Abstract
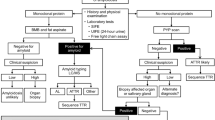
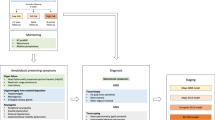
Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis is a protein deposition disorder where the precursor protein represents a monoclonal immunoglobulin light or heavy chain. Deposition in viscera results in restrictive cardiomyopathy, nephrotic range proteinuria, demyelinating peripheral neuropathy, hepatomegaly and malabsorption syndrome. Diagnosis requires biopsy with Congo red staining. Invasive biopsies are not required generally. It is essential that after a histologic diagnosis is obtained, the tissue is validated to have an immunoglobulin light chain composition so patients are spared unnecessary chemotherapy. The disease prognosis and patient monitoring are linked to serialized measurement of cardiac biomarkers and immunoglobulin-free light chains. Most patients require cytotoxic chemotherapy. For some patients, this therapy involves stem cell collection and myeloablative chemotherapy; for others, chemotherapy includes an alkylator and a corticosteroid; and for some, it involves addition of a novel agent in the form of an immunomodulatory drug or a proteasome inhibitor. Delays in diagnosis continue to be an obstacle to initiating effective therapy. Early mortality rates remain high. Effective chemotherapy can result in reversal of organ dysfunction and recovery. Reductions in light chain production translate to improved survival.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baden EM, Sikkink LA, Ramirez-Alvarado M . Light chain amyloidosis: current findings and future prospects. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2009; 10: 500–508.
Randles EG, Thompson JR, Martin DJ, Ramirez-Alvarado M . Structural alterations within native amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chains. J Mol Biol 2009; 389: 199–210.
Biewend ML, Menke DM, Calamia KT . The spectrum of localized amyloidosis: a case series of 20 patients and review of the literature. Amyloid 2006; 13: 135–142.
Santos-Briz A, Canueto J, Antunez P, Bravo J, Garcia-Sanz R, de Unamuno P . Primary cutaneous localized amyloid elastosis. Am J Dermatopathol 2010; 32: 86–90.
DeSouza MA, Rekhi B, Thyavihally YB, Tongaonkar HB, Desai SB . Localized amyloidosis of the urinary bladder, clinically masquerading as bladder cancer. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2008; 51: 415–417.
Takahashi T, Miura H, Matsu-ura Y, Iwana S, Maruyama R, Harada T . Urine cytology of localized primary amyloidosis of the ureter: a case report. Acta Cytol 2005; 49: 319–322.
Merrimen JL, Alkhudair WK, Gupta R . Localized amyloidosis of the urinary tract: case series of nine patients. Urology 2006; 67: 904–909.
Caggiati A, Campanella A, Tenna S, Cogliandro A, Potenza C, Persichetti P . Primary amyloidosis of the eyelid: a case report. In Vivo 2010; 24: 575–578.
Neuner GA, Badros AA, Meyer TK, Nanaji NM, Regine WF . Complete resolution of laryngeal amyloidosis with radiation treatment. Head Neck 2010; e-pub ahead of print 10 November 2010.
Santos JW, Schneider Filho A, Bertolazzi A, Michel GT, Silva LV, Melo CR et al. Primary tracheobronchial amyloidosis. J Bras Pneumol 2008; 34: 881–884. English, Portuguese.
Gaurav K, Panda M . An uncommon cause of bilateral pulmonary nodules in a long-term smoker. J Gen Intern Med 2007; 22: 1617–1620.
Caglar K, Kibar Y, Tahmaz L, Safali M . Laser therapy in patient with intractable haemorrhage due to the bladder involvement of systemic amyloidosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2001; 16: 1724.
Malek RS, Wahner-Roedler DL, Gertz MA, Kyle RA . Primary localized amyloidosis of the bladder: experience with dimethyl sulfoxide therapy. J Urol 2002; 168: 1018–1020.
Brill AK, Woelke K, Schadlich R, Weinz C, Laier-Groeneveld G . Tracheobronchial amyloidosis: bronchoscopic diagnosis and therapy of an uncommon disease: a case report. J Physiol Pharmacol 2007; 58 Suppl 5(Pt 1): 51–55.
Poovaneswaran S, Razak AR, Lockman H, Bone M, Pollard K, Mazdai G . Tracheobronchial amyloidosis: utilization of radiotherapy as a treatment modality. Medscape J Med 2008; 10: 42.
Wu D, Lou JY, Chen J, Fei L, Liu GJ, Shi XY et al. A case report of localized gastric amyloidosis. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9: 2632–2634.
Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A . Localized AL amyloidosis of the colon: an unrecognized entity. Amyloid 2003; 10: 36–41.
Rotondano G, Salerno R, Cipolletta F, Bianco MA, De Gregorio A, Miele R et al. Localized amyloidosis of the stomach: a case report. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13: 1877–1878.
Tanskanen M, Peuralinna T, Polvikoski T, Notkola IL, Sulkava R, Hardy J et al. Senile systemic amyloidosis affects 25% of the very aged and associates with genetic variation in alpha2-macroglobulin and tau: a population-based autopsy study. Ann Med 2008; 40: 232–239.
Kestenbaum B, Belozeroff V . Mineral metabolism disturbances in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur J Clin Invest 2007; 37: 607–622.
Buxbaum J, Alexander A, Koziol J, Tagoe C, Fox E, Kitzman D . Significance of the amyloidogenic transthyretin Val 122 Ile allele in African Americans in the Arteriosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) and Cardiovascular Health (CHS) Studies. Am Heart J 2010; 159: 864–870.
Silva L, Sampaio L, Terroso G, Almeida G, Lucas R, Rios E et al. Amyloidosis secondary to rheumatic diseases: 16 cases. Acta Reumatol Port 2010; 35: 518–523.
Picken MM . Amyloidosis: where are we now and where are we heading? Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010; 134: 545–551.
Sethi S, Theis JD, Leung N, Dispenzieri A, Nasr SH, Fidler ME et al. Mass spectrometry-based proteomic diagnosis of renal immunoglobulin heavy chain amyloidosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2010; 5: 2180–2187.
Vrana JA, Gamez JD, Madden BJ, Theis JD, Bergen III HR, Dogan A . Classification of amyloidosis by laser microdissection and mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis in clinical biopsy specimens. Blood 2009; 114: 4957–4959.
Manenti L, Tansinda P, Vaglio A . Eprodisate in amyloid A amyloidosis: a novel therapeutic approach? Expert Opin Pharmacother 2008; 9: 2175–2180.
Ratner M . Spotlight focuses on protein-misfolding therapies. Nat Biotechnol 2009; 27: 874.
Kurosawa T, Igarashi S, Nishizawa M, Onodera O . Selective silencing of a mutant transthyretin allele by small interfering RNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 337: 1012–1018.
Moini M, Mistry P, Schilsky ML . Liver transplantation for inherited metabolic disorders of the liver. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 2010; 15: 269–276.
Halwani O, Delgado DH . Cardiac amyloidosis: an approach to diagnosis and management. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2010; 8: 1007–1013.
Siragusa S, Morice W, Gertz MA, Kyle RA, Greipp PR, Lust JA et al. Asymptomatic immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL) at the time of diagnostic bone marrow biopsy in newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma and smoldering myeloma: a series of 144 cases and a review of the literature. Ann Hematol 2011; 90: 101–106.
Kyle RA, Linos A, Beard CM, Linke RP, Gertz MA, O’Fallon WM et al. Incidence and natural history of primary systemic amyloidosis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1950 through 1989. Blood 1992; 79: 1817–1822.
Cohen AD, Comenzo RL . Systemic light-chain amyloidosis: advances in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2010; 2010: 287–294.
Perfetto F, Moggi-Pignone A, Livi R, Tempestini A, Bergesio F, Matucci-Cerinic M . Systemic amyloidosis: a challenge for the rheumatologist. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2010; 6: 417–429.
Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Hayman SR . Amyloidosis: diagnosis and management. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma 2005; 6: 208–219.
Dispenzieri A, Merlini G, Comenzo RL . Amyloidosis 2008 BMT Tandem Meetings (February 13–17, San Diego). Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14 (Suppl 1): 6–11.
Wang J, Kong X, Xu H, Zhou G, Chang D, Liu D et al. Noninvasive diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis by MRI and echochardiography. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 2010; 30: 536–540.
Koyama J, Falk RH . Prognostic significance of strain Doppler imaging in light-chain amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2010; 3: 333–342.
Syed IS, Glockner JF, Feng D, Araoz PA, Martinez MW, Edwards WD et al. Role of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2010; 3: 155–164.
Palladini G, Campana C, Klersy C, Balduini A, Vadacca G, Perfetti V et al. Serum N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide is a sensitive marker of myocardial dysfunction in AL amyloidosis. Circulation 2003; 107: 2440–2445.
Gertz M, Lacy M, Dispenzieri A, Hayman S, Kumar S, Buadi F et al. Troponin T level as an exclusion criterion for stem cell transplantation in light-chain amyloidosis. Leuk Lymphoma 2008; 49: 36–41.
Kumar S, Dispenzieri A, Katzmann JA, Larson DR, Colby CL, Lacy MQ et al. Serum immunoglobulin free light-chain measurement in primary amyloidosis: prognostic value and correlations with clinical features. Blood 2010; 116: 5126–5129.
Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Katzmann JA, Rajkumar SV, Abraham RS, Hayman SR et al. Absolute values of immunoglobulin free light chains are prognostic in patients with primary systemic amyloidosis undergoing peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood 2006; 107: 3378–3383.
Kumar S, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Leung N, Zeldenrust SR et al. Serum uric acid: novel prognostic factor in primary systemic amyloidosis. Mayo Clin Proc 2008; 83: 297–303.
Paiva B, Vídriales MB, Perez JJ, Lopez-Berges MC, Garcia-Sanz R, Ocio EM et al. The clinical utility and prognostic value of multiparameter flow cytometry immunophenotyping in light-chain amyloidosis. Blood 2011; 117: 3613–3616.
Kumar SK, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Buadi FK, Zeldenrust SR et al. Changes in serum-free light chain rather than intact monoclonal immunoglobulin levels predicts outcome following therapy in primary amyloidosis. Am J Hematol 2011; 86: 251–255.
Palladini G, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MAA, Wechalekar A, Hawkins PN, Schonland SO et al. Validation of the criteria of response to treatment in AL amylodiosis [abstract]. Blood 2010, 116.
Kumar SK, Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dingli D, Hayman SR, Buadi FK et al. Recent improvements in survival in primary systemic amyloidosis and the importance of an early mortality risk score. Mayo Clin Proc 2011; 86: 12–18.
Jones NF, Hilton PJ, Tighe JR, Hobbs JR . Treatment of ‘primary’ renal amyloidosis with melphalan. Lancet 1972; 2: 616–619.
Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Greipp PR, Witzig TE, Lust JA, Lacy MQ et al. A trial of three regimens for primary amyloidosis: colchicine alone, melphalan and prednisone, and melphalan, prednisone, and colchicine. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 1202–1207.
Skinner M, Anderson J, Simms R, Falk R, Wang M, Libbey C et al. Treatment of 100 patients with primary amyloidosis: a randomized trial of melphalan, prednisone, and colchicine versus colchicine only. Am J Med 1996; 100: 290–298.
Kyle RA, Greipp PR, Garton JP, Gertz MA . Primary systemic amyloidosis: comparison of melphalan/prednisone versus colchicine. Am J Med 1985; 79: 708–716.
Palladini G, Anesi E, Perfetti V, Obici L, Invernizzi R, Balduini C et al. A modified high-dose dexamethasone regimen for primary systemic (AL) amyloidosis. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 1044–1046.
Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Lust JA, Greipp PR, Witzig TE, Kyle RA . Phase II trial of high-dose dexamethasone for untreated patients with primary systemic amyloidosis. Med Oncol 1999; 16: 104–109.
Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Lust JA, Greipp PR, Witzig TE, Kyle RA . Phase II trial of high-dose dexamethasone for previously treated immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis. Am J Hematol 1999; 61: 115–119.
Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Kumar SK, Buadi FK, Dingli D et al. Trends in day 100 and 2-year survival after auto-SCT for AL amyloidosis: outcomes before and after 2006. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 970–975.
Jimenez-Zepeda VH, Franke N, Delgado D, Winter A, Stewart K, Mikhael JR et al. High-dose melphalan for AL amyloidosis: the importance of case selection to improve clinical outcomes [abstract]. Blood 2010, 116.
Mhaskar R, Kumar A, Behera M, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Djulbegovic B . Role of high-dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation in primary systemic amyloidosis: a systematic review. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 893–902.
Jaccard A, Moreau P, Leblond V, Leleu X, Benboubker L, Hermine O et al. High-dose melphalan versus melphalan plus dexamethasone for AL amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 1083–1093.
Mehta J, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA . High-dose chemotherapy with autotransplantation in AL amyloidosis: a flawed meta-analysis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 138–140.
Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Hayman SR, Kumar SK, Dingli D et al. Autologous stem cell transplant for immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis: a status report. Leuk Lymphoma 2010; 51: 2181–2187.
Palladini G, Russo P, Nuvolone M, Lavatelli F, Perfetti V, Obici L et al. Treatment with oral melphalan plus dexamethasone produces long-term remissions in AL amyloidosis. Blood 2007; 110: 787–788.
Palladini G, Perfetti V, Obici L, Caccialanza R, Semino A, Adami F et al. Association of melphalan and high-dose dexamethasone is effective and well tolerated in patients with AL (primary) amyloidosis who are ineligible for stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 103: 2936–2938.
Dietrich S, Schonland SO, Benner A, Bochtler T, Kristen AV, Beimler J et al. Treatment with intravenous melphalan and dexamethasone is not able to overcome the poor prognosis of patients with newly diagnosed systemic light chain amyloidosis and severe cardiac involvement. Blood 2010; 116: 522–528.
Elzawawy A . Treatment of 5-fluorouracil-induced stomatitis by allopurinol mouthwashes. Oncology 1991; 48: 282–284.
Sanchorawala V, Seldin DC, Berk JL, Sloan JM, Doros G, Skinner M . Oral cyclic melphalan and dexamethasone for patients with Al amyloidosis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2010; 10: 469–472.
Gertz MA . I don’t know how to treat amyloidosis. Blood 2010; 116: 507–508.
Seldin DC, Choufani EB, Dember LM, Wiesman JF, Berk JL, Falk RH et al. Tolerability and efficacy of thalidomide for the treatment of patients with light chain-associated (AL) amyloidosis. Clin Lymphoma 2003; 3: 241–246.
Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Rajkumar SV, Geyer SM, Witzig TE, Fonseca R et al. Poor tolerance to high doses of thalidomide in patients with primary systemic amyloidosis. Amyloid 2003; 10: 257–261.
Palladini G, Russo P, Lavatelli F, Nuvolone M, Albertini R, Bosoni T et al. Treatment of patients with advanced cardiac AL amyloidosis with oral melphalan, dexamethasone, and thalidomide. Ann Hematol 2009; 88: 347–350.
Wechalekar AD, Goodman HJ, Lachmann HJ, Offer M, Hawkins PN, Gillmore JD . Safety and efficacy of risk-adapted cyclophosphamide, thalidomide, and dexamethasone in systemic AL amyloidosis. Blood 2007; 109: 457–464.
Wechalekar AD, Kastritis E, Merlini G, Hawkins PN, Dimopoulos MA, Gillmore JD et al. A European collaborative study of treatment outcomes in 428 patients with systemic AL amyloidosis [abstract]. Blood 2010, 116.
Sanchorawala V, Wright DG, Rosenzweig M, Finn KT, Fennessey S, Zeldis JB et al. Lenalidomide and dexamethasone in the treatment of AL amyloidosis: results of a phase 2 trial. Blood 2007; 109: 492–496.
Sanchorawala V, Finn KT, Fennessey S, Shelton A, Doros G, Zeldis JB et al. Durable hematologic complete responses can be achieved with lenalidomide in AL amyloidosis. Blood 2010; 116: 1990–1991.
Waites KB, Duffy LB, Dowzicky MJ . Antimicrobial susceptibility among pathogens collected from hospitalized patients in the United States and in vitro activity of tigecycline, a new glycylcycline antimicrobial. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006; 50: 3479–3484.
Moreau P, Jaccard A, Benboubker L, Royer B, Leleu X, Bridoux F et al. Lenalidomide in combination with melphalan and dexamethasone in patients with newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis: a multicenter phase 1/2 dose-escalation study. Blood 2010; 116: 4777–4782.
Kumar S, Hayman SR, Buadi F, Allred J, Laumann K, Roy V et al. A phase II trial of lenalidomide, cyclophophamide and dexamethasone (RCD) in patients with light chain amyloidosis [abstract]. Blood 2009, 114.
Gillmore J, Cocks K, Gibbs SDJ, Sattianayagam PT, Lane T, Lachmann H et al. Cyclophosphamide, thalidomide and dexamethasone (CTD) versus melphalan plus dexamethasone (MD) for newly-diagnosed systemic AL amyloidosis: results from the UK Amyloidosis Treatment Trial [abstract]. Blood 2009, 114.
Dispenzieri A, Dingli D, Kumar SK, Rajkumar SV, Lacy MQ, Hayman S et al. Discordance between serum cardiac biomarker and immunoglobulin-free light-chain response in patients with immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis treated with immune modulatory drugs. Am J Hematol 2010; 85: 757–759.
Tapan U, Seldin DC, Finn KT, Fennessey S, Shelton A, Zeldis JB et al. Increases in B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) during treatment with lenalidomide in AL amyloidosis. Blood 2010; 116: 5071–5072.
Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Hayman SR, Buadi F, Kumar S, Reeder CR et al. A phase-2 study of pomalidomide and dexamethasone in previously-treated light-chain (AL) amyloidosis [abstract]. Blood 2010, 116.
Wechalekar AD, Lachmann HJ, Offer M, Hawkins PN, Gillmore JD . Efficacy of bortezomib in systemic AL amyloidosis with relapsed/refractory clonal disease. Haematologica 2008; 93: 295–298.
Reece DE, Sanchorawala V, Hegenbart U, Merlini G, Palladini G, Fermand JP et al. VALCADE CAN2007 Study Group. Weekly and twice-weekly bortezomib in patients with systemic AL amyloidosis: results of a phase 1 dose-escalation study. Blood 2009; 114: 1489–1497.
Reece DE, Hegenbart U, Sanchorawala V, Merlini G, Palladini G, Blade J et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly and twice-weekly bortezomib in patients with relapsed systemic AL amyloidosis: results of a phase 1/2 study. Blood 2011; 118: 865–873.
Brunvand MW, Bitter M . Amyloidosis relapsing after autologous stem cell transplantation treated with bortezomib: normalization of detectable serum-free light chains and reversal of tissue damage with improved suitability for transplant. Haematologica 2010; 95: 519–521.
Lamm W, Willenbacher W, Lang A, Zojer N, Muldur E, Ludwig H et al. Efficacy of the combination of bortezomib and dexamethasone in systemic AL amyloidosis. Ann Hematol 2011; 90: 201–206.
Kastritis E, Wechalekar AD, Dimopoulos MA, Merlini G, Hawkins PN, Perfetti V et al. Bortezomib with or without dexamethasone in primary systemic (light chain) amyloidosis. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 1031–1037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author receives honoraria from Celgene and Millennium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gertz, M. How to manage primary amyloidosis. Leukemia 26, 191–198 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.219
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.219
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Updates in the Diagnosis and Management of AL Amyloidosis
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2020)
-
Incomplete ileus and hemafecia as the presenting features of multi-organ involved primary systemic AL amyloidosis: a rare case report
BMC Gastroenterology (2017)
-
Pathophysiology and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2015)
-
Melphalan and dexamethasone with or without bortezomib in newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis: a matched case–control study on 174 patients
Leukemia (2014)