Abstract
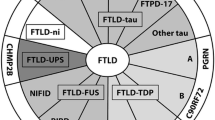
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is increasingly recognized to be a syndromic disorder in which the degeneration of motor neurons is frequently accompanied by a range of syndromes reflective of frontotemporal dysfunction, including a behavioural or cognitive syndrome, a dysexecutive syndrome or a frontotemporal dementia. Both sporadic and familial variants of ALS can be affected. The anatomic substrate of each is a frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) characterized by superficial linear spongiosus, atrophy and neuronal loss, and both astrocytic and neuronal deposition of TDP-43 as pathological inclusions. Largely unrecognized however is the extent of alterations in tau protein metabolism, particularly in cognitively impaired patients (ALSci). This includes hyper-phosphorylation (pThr175) and tau phosphatase resistance, increased fibril formation ex vivo of tau isolated from ALSci and tau immunoreactive aggregates in neurons, dystrophic neurites and astrocytes. In this article, we will review the contemporary clinical, genetic and neuropathological characteristics of the frontotemporal syndromes of ALS and propose that as opposed to being a FTLD in which TDP-43 is the primary disease protein (FTLD-TDP) and that the frontotemporal syndromes of ALS represent a hybrid of both TDP-43 and tau pathology.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Chalabi A, Enayat ZE, Bakker MC et al (1996) Association of apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele with bulbar-onset motor neuron disease. Lancet 347:159–160
Amador-Ortiz C, Lin W-L, Ahmed Z et al (2007) TDP-43 immunoreactivity in hippocampal sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 61:435–445
Andersen PM, Nilsson P, Keränen M-L et al (1997) Phenotypic heterogeneity in motor neuron disease patients with CuZn-superoxide dismutase mutations in Scandinavia. Brain 120:1723–1737
Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H et al (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:602–611
Bachus R, Bader S, Gessner R, Ludolph AC (1997) Lack of association of apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele with bulbar-onset motor neuron disease. Ann Neurol 41:417
Battistini S, Giannini F, Greco G et al (2005) SOD1 mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Results from a multicenter Italian study. J Neurol 252:782–788
Blair IP, Williams KL, Warraich ST et al (2010) FUS mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: clinical, pathological, neurophysiological and genetic analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:639–645
Boxer AL, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF et al (2011) Clinical, neuroimaging and neuropathological features of a new chromosome 9p-linked FTD-ALS family. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:196–203
Broustal O, Camuzat A, Guillot-Noel L et al (2010) FUS mutations in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Alzheimers Dis 22:765–769
Colombrita C, Onesto E, Tiloca C, Ticozzi N, Silani V, Ratti A (2011) RNA-binding proteins and RNA metabolism: a new scenario in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Ital Biol 149:83–99
Donaghy C, Thurtell MJ, Pioro EP, Gibson JM, Leigh RJ (2011) Eye movements in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and its mimics: a review with illustrative cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:110–116
Drory VE, Birnbaum M, Korczyn AD, Chapman J (2001) Association of APOE ε4 allele with survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 190:17–20
Forno LS, Langston JW, Herrick MK, Wilson JD, Murayama S (2002) Ubiquitin-positive neuronal and tau 2-positive glial inclusions in frontotemporal dementia of motor neuron type. Acta Neuropathol 103:599–606
Gellera C, Colobrita C, Ticozzi N et al (2008) Identification of new ANG gene mutations in a large cohort of Italian patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurogenetics 9:33–40
Geser F, Brandmeir NJ, Kwong LK et al (2008) Evidence of multisystem disorder in whole-brain map of pathological TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 65:636–641
Gibbons ZC, Snowden JS, Thompson JC, Happe F, Richardson A, Neary D (2007) Inferring thought and action in motor neurone disease. Neuropsychologia 45:1196–1207
Giordana MT, Ferrero P, Grifoni S, Pellerino A, Naldi A, Montuschi A (2011) Dementia and cognitive impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a review. Neurol Sci 32:9–16
Girardi A, Macpherson SE, Abrahams S (2011) Deficits in emotional and social cognition in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropsychology 25:53–65
Gitcho MA, Bigio EH, Mishra M et al (2009) TARDBP 3′-UTR variant in autopsy-confirmed frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 proteinopathy. Acta Neuropathol 118:633–645
Gohar M, Yang W, Strong WL, Volkening K, Leystra-Lantz C, Strong MJ (2009) Tau phosphorylation at 175Thr leads to fibril formation. Implications for the tauopathy of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 108:634–643
Grace GM, Orange JB, Rowe A, Findlater K, Freedman M, Strong MJ (2011) Neuropsychological functioning in PLS: a comparison with ALS. Can J Neurol Sci 38:88–97
Hamilton RL, Bowser R (2004) Alzheimer disease pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 107:515–522
Hirano A, Malamud N, Elizan TS, Kurland LT (1966) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinsonism–dementia complex on Guam. Further pathologic studies. Arch Neurol 15:35–51
Hirano A, Arumugasamy N, Zimmerman HM (1967) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A comparison of Guam and classical cases. Arch Neurol 16:357–363
Hirano A, Dembitzer HM, Kurland LT, Zimmerman HM (1968) The fine structure of some intraganglionic alterations: neurofibrillary tangles, granulovacuolar bodies, and “rod-like” structures in Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism–dementia complex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 27:167–182
Hulette CM, Pericak-Vance MA, Roses AD et al (1999) Neuropathological features of frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17q21-22 (FTDP-17): Duke family 1684. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:859–866
Ito H, Nakamura M, Komure O et al (2011) Clinicopathologic study on an ALS family with a heterozygous E478G optineurin mutation. Acta Neuropathol 122:223–229
Johansson A, Engler H, Blomquist G et al (2007) Evidence for astrocytosis in ALS demonstrated by [11C](l)-deprenyl-D2 PET. J Neurol Sci 255:17–22
Kwiatkowski TJ Jr, Bosco DA, Leclerc AL et al (2009) Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 323:1205–1208
Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW (2010) TDP-43 and FUS/TLS: emerging roles in RNA processing and neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet 19:R46–R64
Lillo P, Garcin B, Hornberger M, Bak TH, Hodges JR (2010) Neurobehavioral features in frontotemporal dementia with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 67:826–830
Lomen-Hoerth C, Strong MJ (2006) Cognition in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In: Mitsumoto H, Przedborksi S, Gordon P, De Bene M (eds) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Marcel Dekker, London, pp 115–138
Lomen-Hoerth C, Anderson T, Miller B (2002) The overlap of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 59:1077–1079
Lomen-Hoerth C, Murphy J, Langmore S, Kramer JH, Olney RK, Miller B (2003) Are amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients cognitively normal? Neurology 60:1094–1097
Lynch T, Sano M, Marder KS et al (1994) Clinical characteristics of a family with chromosome 17-linked disinhibition-dementia-parkinsonism-amyotrophy complex. Neurology 44:1878–1884
Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Bigio EH et al (2010a) Nomenclature and nosology for neuropathologic subtypes of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: an update. Acta Neuropathol 119:1–4
Mackenzie IR, Rademakers R, Neumann M (2010b) TDP-43 and FUS in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Lancet Neurol 9:995–1007
Malamud N, Hirano A, Kurland LT (1961) Pathoanatomic changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis on Guam. Arch Neurol 5:401–415
Martinaud O, Laquerrière A, Guyant-Maréchal L et al (2005) Frontotemporal dementia, motor neuron disease and tauopathy: clinical and neuropathological study in a family. Acta Neuropathol 110:84–92
Masè G, Ros S, Gemma A et al (2001) ALS with variable phenotypes in a six-generation family caused by leu144phe mutation in the SOD1 gene. J Neurol Sci 191:11–18
Massman PJ, Sims J, Cooke N, Haverkamp LJ, Appel V, Appel SH (1996) Prevalence and correlates of neuropsychological deficits in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 61:450–455
Millecamps S, Salachas F, Cazeneuve C et al (2010) SOD1, ANG, VAPB, TARDBP, and FUS mutations in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: genotype-phenotype correlations. J Med Genet 47:554–560
Moisse K, Volkening K, Leystra-Lantz C, Welch I, Hill T, Strong MJ (2009) Divergent patterns of cytosolic TDP-43 and neuronal progranulin expression following axotomy. Brain Res 1249:202–211
Morita M, Al-Chalabi A, Andersen PM et al (2006) A locus on chromosome 9p confers susceptibility to ALS and frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 66:839–844
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK et al (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Papps B, Abrahams S, Wicks P, Leigh PN, Goldstein LH (2005) Changes in memory for emotional material in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Neuropsychologia 43:1107–1114
Raaphorst J, de Visser M, Linssen WH, de Haan RJ, Schmand B (2010) The cognitive profile of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a meta-analysis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 11:27–37
Ringholz GM, Appel SH, Bradshaw M, Cooke NA, Mosnik DM, Schulz PE (2005) Prevalence and patterns of cognitive impairment in sporadic ALS. Neurology 65:586–590
Smith RG, Haverkamp LJ, Case S, Appel V, Appel SH (1996) Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 in bulbar-onset motor neuron disease. Lancet 348:334–335
Strong MJ (2001) The evidence for ALS as a multisystems disorder of limited phenotypic expression. Can J Neurol Sci 28:283–298
Strong MJ (2003) The basic aspects of therapeutics in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Pharmacol Ther 98:379–414
Strong MJ (2004) Recent developments in the biochemistry and pharmacotherapy of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 13:1593–1614
Strong MJ (2008) The syndromes of frontotemporal dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 9:323–338
Strong MJ (2010) The evidence for altered RNA metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J Neurol Sci 288:1–12
Strong MJ, Gordon PH (2005) Primary lateral sclerosis, hereditary spastic paraplegia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—discrete entities or spectrum? Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 6:8–16
Strong MJ, Grace GM, Orange JB, Leeper HA, Menon R, Aere C (1999) A prospective study of cognitive impairment in ALS. Neurology 53:1665–1670
Strong MJ, Yang W, Strong WL, Leystra-Lantz C, Jaffe H, Pant HC (2006) Tau protein hyperphosphorylation in sporadic ALS with cognitive impairment. Neurology 66:1770–1771
Strong MJ, Grace GM, Freedman M et al (2009) Consensus criteria for the diagnosis of frontotemporal cognitive and behavioural syndromes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 10:131–146
Sutedja NA, van der Schouw YT, Fischer K et al (2011) Beneficial vascular risk profile is associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:638–642
Tsai KJ, Yang CH, Fang YH et al (2010) Elevated expression of TDP-43 in the forebrain of mice is sufficient to cause neurological and pathological phenotypes mimicking FTLD-U. J Exp Med 207:1661–1673
Turner MR, Cagnin A, Turkheimer FE et al (2004) Evidence of widespread cerebral microglial activation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Neurobiol Dis 15:601–609
Turner MR, Hammers A, Al-Chalabi A et al (2005a) Distinct cerebral lesions in sporadic and ‘D90A’ SOD1 ALS: studies with [11C]flumazenil PET. Brain 128:1323–1329
Turner MR, Rabiner EA, Hammers A et al (2005b) [11C]-WAY100635 PET demonstrates marked 5-HT1A receptor changes in sporadic ALS. Brain 128:896–905
van Es MA, Diekstra FP, Baas F et al (2009) A case of ALS-FTD in a large FALS pedigree with a K17I ANG mutation. Neurology 72:287–288
Vance C, Al-Chalabi A, Ruddy D et al (2006) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal dementia is linked to a locus on chromosome 9p13.2-21.3. Brain 129:868–876
Vance C, Rogelj B, Hortobágyi T et al (2009) Mutations in FUS, an RNA processing protein, cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 6. Science 323:1208–1211
Wegorzewska I, Bell S, Cairns NJ, Miller TM, Baloh RH (2009) TDP-43 mutant transgenic mice develop features of ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:18809–18814
Wicks P, Abrahams S, Papps B et al (2009) SOD1 and cognitive dysfunction in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol 256:234–241
Wightman G, Anderson VER, Martin J et al (1992) Hippocampal and neocortical ubiquitin-immunoreactive inclusions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with dementia. Neurosci Lett 139:269–274
Wils H, Kleinberger G, Janssens J et al (2010) TDP-43 transgenic mice develop spastic paralysis and neuronal inclusions characteristic of ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:3858–3863
Wilson CM, Grace GM, Munoz DG, He BP, Strong MJ (2001) Cognitive impairment in sporadic ALS. A pathological continuum underlying a multisystem disorder. Neurology 57:651–657
Wilson AC, Dugger BN, Dickson DW, Wang DS (2011) TDP-43 in aging and Alzheimer's disease—a review. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 4:147–155
Yan J, Deng HX, Siddique N et al (2010) Frameshift and novel mutations in FUS in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and ALS/dementia. Neurology 75:807–814
Yang W, Sopper MM, Leystra-Lantz C, Strong MJ (2003) Microtubule-associated tau protein positive neuronal and glial inclusions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 61:1766–1773
Yang W, Ang L-C, Strong MJ (2005) Tau protein aggregation in the frontal and entorhinal cortices as a function of aging. Dev Brain Res 156:127–138
Yang W, Leystra-Lantz C, Strong MJ (2008) Upregulation of GSK3β expression in frontal and temporal cortex of ALS with cognitive impairment (ALSci). Brain Res 1196:131–139
Zhou H, Huang C, Chen H et al (2010) Transgenic rat model of neurodegeneration caused by mutation in the TDP gene. PLoS Genet 6:e1000887
Zimmerman EK, Eslinger PJ, Simmons Z, Barrett AM (2007) Emotional perception deficits in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cogn Behav Neurol 20:79–82
Acknowledgements
Research supported by the Michael Halls endowment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strong, M.J., Yang, W. The Frontotemporal Syndromes of ALS. Clinicopathological Correlates. J Mol Neurosci 45, 648–655 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9609-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9609-0