Abstract
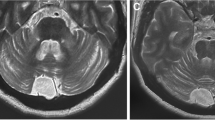
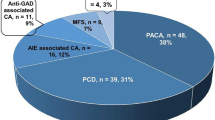
A prompt diagnosis and treatment of patients with autoimmune cerebellar ataxia (CA) with antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD-Abs) may lead to a better prognosis. Herein, we report prodromal transient neurological symptoms that should raise clinical suspicion of CA with GAD-Abs. We initially identified a 70-year-old man who presented a first acute episode of vertigo, diplopia, and ataxia lasting 2 weeks. Two months later, he experienced a similar episode along with new-onset gaze-evoked nystagmus. After 4 months, downbeat nystagmus, left limb dysmetria, and gait ataxia progressively appeared, and an autoimmune CA was diagnosed based on the positivity of GAD-Abs in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). We searched retrospectively for similar presentations in a cohort of 31 patients diagnosed with CA and GAD-Abs. We found 11 (35.4%) patients (all women, median age 62 years; 8/11 [72.7%] with autoimmune comorbidities) with transient neurological symptoms antedating CA onset by a median of 3 months, including vertigo in 9 (81.8%; described as paroxysmal in 8) and fluctuating diplopia in 3 (27.3%) patients. The identification of transient neurological symptoms of unknown etiology, such as paroxysmal vertigo and fluctuating diplopia, should lead to GAD-Abs testing in serum and CSF, especially in patients with autoimmune comorbidities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Honnorat J, Saiz A, Giometto B, Vincent A, Brieva L, de Andres C, et al. Cerebellar ataxia with anti–glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies: study of 14 patients. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:225–30.
Saiz A, Blanco Y, Sabater L, González F, Bataller L, Casamitjana R, et al. Spectrum of neurological syndromes associated with glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies: diagnostic clues for this association. Brain. 2008;131:2553–63.
García García ME, Castrillo SM, Morales IG, Sacoto DDC, Dolado AM. Acute amnesia and seizures in a young female. Epileptic Disord. 2013;15:455–60.
Mitoma H, Hadjivassiliou M, Honnorat J. Guidelines for treatment of immune-mediated cerebellar ataxias. Cerebellum Ataxias. 2015;2:14.
Ariño H, Gresa-Arribas N, Blanco Y, Martínez-Hernández E, Sabater L, Petit-Pedrol M, et al. Cerebellar ataxia and glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies: immunologic profile and long-term effect of immunotherapy. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71:1009–16.
Matsumoto S. Acute attacks and brain stem signs in a patient with glutamic acid decarboxylase autoantibodies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;73:345–6.
Gresa-Arribas N, Ariño H, Martínez-Hernández E, Petit-Pedrol M, Sabater L, Saiz A, et al. Antibodies to inhibitory synaptic proteins in neurological syndromes associated with glutamic acid decarboxylase autoimmunity. Ruprecht K, editor. PLOS ONE. 2015;10:e0121364.
Muñiz-Castrillo S, Ambati A, Dubois V, Vogrig A, Joubert B, Rogemond V, et al. Primary DQ effect in the association between HLA and neurological syndromes with anti-GAD65 antibodies. J Neurol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09782-8.
Rakocevic G, Raju R, Dalakas MC. Anti–glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with stiff-person syndrome: correlation with clinical severity. Arch Neurol. 2004;61:902–4.
Manto MU, Hampe CS, Rogemond V, Honnorat J. Respective implications of glutamate decarboxylase antibodies in stiff person syndrome and cerebellar ataxia. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2011;6:3.
Takenoshita H, Shizuka-Ikeda M, Mitoma H, Song S, Harigaya Y, Igeta Y, et al. Presynaptic inhibition of cerebellar GABAergic transmission by glutamate decarboxylase autoantibodies in progressive cerebellar ataxia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001;70:386–9.
Tilikete C, Vighetto A, Trouillas P, Honnorat J. Anti-GAD antibodies and periodic alternating Nystagmus. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1300–3.
Manto M-U, Laute M-A, Aguera M, Rogemond V, Pandolfo M, Honnorat J. Effects of anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies associated with neurological diseases: GAD-Ab and cerebellar function. Ann Neurol. 2007;61:544–51.
Piccolo G, Tavazzi E, Cavallaro T, Romani A, Scelsi R, Martino G. Clinico-pathological findings in a patient with progressive cerebellar ataxia, autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome, hepatocellular carcinoma and anti-GAD autoantibodies. J Neurol Sci. 2010;290:148–9.
Dalmau J, Gonzalez RG, Lerwill MF. Case 4-2007: a 56-year-old woman with rapidly progressive Vertigo and Ataxia. Cabot RC, Harris NL, Shepard J-AO, Rosenberg ES, Cort AM, Ebeling SH, et al., editors. N Engl J Med 2007;356:612–620.
Ogawa E, Sakakibara R, Kawashima K, Yoshida T, Kishi M, Tateno F, et al. VGCC antibody-positive paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration presenting with positioning vertigo. Neurol Sci. 2011;32:1209–12.
Mandel-Brehm C, Dubey D, Kryzer TJ, O’Donovan BD, Tran B, Vazquez SE, et al. Kelch-like protein 11 antibodies in seminoma-associated paraneoplastic encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:47–54.
Martins AI, Carvalho JN, Amorim AM, Geraldo A, Eggenberger E, Lemos J. Disabling Central Paroxysmal Positioning Upbeat Nystagmus and Vertigo Associated With the Presence of Anti–Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Antibodies: J Neuroophthalmol. 2018;38:32–5.
Tilikete C, Vighetto A, Trouillas P, Honnorat J. Potential role of anti-GAD antibodies in abnormal eye movements. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1039:446–54.
Yshii LM, Gebauer CM, Pignolet B, Mauré E, Quériault C, Pierau M, et al. CTLA4 blockade elicits paraneoplastic neurological disease in a mouse model. Brain. 2016;139:2923–34.
Vogrig A, Bernardini A, Gigli GL, Corazza E, Marini A, Segatti S, et al. Stroke-like presentation of paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration: a single-center experience and review of the literature. Cerebellum. 2019;18:976–82.
Hadjivassiliou M, Aeschlimann P, Strigun A, Sanders DS, Woodroofe N, Aeschlimann D. Autoantibodies in gluten ataxia recognize a novel neuronal transglutaminase. Ann Neurol. 2008;64:332–43.
Hadjivassiliou M, Aeschlimann P, Sanders DS, Mäki M, Kaukinen K, Grünewald RA, et al. Transglutaminase 6 antibodies in the diagnosis of gluten ataxia. Neurology. 2013;80:1740–5.
Hadjivassiliou M, Aeschlimann D, Grünewald RA, Sanders DS, Sharrack B, Woodroofe N. GAD antibody-associated neurological illness and its relationship to gluten sensitivity. Acta Neurol Scand. 2011;123:175–80.
Mitoma H, Adhikari K, Aeschlimann D, Chattopadhyay P, Hadjivassiliou M, Hampe CS, et al. Consensus paper: neuroimmune mechanisms of cerebellar ataxias. Cerebellum. 2016;15:213–32.
Wilkinson ID, Hadjivassiliou M, Dickson JM, Wallis L, Grünewald RA, Coley SC, et al. Cerebellar abnormalities on proton MR spectroscopy in gluten ataxia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:1011–3.
Hadjivassiliou M, Currie S, Hoggard N. MR spectroscopy in paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. J Neuroradiol J Neuroradiol. 2013;40:310–2.
Hadjivassiliou M, Graus F, Honnorat J, Jarius S, Titulaer M, Manto M, et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Primary Autoimmune Cerebellar Ataxia-Guidelines from an International Task Force on Immune-Mediated Cerebellar Ataxias. Cerebellum Lond Engl. 2020;
Joubert B, Gobert F, Thomas L, Saint-Martin M, Desestret V, Convers P, et al. Autoimmune episodic ataxia in patients with anti-CASPR2 antibody-associated encephalitis. Neurol - Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation. 2017;4:e371.
Jen JC, Wan J. Episodic ataxias. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;155:205–15.
Acknowledgments
We thank NeuroBioTec Hospices Civils de Lyon BRC (France, AC-2013-1867, NFS96-900) for banking sera and CSF samples. We thank Philip Robinson for his help in the manuscript preparation (Direction de la Recherche Clinique, Hospices Civils de Lyon).
Funding
This study is supported by research grants from the Fondation pour la recherche médicale (reference DQ20170336751) and has been developed within the BETPSY project, which is supported by a public grant overseen by the French national research agency (Agence nationale de la recherche, ANR), as part of the second “Investissements d’Avenir” program (reference ANR-18-RHUS-0012). SM-C was supported by a clinical fellowship grant from the European Academy of Neurology (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sergio Muñiz-Castrillo and Jérôme Honnorat conceptualized and designed the study. Sergio Muñiz-Castrillo, Alberto Vogrig, Bastien Joubert, Anne-Laurie Pinto, David Gonçalves, Hugo Chaumont, Véronique Rogemond, Géraldine Picard, Nicole Fabien, and Jérôme Honnorat collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data. Sergio Muñiz-Castrillo and Jérôme Honnorat drafted the manuscript. Sergio Muñiz-Castrillo, Alberto Vogrig, Bastien Joubert, Anne-Laurie Pinto, David Gonçalves, Hugo Chaumont, Véronique Rogemond, Géraldine Picard, Nicole Fabien, and Jérôme Honnorat revised the manuscript. Jérôme Honnorat supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study followed the Declaration of Helsinki and was performed according to the guidelines of the Institutional Review Board of the Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 and Hospices Civils de Lyon.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muñiz-Castrillo, S., Vogrig, A., Joubert, B. et al. Transient Neurological Symptoms Preceding Cerebellar Ataxia with Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Antibodies. Cerebellum 19, 715–721 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-020-01159-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-020-01159-x