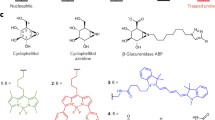
Abstract
β-Hexosaminidases (EC 3.2.1.52) are lysosomal enzymes that remove terminal β-glycosidically bound N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylgalactosamine residues from a number of glycoconjugates. Reliable assay systems are particularly important for the diagnosis of a family of lysosomal storage disorders, the GM2 gangliosidoses that result from inherited β-hexosaminidase deficiency. More recently, aberrant hexosaminidase levels have also been found to be associated with a variety of inflammatory diseases. Apart from patient testing and carrier screening, practical in vitro assays are indispensable for the characterization of knock-out mice with potentially altered hexosaminidase activities, for detailed structure-function studies aimed at elucidating the enzymatic mechanism, and to characterize newly described enzyme variants from other organisms. The purpose of this article is to discuss convenient hexosaminidase assay procedures for these and other applications, using fluorogenic or chromogenic artificial substrates as well as the physiological glycolipid substrate GM2. Attempts are also made to provide an overview of less commonly used alternative techniques and to introduce recent developments enabling high-throughput screening for enzyme inhibitors.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For comprehensive advice in performing the assay for diagnosis work and for calibration and testing of procedures employed in individual laboratories, we would like to refer the reader to The International Laboratory Quality Control Carrier Testing Tay-Sachs Program of the National Tay-Sachs & Allied Disease Association (NTSAD), www.ntsad.org.
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- GM2:
-
ganglioside GM2
- GM2AP:
-
GM2-activator protein
- GSLs:
-
glycosphingolipids
- HexA:
-
β-hexosaminidase A
- HexB:
-
β-hexosaminidase B
- HexS:
-
β-hexosaminidase S
- HAS:
-
human serum albumin
- LUVs:
-
large unilamellar vesicles
- MUG:
-
4-methylumbelliferyl-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranoside
- MUGS:
-
4-methylumbelliferyl-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-6-sulfo-β-D-glucopyranoside
- TLC:
-
thin-layer chromatography
- TSD:
-
Tay-Sachs disease
References
Gravel, R.A., Kaback, M., Proia, R.L., Sandhoff, K., Suzuki, K., Suzuki, K.: The GM2 Gangliosidoses. In: Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W., Valle, D. (eds.) The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, pp. 3827–3876. Mc Graw-Hill, New York (2001)
Watanabe, K.: Biochemical studies on carbohydrates: XXII. On animal β-N-Monoacetylglucosaminidase. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 24, 297–303 (1936)
Sandhoff, K., Wassle, W.: Enrichment and characterization of 2 forms of human N-acetyl-beta-d-hexosaminidase. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 352, 1119–1133 (1971)
Kolter, T., Sandhoff, K.: Sphingolipids—their metabolic pathways and the pathobiochemistry of neurodegenerative diseases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 38, 1532–1568 (1999)
Kolter, T., Sandhoff, K.: Sphingolipid metabolism diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1758, 2057–2079 (2006)
Proia, R.L.: Gene encoding the human beta-hexosaminidase beta chain: extensive homology of intron placement in the alpha-and beta chain genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 1883–1887 (1988)
Kytzia, H.J., Sandhoff, K.: Evidence for two different active sites on human beta-hexosaminidase A. Interaction of GM2 activator protein with beta-hexosaminidase A. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 7568–7572 (1985)
Maier, T., Strater, N., Schuette, C.G., Klingenstein, R., Sandoff, K., Saenger, W.: The X-ray crystal structure of human beta-hexosaminidase B provides new insights into Sandhoff disease. J. Mol. Biol. 328, 669–681 (2003)
Mark, B.L., Mahuran, D.J., Cherney, M.M., Zhao, D., Knapp, S., James, M.N.: Crystal structure of human beta-hexosaminidase B: understanding the molecular basis of Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs disease. J. Mol. Biol. 327, 1093–1109 (2003)
Lemieux, M.J., Mark, B.L., Cherney, M.M., Withers, S.G., Mahuran, D.J., James, M.N.: Crystallographic structure of human beta-hexosaminidase A: interpretation of Tay-Sachs mutations and loss of GM2 ganglioside hydrolysis. J. Mol. Biol. 359, 913–929 (2006)
Conzelmann, E., Sandhoff, K.: Purification and characterization of an activator protein for the degradation of glycolipids GM2 and GA2 by hexosaminidase A. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 360, 1837–1849 (1979)
Furst, W., Sandhoff, K.: Activator proteins and topology of lysosomal sphingolipid catabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1126, 1–16 (1992)
Li, Y.T., Li, S.C., Hasegawa, A., Ishida, H., Kiso, M., Bernardi, A., Brocca, P., Raimondi, L., Sonnino, S.: Structural basis for the resistance of Tay-Sachs ganglioside GM2 to enzymatic degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 10014–10018 (1999)
Yadao, F., Hechtman, P., Kaplan, F.: Formation of a ternary complex between GM2 activator protein, GM2 ganglioside and hexosaminidase A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1340, 45–52 (1997)
Xie, B., Rigat, B., Smiljanic-Georgijev, N., Deng, H., Mahuran, D.: Biochemical characterization of the Cys138Arg substitution associated with the AB variant form of GM2 gangliosidosis: evidence that Cys138 is required for the recognition of the GM2 activator/GM2 ganglioside complex by beta-hexosaminidase A. Biochemistry 37, 814–821 (1998)
Sandhoff, K.: The hydrolysis of Tay-Sachs ganglioside (TSG) by human N-acetyl-beta-d-hexosaminidase A. FEBS Lett. 11, 342–344 (1970)
Sandhoff, K.: Variation of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase-pattern in Tay-Sachs disease. FEBS Lett. 4, 351–354 (1969)
Okada, S., O’Brien, J.S.: Tay-Sachs disease: generalized absence of a beta-d-N-acetylhexosaminidase component. Science 165, 698–700 (1969)
Kytzia, H.J., Hinrichs, U., Maire, I., Suzuki, K., Sandhoff, K.: Variant of GM2-gangliosidosis with hexosaminidase A having a severely changed substrate specificity. EMBO J. 2, 1201–1205 (1983)
Conzelmann, E., Sandhoff, K.: AB variant of infantile GM2 gangliosidosis: deficiency of a factor necessary for stimulation of hexosaminidase A-catalyzed degradation of ganglioside GM2 and glycolipid GA2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 3979–3983 (1978)
Kolter, T., Sandhoff, K.: Principles of lysosomal membrane digestion: stimulation of sphingolipid degradation by sphingolipid activator proteins and anionic lysosomal lipids. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 21, 81–103 (2005)
Conzelmann, E., Kytzia, H.J., Navon, R., Sandhoff, K.: Ganglioside GM2 N-acetyl-beta-d-galactosaminidase activity in cultured fibroblasts of late-infantile and adult GM2 gangliosidosis patients and of healthy probands with low hexosaminidase level. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 35, 900–913 (1983)
Leinekugel, P., Michel, S., Conzelmann, E., Sandhoff, K.: Quantitative correlation between the residual activity of beta-hexosaminidase A and arylsulfatase A and the severity of the resulting lysosomal storage disease. Hum. Genet. 88, 513–523 (1992)
Klein, A., Henseler, M., Klein, C., Suzuki, K., Harzer, K., Sandhoff, K.: Sphingolipid activator protein D (sap-D) stimulates the lysosomal degradation of ceramide in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 200, 1440–1448 (1994)
Yamashita, T., Hashiramoto, A., Haluzik, M., Mizukami, H., Beck, S., Norton, A., Kono, M., Tsuji, S., Daniotti, J.L., Werth, N., Sandhoff, R., Sandhoff, K., Proia, R.L.: Enhanced insulin sensitivity in mice lacking ganglioside GM3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 3445–3449 (2003)
Sango, K., McDonald, M.P., Crawley, J.N., Mack, M.L., Tifft, C.J., Skop, E., Starr, C.M., Hoffmann, A., Sandhoff, K., Suzuki, K., Proia, R.L.: Mice lacking both subunits of lysosomal beta-hexosaminidase display gangliosidosis and mucopolysaccharidosis. Nat. Genet. 14, 348–352 (1996)
Liu, Y., Wada, R., Kawai, H., Sango, K., Deng, C., Tai, T., McDonald, M.P., Araujo, K., Crawley, J.N., Bierfreund, U., Sandhoff, K., Suzuki, K., Proia, R.L.: A genetic model of substrate deprivation therapy for a glycosphingolipid storage disorder. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 497–505 (1999)
Tsui, Z.C., Chen, Q.R., Thomas, M.J., Samuel, M., Cui, Z.: A method for profiling gangliosides in animal tissues using electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 341, 251–258 (2005)
Tsuji, D., Kuroki, A., Ishibashi, Y., Itakura, T., Kuwahara, J., Yamanaka, S., Itoh, K.: Specific induction of macrophage inflammatory protein 1-alpha in glial cells of Sandhoff disease model mice associated with accumulation of N-acetylhexosaminyl glycoconjugates. J. Neurochem. 92, 1497–1507 (2005)
Tsuji, D., Higashine, Y., Matsuoka, K., Sakuraba, H., Itoh, K.: Therapeutic evaluation of GM2 gangliosidoses by ELISA using anti-GM2 ganglioside antibodies. Clin. Chim. Acta 378, 38–41 (2007)
Leaback, D.H., Walker, P.G.: Studies on glucosaminidase. 4. The fluorimetric assay of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase. Biochem. J. 78, 151–156 (1961)
Potier, M., Mameli, L., Belisle, M., Dallaire, L., Melancon, S.B.: Fluorometric assay of neuraminidase with a sodium (4-methylumbelliferyl-alpha-d-N-acetylneuraminate) substrate. Anal. Biochem. 94, 287–296 (1979)
Kresse, H., Fuchs, W., Glossl, J., Holtfrerich, D., Gilberg, W.: Liberation of N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate by human beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase A. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 12926–12932 (1981)
Sandhoff, K., Conzelmann, E., Nehrkorn, H.: Specificity of human liver hexosaminidases A and B against glycosphingolipids GM2 and GA2. Purification of the enzymes by affinity chromatography employing specific elution. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 358, 779–787 (1977)
Srivastava, S.K., Awasthi, Y.C., Yoshida, A., Beutler, E.: Studies on human beta-d-N-acetylhexosaminidases. I. Purification and properties. J. Biol. Chem. 249, 2043–2048 (1974)
Suzuki, K.: Enzymatic diagnosis of sphingolipidoses. Methods Enzymol. 138, 727–762 (1987)
Hepbildikler, S.T., Sandhoff, R., Kolzer, M., Proia, R.L., Sandhoff, K.: Physiological substrates for human lysosomal beta-hexosaminidase S. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 2562–2572 (2002)
Hechtman, P., Kaplan, F.: Tay-Sachs disease screening and diagnosis: evolving technologies. DNA Cell. Biol. 12, 651–665 (1993)
Kaback, M.M.: Thermal fractionation of serum hexosaminidases: applications to heterozygote detection and diagnosis of Tay-Sach’s disease. Methods Enzymol. XXXVIII, 862–867 (1972)
O’Brien, J.S., Okada, S., Chen, A., Fillerup, D.L.: Tay-Sachs disease. Detection of heterozygotes and homozygotes by serum hexosaminidase assay. N. Engl. J. Med. 283, 15–20 (1970)
Natowicz, M.R., Prence, E.M.: Heterozygote screening for Tay-Sachs disease: past successes and future challenges. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 8, 625–629 (1996)
Isaksson, A., Hultberg, B., Masson, P., Landels, E., Fensom, A.: Enzyme immunoassay of beta-hexosaminidase A and B in serum: carrier detection of GM2-gangliosidoses, and equivalence of enzyme activity and enzyme protein reactivity. Clin. Chem. 39, 1412–1415 (1993)
Okada, S., Veath, M.L., Leroy, J., O’Brien, J.S.: Ganglioside GM2 storage diseases: hexosaminidase deficiencies in cultured fibroblasts. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 23, 55–61 (1971)
Grabowski, G.A., Kruse, J.R., Goldberg, J.D., Chokkalingham, K., Gordon, R.E., Blakemore, K.J., Mahoney, M., Desnick, R.J.: First-trimester prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Am. J. Hum.Genet. 36, 1369–1378 (1984)
Callahan, J.W., Archibald, A., Skomorowski, M.A., Shuman, C., Clarke, J.T.R.: First trimester prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease using the sulfated synthetic substrate for hexosaminidase A. Clin. Biochem. 23, 533–536 (1990)
Chamoles, N.A., Blanco, M., Gaggioli, D., Casentini, C.: Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff diseases: enzymatic diagnosis in dried blood spots on filter paper: retrospective diagnoses in newborn-screening cards. Clin. Chim. Acta 318, 133–137 (2002)
Lukacs, Z., Keil, A., Peters, V., Kohlschutter, A., Hoffman, G.F., Cantz, M., Kopitz, J.: Towards quality assurance in the determination of lysosomal enzymes: a two-centre study. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 26, 571–581 (2003)
Civallero, G., Michelin, K., de Mari, J., Viapiana, M., Burin, M., Coelho, J.C., Giugliani, R.: Twelve different enzyme assays on dried-blood filter paper samples for detection of patients with selected inherited lysosomal storage diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 372, 98–102 (2006)
Sutton, V.R.: Tay-Sachs disease. Screening and counseling families at risk for metabolic disease. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. North Am. 29, 287–296 (2002)
Ben-Yoseph, Y., Reid, J.E., Shapiro, B., Nadler, H.L.: Diagnosis and carrier detection of Tay-Sachs disease: direct determination of hexosaminidase A using 4-Methylumbelliferyl derivatives of b-N-Acetylglucosamine-6-Sulfate and b-N-Acetylgalactosamine-6-Sulfate. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 37, 733–748 (1985)
Vallance, H., Morris, T.J., Coulter-Mackie, M., Lim-Steele, J., Kaback, M.: Common HEXB polymorphisms reduce serum HexA and HexB enzymatic activities, potentially masking Tay-Sachs disease carrier identification. Molec Genet Metab. 87, 122–127 (2006)
Walker, P.G., Woollen, J.W., Heyworth, R.: Studies on glucosaminidase. 5. Kidney N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase and N-acetyl-b-galactosaminidase. Biochem. J. 79, 288–294 (1961)
Chatterjee, S., Velicer, L.F., Sweeley, C.C.: Glycosphingolipid glycosyl hydrolases and glycosidases of synchronized human KB cells. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 4972–4979 (1975)
Marciniak, J., Zalewska, A., Popko, J., Zwierz, K.: Optimization of an enzymatic method for the determination of lysosomal N-acetyl-beta-d-hexosaminidase and beta-glucuronidase in synovial fluid. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 44, 933–937 (2006)
Zwierz, K., Gindzienski, A., Glowacka, D., Porowski, T.: The degradation of glycoconjugates in the human gastric mucous membrane. Acta Med Acad Sci Hung. 38, 145–152 (1981)
Casal, J.A., Cano, E., Tutor, J.C.: Beta-hexosaminidase isoenzyme profiles in serum, plasma, platelets and mononuclear, polymorphonuclear and unfractionated total leukocytes. Clin. Biochem. 38, 938–942 (2005)
Casal, J.A., Vizcaino, L., Garcia-Devesa, J., Tutor, J.C.: Thermodynamic study of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase enzyme heterogeneity in human seminal plasma. Clin. Chim. Acta 355, 55–60 (2005)
Perez, L.F., Tutor, J.C.: Assay of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase isoenzymes in different biological specimens by means of determination of their activation energies. Clin. Chem. 44, 226–231 (1998)
Perez, L.F., Ribeiro, H.M., Casal, J.A., Pinto, R.A., Sa Miranda, M.C., Tutor, J.C.: Thermodynamic characterisation of the mutated isoenzyme A of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase in GM2-gangliosidosis B1 variant. Clin. Chim. Acta 285, 45–51 (1999)
Tropak, M.B., Reid, S.P., Guiral, M., Withers, S.G., Mahuran, D.: Pharmacological enhancement of beta-hexosaminidase activity in fibroblasts from adult Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff Patients. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 13478–13487 (2004)
Tropak, M.B., Blanchard, J.E., Withers, S.G., Brown, E.D., Mahuran, D.: High-throughput screening for human lysosomal beta-N-Acetyl hexosaminidase inhibitors acting as pharmacological chaperones. Chem. Biol. 14, 153–164 (2007)
Tropak, M.B., Mahuran, D.: Lending a helping hand, screening chemical libraries for compounds that enhance beta-hexosaminidase A activity in GM2 gangliosidosis cells. FEBS J. 274, 4951–4961 (2007)
Shulman, M.L., Kulshin, V.A., Khorlin, A.Y.: A continuous fluorimetric assay for glycosidase activity: human N-acetyl-beta-d-hexosaminidase. Anal. Biochem. 101, 342–348 (1980)
Erzberger, A., Conzelmann, E., Sandhoff, K.: Assay of ganglioside GM2-N-acetyl-beta-d-galactosaminidase activity in human fibroblasts employing the natural activator protein-diagnosis of variant forms of GM2 gangliosidosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 108, 361–368 (1980)
O’Brien, J.S., Norden, G.W., Miller, A.L., Frost, R.G., Kelly, T.E.: Ganglioside GM2 N-acetyl-beta-d-galactosaminidase and asialo GM2 (GA2) N-acetyl-beta-d-galactosaminidase; studies in human skin fibroblasts. Clin. Genet. 11, 171–183 (1977)
Svennerholm, L., Hakansson, G., Mansson, J.E., Vanier, M.T.: The assay of sphingolipid hydrolases in white blood cells with labelled natural substrates. Clin. Chim. Acta 92, 53–64 (1979)
Klima, H., Klein, A., van Echten, G., Schwarzmann, G., Suzuki, K., Sandhoff, K.: Over-expression of a functionally active human GM2-activator protein in Escherichia coli. Biochem. J. 292, 571–576 (1993)
Wu, Y.Y., Lockyer, J.M., Sugiyama, E., Pavlova, N.V., Li, Y.T., Li, S.C.: Expression and specificity of human GM2 activator protein. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 16276–16283 (1994)
Wendeler, M., Lemm, T., Weisgerber, J., Hoernschemeyer, J., Bartelsen, O., Schepers, U., Sandhoff, K.: Expression of recombinant human GM2-activator protein in insect cells: purification and characterization by mass spectrometry. Protein Expr. Purif. 27, 259–266 (2003)
Wendeler, M., Hoernschemeyer, J., John, M., Werth, N., Schoeniger, M., Lemm, T., Hartmann, R., Kessler, H., Sandhoff, K.: Expression of the GM2-activator protein in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris, purification, isotopic labeling, and biophysical characterization. Protein Expr. Purif. 34, 147–157 (2004)
Werth, N., Schuette, C.G., Wilkening, G., Lemm, T., Sandhoff, K.: Degradation of membrane-bound ganglioside GM2 by beta-hexosaminidase A. Stimulation by GM2 activator protein and lysosomal lipids. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 12685–12690 (2001)
Novak, A., Lowden, J.A., Gravel, Y.L., Wolfe, L.S.: Preparation of radiolabeled GM2 and GA2 gangliosides. J. Lipid Res. 20, 678–681 (1979)
Suzuki, Y., Suzuki, K.: Specific radioactive labeling of terminal N-acetylgalactosamine of glycosphingolipids by the galactose oxidase-sodium borohydride method. J. Lipid Res. 13, 687–690 (1972)
Sonnino, S., Nicolini, M., Chigorno, V.: Preparation of radiolabeled gangliosides. Glycobiology 6, 479–487 (1996)
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Thomas Kolter and Hichem Gallala, Bonn, for carefully reading the manuscript and to Thomas Kolter for kindly providing Fig. 1. We thank the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft for financial support (SFB 645).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wendeler, M., Sandhoff, K. Hexosaminidase assays. Glycoconj J 26, 945–952 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-008-9137-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-008-9137-5