Abstract
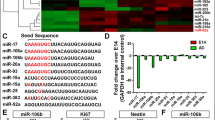
Differentiation of neural stem cells (NSC’s) to mature and functional neurons requires coordinated expression of mRNA, microRNAs (miRNAs) and regulatory proteins. Our earlier unbiased miRNA profiling studies have identified miR-200, miR-34 and miR-221/222 as maximally up-regulated miRNA families in differentiating PC12 cells and demonstrated the capability of miR-200 family in inducing neuronal differentiation (J. Neurochem, 2015, 133, 640–652). In present study, we have investigated role of miR-34 family in neuronal differentiation and identified P53 as mediator of nerve growth factor (NGF) induced miR-34a expression in differentiating PC12 cells. Our studies have shown that NGF induced miR-34a, arrests proliferating PC12 cells to G1 phase, which is pre-requisite for neuronal differentiation. Our studies have also shown that increased expression of miR-34a controls the P53 level in differentiated PC12 cells in feedback inhibition manner, which probably prevents differentiated cells from P53 induced apoptosis. Expression profiling of miR-34 family in different neuronal, non-neuronal and developing cells have identified differentiated and aged brain cells as richest source of miR-34, which also indicates that higher expression of miR-34 family helps in maintaining the mature neurons in non-proliferative stage. In conclusion, our studies have shown that miR-34 is brain enriched miRNA family, which up-regulates with neuronal maturation and brain ageing and co-operative regulation of P53 and miR-34a helps in neuronal differentiation by arresting cells in G1 phase.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee E, Hu N, Yuan S, Cox LA, Bradley A, Lee W-H, Herrup K (1994) Dual roles of the retinoblastoma protein in cell cycle regulation and neuron differentiation. Genes Dev 8(17):2008–2021
Galderisi U, Jori FP, Giordano A (2003) Cell cycle regulation and neural differentiation. Oncogene 22(33):5208–5219
Stiles J, Jernigan TL (2010) The basics of brain development. Neuropsychol Rev 20(4):327–348
Zhang Y, Ueno Y, Liu XS, Buller B, Wang X, Chopp M, Zhang ZG (2013) The microRNA-17–92 cluster enhances axonal outgrowth in embryonic cortical neurons. J Neurosci 33(16):6885–6894
Kutty RK, Samuel W, Jaworski C, Duncan T, Nagineni CN, Raghavachari N, Wiggert B, Redmond TM (2010) MicroRNA expression in human retinal pigment epithelial (ARPE-19) cells: increased expression of microRNA-9 by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide
Santra M, Chopp M, Santra S, Nallani A, Vyas S, Zhang ZG, Morris DC (2016) Thymosin beta 4 up-regulates miR-200a expression and induces differentiation and survival of rat brain progenitor cells. J Neurochem 136(1):118–132
Singh T, Jauhari A, Pandey A, Singh P, Pant AB, Parmar D, Yadav S (2014) Regulatory triangle of neurodegeneration, adult neurogenesis and microRNAs. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders) 13(1):96–103
Yadav S, Jauhari A, Singh N, Singh T, Srivastav AK, Singh P, Pant A, Parmar D (2015) MicroRNAs are Emerging as Most Potential Molecular Biomarkers. Biochemistry & Analytical Biochemistry 2015
Pandey A, Singh P, Jauhari A, Singh T, Khan F, Pant AB, Parmar D, Yadav S (2015) Critical role of the miR-200 family in regulating differentiation and proliferation of neurons. J Neurochem 133(5):640–652
Jauhari A, Singh T, Pandey A, Singh P, Singh N, Srivastava AK, Pant AB, Parmar D et al (2016) Differentiation induces dramatic changes in miRNA profile, where loss of dicer diverts differentiating SH-SY5Y cells toward senescence. Mol Neurobiol . doi:10.1007/s12035-016-0042-91-10
Ko MH, Kim S, Hwang DW, Ko HY, Kim YH, Lee DS (2008) Bioimaging of the unbalanced expression of microRNA9 and microRNA9* during the neuronal differentiation of P19 cells. FEBS J 275(10):2605–2616
Dewing AS, Rueli RH, Robles MJ, Nguyen-Wu ED, Zeyda T, Berry MJ, Bellinger FP (2012) Expression and regulation of mouse selenoprotein P transcript variants differing in non-coding RNA. RNA Biol 9(11):1361–1369
Hermeking H (2010) The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death & Differentiation 17(2):193–199
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A, Berking C, Knyazeva T, Körner H, Knyazev P, Diebold J et al (2008) Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple types of cancer. Cell Cycle 7(16):2591–2600
Aranha MM, Santos DM, Solá S, Steer CJ, Rodrigues CM (2011) miR-34a regulates mouse neural stem cell differentiation. PLoS One 6(8):e21396
Okada N, Lin C-P, Ribeiro MC, Biton A, Lai G, He X, Bu P, Vogel H et al (2014) A positive feedback between p53 and miR-34 miRNAs mediates tumor suppression. Genes Dev 28(5):438–450
Culmsee C, Mattson MP (2005) p53 in neuronal apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331(3):761–777
Fulci G, Van Meir EG (1999) p53 and the CNS. Mol Neurobiol 19(1):61–77
Miller F, Pozniak C, Walsh G (2000) Neuronal life and death: an essential role for the p53 family. Cell Death & Differentiation 7(10):880–888
Tedeschi A, Di Giovanni S (2009) The non-apoptotic role of p53 in neuronal biology: enlightening the dark side of the moon. EMBO Rep 10(6):576–583
Molchadsky A, Rivlin N, Brosh R, Rotter V, Sarig R (2010) p53 is balancing development, differentiation and de-differentiation to assure cancer prevention. Carcinogenesis 31(9):1501–1508
Choi J, Donehower L (1999) p53 in embryonic development: maintaining a fine balance. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences CMLS 55(1):38–47
Danilova N, Sakamoto KM, Lin S (2008) p53 family in development. Mech Dev 125(11):919–931
Brynczka C, Labhart P, Merrick BA (2007) NGF-mediated transcriptional targets of p53 in PC12 neuronal differentiation. BMC Genomics 8(1):139
Feng Z, Zhang C, Wu R, Hu W (2011) Tumor suppressor p53 meets microRNAs. J Mol Cell Biol 3(1):44–50
Hünten S, Siemens H, Kaller M, Hermeking H (2013) The p53/microRNA network in cancer: experimental and bioinformatics approaches. In: MicroRNA Cancer Regulation. Springer, pp 77–101
Hermeking H (2012) MicroRNAs in the p53 network: micromanagement of tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer 12(9):613–626
Tarasov V, Jung P, Verdoodt B, Lodygin D, Epanchintsev A, Menssen A, Meister G, Hermeking H (2007) Differential regulation of microRNAs by p53 revealed by massively parallel sequencing: miR-34a is a p53 target that induces apoptosis and G1-arrest. Cell Cycle 6(13):1586–1593
Suzuki HI, Yamagata K, Sugimoto K, Iwamoto T, Kato S, Miyazono K (2009) Modulation of microRNA processing by p53. Nature 460(7254):529–533
Yamakuchi M, Lowenstein CJ (2009) MiR-34, SIRT1, and p53: the feedback loop. Cell Cycle 8(5):712–715
Navarro F, Gutman D, Meire E, Cáceres M, Rigoutsos I, Bentwich Z, Lieberman J (2009) miR-34a contributes to megakaryocytic differentiation of K562 cells independently of p53. Blood 114(10):2181–2192
Pandey A, Jauhari A, Singh T, Singh P, Singh N, Srivastava AK, Khan F, Pant AB et al (2015) Transactivation of P53 by cypermethrin induced miR-200 and apoptosis in neuronal cells. Toxicology Research 4(6):1578–1586
Yadav S, Pandey A, Shukla A, Talwelkar SS, Kumar A, Pant AB, Parmar D (2011) miR-497 and miR-302b regulate ethanol-induced neuronal cell death through BCL2 protein and cyclin D2. J Biol Chem 286(43):37347–37357
Yadav S, Dhawan A, Seth PK, Singh RL, Parmar D (2006) Cytochrome P4503A: evidence for mRNA expression and catalytic activity in rat brain. Mol Cell Biochem 287(1–2):91–99
Liu N, Landreh M, Cao K, Abe M, Hendriks G-J, Kennerdell JR, Zhu Y, Wang L-S et al (2012) The microRNA miR-34 modulates ageing and neurodegeneration in drosophila. Nature 482(7386):519–523
Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L, Hermeking H (2014) The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol 6(3):214–230
Wu J, Bao J, Kim M, Yuan S, Tang C, Zheng H, Mastick GS, Xu C et al (2014) Two miRNA clusters, miR-34b/c and miR-449, are essential for normal brain development, motile ciliogenesis, and spermatogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(28):E2851–E2857
Mollinari C, Racaniello M, Berry A, Pieri M, De Stefano M, Cardinale A, Zona C, Cirulli F et al (2015) miR-34a regulates cell proliferation, morphology and function of newborn neurons resulting in improved behavioural outcomes. Cell Death Dis 6(1):e1622
Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E, Spector Y, Rosenfeld N, Moskovits N, Bentwich Z, Oren M (2007) Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell 26(5):731–743
Welch C, Chen Y, Stallings R (2007) MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene 26(34):5017–5022
Chang T-C, Wentzel EA, Kent OA, Ramachandran K, Mullendore M, Lee KH, Feldmann G, Yamakuchi M et al (2007) Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell 26(5):745–752
Acknowledgments
Funding for the work carried out in the present study has been provided by CSIR network projects InDepth (BSC0111) and Department of Biotechnology project (GAP-254). Mr. Abhishek Jauhari is grateful to UGC, New Delhi, and Ms. Tanisha Singh is grateful to Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi for providing the research fellowships. The technical assistance of Mr. B S Pandey and Mr. Puneet Khare is also gratefully acknowledged. The CSIR-IITR communication reference number is 3417.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Additional information
Abhishek Jauhari and Tanisha Singh both author’s contributed equally
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jauhari, A., Singh, T., Singh, P. et al. Regulation of miR-34 Family in Neuronal Development. Mol Neurobiol 55, 936–945 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0359-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0359-4