 122:17–26
Calabrese M, De Stefano N, Atzori M et al (2007) Detection of cortical inflammatory lesions by double inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging in patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 64(10):1416–1422
Calabrese M, Filippi M, Rovaris M et al (2008) Morphology and evolution of cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal MRI study. Neuroimage 42(4):1324–1328
Geurts JJ, Pouwels PJ, Uitdehaag BM et al (2005) Intracortical lesions in multiple sclerosis: improved detection with 3D double inversion-recovery MR imaging. Radiology 236:254–260
Calabrese M, De Stefano N, Atzori M et al (2008) Extensive cortical inflammation is associated with epilepsy in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 255:581–586
Calabrese M, Filippi M, Rovaris M et al (2009) Evidence for relative cortical sparing in benign multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study. Mult Scler 15:36–41
Calabrese M, Gallo P (2009) Magnetic resonance evidence of cortical onset of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 15:933–941
Calabrese M, Rocca MA, Atzori M et al (2009) Cortical lesions in primary progressive multiple sclerosis: a 2-year longitudinal MR study. Neurology 72:1330–1336
Calabrese M, Rocca MA, Atzori M et al (2010) A three-year MRI study of cortical lesions in relapse-onset multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol (in press)
Roosendaal SD, Moraal B, Pouwels PJ et al (2009) Accumulation of cortical lesions in MS: relation with cognitive impairment. Mult Scler 15(6):708–714
Calabrese M, Agosta F, Rinaldi F et al (2009) Cortical lesions and atrophy associated with cognitive impairment in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 66:1144–1150
Geurts JJ, Barkhof F (2008) Grey matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 7(9):841–851
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Rinaldi and M. Calabrese have equally contributed to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rinaldi, F., Calabrese, M., Grossi, P. et al. Cortical lesions and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurol Sci 31 (Suppl 2), 235–237 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0368-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0368-4