Abstract
Background
The Guglielmi Detachable Coil introduced by the Boston Scientific Corporation has been widely used for endovascular coiling of aneurysm. Recently, Sapphire® platinum detachable coils (eV3, Irvine, CA) have been introduced for aneurysm coiling. Herein, we report our clinical experience with the Sapphire® coil to evaluate the incidence of coil related complications and the rate of aneurysm occlusion.
Methods
Consecutive patients who underwent embolization with Sapphire® detachable coils were prospectively enrolled from January 2004 to September 2004 and the data were retrospectively analyzed. Patient demographics, including age, gender, presenting symptoms, Hunt and Hess grade, Fisher grade and locations of the vascular anomalies were collected. Additionally, complications associated with the coils and rates of aneurysm occlusion were observed and the data compiled.
Results
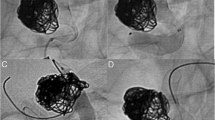
29 patients underwent Sapphire® coil embolization for intracranial aneurysms. Mean age was 50 ± 18 (mean ± SD) years with 81% being females. Aneurysm neck reconstruction was required in 7 cases, 6 with Neuroform stent (5 unruptured aneurysms) and 1 with balloon assistance (ruptured aneurysm). In 7 cases, Sapphire® coils were used along with other coils. There were no events of thromboembolism or ruptures of aneurysms during coil embolization. However, multi-diameter coils demonstrated stretching in 4 stent-assisted cases without any adverse consequences. Complete occlusion of the aneurysm was achieved in 79.31% of the patients, neck remnant in 6.89, and partial coiling was achieved in 13.79%.
Conclusion
The Sapphire® coil could safely be used in the treatment of both ruptured and unruptured aneurysms. However, multi-diameter non-stretch resistant coils may be associated with coil stretching when used in conjunction with a stent. Further study is still required for definitive results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brilstra EH, Rinkel GJE, Van Der Graaf Y, van Rooij WJJ, Algra A. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by embolization with coils: systemic review. Stroke 1999;30:470–76.
Kremer C, Groden C, Hansen HC, Gzyska U, Zeumer H. Outcome after endovascular treatment of Hunt and Hess Grade IV or V aneurysms: Comparison of anterior versus posterior circulation. Stroke 1999;30:2617–22.
Lempert TE, Malek AM, Halbach VV, Phatouros CC, Meyers PM, Dowd CF, Higashida RT. Endovascular treatment of ruptured posterior circulation cerebral aneurysms: clinical and angiographic outcomes. Stroke 2000;31:100–10.
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, Holman R. International Subarachnoid Aneurysms Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group: International Subarachnoid Aneurysms Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: A randomized trial. Lancet 2002;360:1267–74.
Sturaitis MK, Rinne J, Chaloupka JC, Kaynar M, Lin Z, Awad IA. Impact of Guglielmi Detachable Coils on outcomes of patients with intracranial aneurysms treated by a multidisciplinary team at a single institution. J Neurosurg 2000;93: 569–80.
Lubicz B, Leclerc X, Gauvrit J-Y, Lejeune J-P, Pruvo J-P. Selective endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with Sapphire® coils. AJANR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:1368–72.
Casasco AE, Aymard A, Gobin YP, Houdart E, Rogopoulos A, George B, Hodes JE, Cophignon J, Merland JJ. Selective endovascular treatment of 71 intracranial aneurysms with platinum coils. J Neurosurge 1993;79:3–10.
David N, Richard A, Caroline C, Mary S, Andrew JM. Anatomically comformable three-dimensional, detachable platinum Microcoil system for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:813–8.
Eskridge JM, Song Jk. Endovascular embolization of 150 basilar tip aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils: results of the Food and Drug Administration multicenter clinical trial. J Neurosurg 1998;89:81–6.
Johnston SC, Wilson CB, Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Dowd CF, McDermott MW, Applebury CB, Farley TL, Gress DR. Endovascular and Surgical treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms: Comparison of risks. Ann Neurolo 2000;48:11–9.
Raftopoulos C, Mathurin P, Boscherini D, Billa RF, Van Boven M, Hantson P. Prospective analysis of aneurysm treatment in a series of 103 consecutive patients when endovascular embolization is considered the first option. J Neurosurgery 2000;93: 175–82.
Kuether TA, Nesbit GM, Barnwell SL. Clinical and angiographic outcomes, with the treatment data, for patients with cerebral aneurysms treatment with Guglielmi Detachable Coils: A single-center experience. Neurosurgery 1998;43(5):1016–25.
Bonafe A, Picot MC, Jean B, Bourbotte G, Seris C, Margarot M, Khoury K, Coubes P, Segnarbieux F. Acutely ruptured intracranial aneurysms treated with GDC. Neurochirurgie 2005;51(3–4 Pt 1): 155–64.
Graves VB, Stother CM, Duff TA, Perl J II. Early treatment of ruptured aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils: effect on subsequent bleeding. Neurosurgery 1995;37:640–8.
Gruber DP, Zimmerman GA, Tomsick TA, van Loveren HR, Link MJ, Tew JM Jr. A comparison between endovascular and surgical management of basilar artery apex aneurysms. J Neurosurg 1999;90:868–74.
Johnston HC, Higashida RT, Barrow DL, Caplan LR, Dion JE, Hademenos G, Hopkins LN, Molyneux A, Rosenwasser RH, Vinuela F, Wilson CB. Committee on Cerebrovascular Imaging of the American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Radiology: recommendation for the endovascular treatment of the intracranial aneurysms: a statement for healthcare professionals from the committee on Cerebrovascular Imaging of the America Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Radiology. Stroke 2002;33:2536–44.
Johnston SC, Zhao S, Dudley RA, Berman MF, Gress DR. Treatment of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in California. Stroke 2001;32:597–605.
Koivisto T, Vanninen R, Hurskainen H, Saari T, Hernesniemi J, Vapalathi M. Outcome of early endovascular versus surgical treatment of o ruptured cerebral aneurysms: a prospective randomized study. Stroke 2000;31:2369–77.
Vannien R, Koivisto T, Saari T, Hermesniemi J, Vapalahti M. Ruptured intracranial aneurysms: Acute endovascular treatment with electrolytically detachable coils—a prospectively randomized study. Radiology 1999;211:325–336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yahia, A.M., Gordon, V., Whapham, J. et al. Sapphire® platinum detachable coil experience in a tertiary-care facility. Neurocrit Care 7, 128–135 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-007-0031-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-007-0031-y